Mercer Mettl interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
Software Developer
Mercer Mettl
3 rounds | 9 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Journey
I was advised by my seniors to practice DSA from the very starting of B.Tech but I did not took that seriously. Honestly speaking, I regretted not taking their advice and in third year I started doing coding and I had to increase practice hours because I started late. But by the end of Third year, I was confident in both DSA and development but even then, I kept on revising the concepts.
Application story
This company visited to my campus for the placement. We just had to upload resume and fill all details in the form. First, they took the online assessment. Later, they called us for the interview rounds.
Why selected/rejected for the role?
The basic reason for my rejection was my not that much strong knowledge of core DSA fundamentals and my problem-solving ability is also not that much good.
Preparation
Duration: 3 Months
Topics: Data Structures, Algorithms, OOPS, Dynamic Programming
Tip
Tip 1 : Practice popular questions from Arrays, Binary Trees, LinkedLists from CodeStudio's Interview Problems
Tip 2 : Make sure you are aware of calculating the time and space complexity for every problem you're coding.
Tip 3 : Prepare through Mock Interviews to practice explaining your approach while solving in an actual interview.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: Above 6 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Describe best of your projects in minimum words. Don't forget to add buzz words like REST APIs/ DB Indexing/ Benchmarking etc if you worked on backend.
Tip 2 : Don't add school achievements like Olympiads or Class Topper in your resume.
Tip 3 : If you've some work experience, put it in a way ,you're marketing yourself. Add terms like 'Created/Owned the Project through entire SDLC'
Tip 4 : Make sure you mention how your work experience actually impacted the company. Or how your self project can be actually useful to end user.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration60 Minutes
Interview date17 Feb 2023
Coding problem3
1. Longest Increasing Subsequence
Moderate
30m average time
65% success
0/80
Asked in companies



For a given array with N elements, you need to find the length of the longest subsequence from the array such that all the elements of the subsequence are sorted in strictly increasing order.
Strictly Increasing Sequence is when each term in the sequence is larger than the preceding term.
For example:
[1, 2, 3, 4] is a strictly increasing array, while [2, 1, 4, 3] is not.
2. Technical Question
How does C++ support Polymorphism?
3. DS Question
Which data structure is used by Map?
02
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration60 Minutes
Interview date17 Feb 2023
Coding problem3
1. Merge Sort
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



Given a sequence of numbers ‘ARR’. Your task is to return a sorted sequence of ‘ARR’ in non-descending order with help of the merge sort algorithm.
Example :
Merge Sort Algorithm -
Merge sort is a Divide and Conquer based Algorithm. It divides the input array into two-parts, until the size of the input array is not ‘1’. In the return part, it will merge two sorted arrays a return a whole merged sorted array.
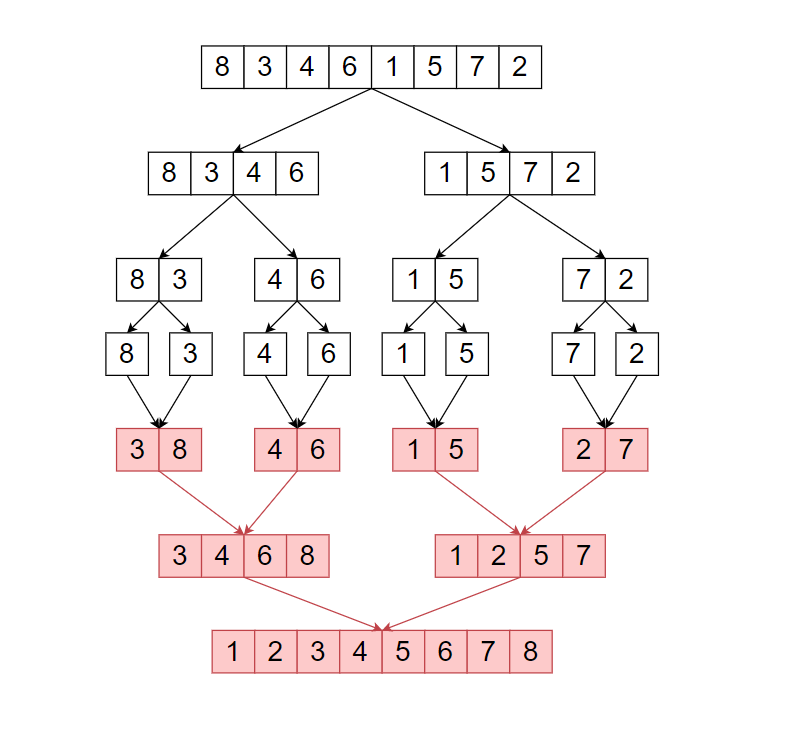
The above illustrates shows how merge sort works.
Note :
It is compulsory to use the ‘Merge Sort’ algorithm.
2. Regular Expression Match
Easy
10m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



