Morgan Stanley interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - Intern
Morgan Stanley
2 rounds | 4 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Application story
The entire process is conducted through a third-party company named Kalvium, which operates batches at Chitkara and other universities, and provides opportunities to apply for internships at various companies.
Preparation
Duration: 3 Months
Topics: HTML, CSS, JavaScript, React, Node.js, Next.js, React Native, Expo
Tip
Tip 1: Spend as much time as possible on DSA.
Tip 2: Try to target real-life problems, not just those limited to computers.
Tip 3: Focus on and practice presenting your thoughts clearly.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: CGPA above 8, more than 8 projects. (Stipend: 25k)
Resume tip
Tip 1: Create a portfolio website showcasing all your projects.
Tip 2: Focus on demonstrating that you work on real-life problems.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Hard
Online Coding Interview
Duration90 minutes
Interview date17 Jun 2024
Coding problem3
1. Furthest Building You Can Reach
Moderate
10m average time
90% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Ninja is in the mood for a walk over the city, but being a ninja he prefers jumping over building roofs instead of walking through the streets.
The height of the buildings in his city can be represented through an array ‘HEIGHTS’ where ‘HEIGHT[i]’ is the height of the ith building. Ninja starts his journey from the 1st building and in one step can only travel to the roof of the next building.
While traveling from the ‘i’th to (i+1)th building:
1. If the ith building has a height greater than or equal to the next i.e (i+1)th building then he simply jumps to the next building.
2. Otherwise he uses either {‘HEIGHTS[i+1] -‘HEIGHTS[i]} bricks or just 1 ladder to climb up to the next building.
Having a limited number of bricks say ‘BRICKS’ and a limited number of ladders say ‘LADDERS’ in his Ninja pocket, he wants to know which is the farthest building he can travel up to if he uses the bricks and ladders optimally.
As Ninja is weak in mathematics so he asks for your help, can you help Ninja to find the maximum index of the building he can reach up to(1 based indexing)?
2. Find Peak Element
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given an array 'arr' of length 'n'. Find the index(0-based) of a peak element in the array. If there are multiple peak numbers, return the index of any peak number.
Peak element is defined as that element that is greater than both of its neighbors. If 'arr[i]' is the peak element, 'arr[i - 1]' < 'arr[i]' and 'arr[i + 1]' < 'arr[i]'.
Assume 'arr[-1]' and 'arr[n]' as negative infinity.
Note:
1. There are no 2 adjacent elements having same value (as mentioned in the constraints).
2. Do not print anything, just return the index of the peak element (0 - indexed).
3. 'True'/'False' will be printed depending on whether your answer is correct or not.
Example:
Input: 'arr' = [1, 8, 1, 5, 3]
Output: 3
Explanation: There are two possible answers. Both 8 and 5 are peak elements, so the correct answers are their positions, 1 and 3.
3. Check Identical Trees
Moderate
20m average time
85% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given two binary trees with 'n' and 'm' nodes respectively.
You need to return true if the two trees are identical. Otherwise, return false.
Example:
For the trees given below:-
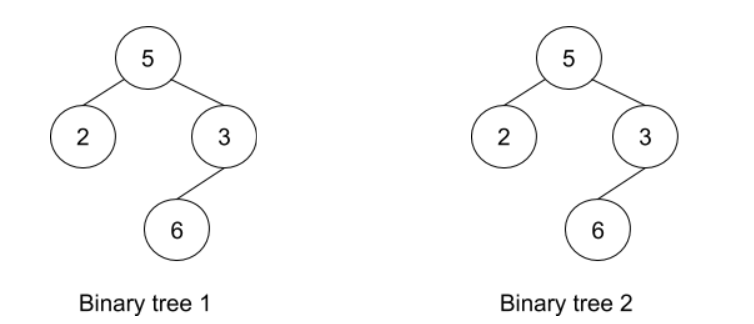
The given trees are identical as:-
1. The number of nodes in both trees is the same.
2. The number of edges in both trees is the same.
3. The data for root for both the trees is the same i.e 5.
4. The data of root -> left (root’s left child) for both the trees is the same i.e 2.
5. The data of root -> right (root’s right child) for both the trees is the same i.e 3.
6. The data of root -> right -> left ( left child of root’s right child) for both the trees is the same i.e 6.
7. Nodes with data 2 and 6 are the leaf nodes for both the binary trees.
02
Round
Medium
Face