Given a string ‘str’ and a string ‘pat’. The string s has some wildcard characters i.e ‘?’ and ‘*’.
If any character is a ‘?’ we can replace that character with any other character.
If a character is a * we can replace * with any sequence of characters including the empty sequence.
Your task is to determine if it is possible that we can make ‘str' = 'pat’ using appropriate conversions in ‘str’.
For example:
Let str = “abc?" and pat= “abcd”
We return true as ‘?’ can be replaced with ‘d’ and this makes ‘str’ and ‘pat’ same.
3. System Design Question
Design a Whatsapp Chat System
03
Round
Hard
Video Call
Duration60 Minutes
Interview date17 Feb 2023
Coding problem3
1. Program for Priority CPU Scheduling | Set 1
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given the ‘N’ processes with their “burst times”, and the “arrival time” for all processes is ‘0’. You are also given the ‘priority’ of each process.
Your task is to find the “waiting time” and the “turn-around time” of each process using the ‘Priority CPU Scheduling’ algorithm.
Note:
1. The highest priority process will be scheduled first, followed by the next highest priority, and so on.
2. If the two processes have the same priority, then you have to run the process with the lowest number (id) first.
2. Networking Question
Classful vs Classless Addressing
Problem approach
Classful addressing and classless addressing are two different approaches used in IP (Internet Protocol) addressing to allocate and manage IP addresses in a computer network.
Classful Addressing: In classful addressing, IP addresses are divided into fixed classes, namely Class A, Class B, Class C, Class D, and Class E, based on the range of IP addresses they can represent. Each class has a predefined range of IP addresses and is associated with a fixed network mask (also known as subnet mask). The network mask determines the number of bits used for the network portion and the host portion of the IP address. Classful addressing is based on a fixed hierarchical structure and assumes that all networks within a class have the same network size.
Classless Addressing: In classless addressing, IP addresses are not limited to predefined classes, and the network mask is not fixed. Instead, a more flexible approach is used, where the network mask can vary for each network, allowing for more efficient allocation of IP addresses. Classless addressing uses Variable Length Subnet Mask (VLSM) or CIDR (Classless Inter-Domain Routing) notation, which allows for a more granular allocation of IP addresses and finer control over network size.
Here are some key differences between classful and classless addressing:
Address Allocation: In classful addressing, IP addresses are allocated based on fixed classes, and each class has a predefined range of IP addresses. In contrast, classless addressing allows for more flexible allocation of IP addresses without the constraints of fixed classes, using VLSM or CIDR notation.
Network Mask: In classful addressing, the network mask is fixed and determined by the class of the IP address. For example, Class A has a fixed network mask of 255.0.0.0, Class B has 255.255.0.0, and Class C has 255.255.255.0. In classless addressing, the network mask can vary for each network, allowing for more fine-grained control over the size of the network.
Efficiency: Classless addressing is generally more efficient than classful addressing, as it allows for better utilization of IP address space by allocating IP addresses based on the actual requirements of the network, rather than predefined classes. Classless addressing also reduces the number of IP addresses wasted due to overly large network masks, which is a common issue with classful addressing.
Scalability: Classless addressing is more scalable than classful addressing, as it allows for more flexibility in allocating IP addresses and designing networks of different sizes. Classful addressing can lead to IP address wastage and inefficient utilization of IP address space, especially in networks that do not fit neatly into the predefined class ranges
3. Networking Question
Difference between TCP and UDP
Problem approach
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) and UDP (User Datagram Protocol) are two widely used protocols for transmitting data over a network, but they have fundamental differences in terms of their characteristics and use cases.
Connection-oriented vs. connectionless: TCP is connection-oriented, which means it establishes a reliable connection between two devices before transmitting data. It guarantees the delivery of data in the order it was sent, and it provides error checking and flow control mechanisms. On the other hand, UDP is connectionless, which means it does not establish a connection before transmitting data. It does not guarantee the delivery of data or the order in which it was sent, and it does not provide error checking or flow control.
Reliability: TCP is reliable, as it ensures that data is received without errors and in the correct order. It uses acknowledgment packets, retransmissions, and sequence numbers to ensure reliable data delivery. UDP, on the other hand, does not guarantee reliable data delivery, as it does not use acknowledgments or retransmissions. It is often used for applications where occasional data loss is acceptable, such as real-time streaming or online gaming.
Overhead: TCP has higher overhead compared to UDP. It requires more bandwidth and resources due to the additional overhead of establishing and maintaining a connection, managing acknowledgments, and ensuring reliable data delivery. UDP, being connectionless and lacking error checking mechanisms, has lower overhead, making it more efficient in terms of bandwidth and resources.
Speed: UDP is generally faster than TCP due to its connectionless nature and lower overhead. It is suitable for applications where speed and low latency are critical, such as real-time applications, multimedia streaming, and online gaming. TCP, being connection-oriented and providing reliable data delivery, may introduce additional delays due to the need for establishing connections, managing acknowledgments, and retransmitting lost data.
Use cases: TCP is commonly used for applications that require reliable data delivery, such as web browsing, file transfer, email, and other applications where data integrity and order are crucial. UDP is typically used for applications that prioritize speed and low latency over reliable data delivery, such as online gaming, VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol), DNS (Domain Name System), multimedia streaming, and IoT (Internet of Things) devices.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the result of len([1, 2, 3, 4])?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by Mercer Mettl
869 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Mercer Mettl
936 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Software Developer
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Mercer Mettl
974 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Mercer Mettl
988 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
Software Developer
5 rounds | 14 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
3999 views
1 comments
0 upvotes
Software Developer
6 rounds | 12 problems
Interviewed by SAP Labs
2884 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Software Developer
3 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
1232 views
0 comments
0 upvotes







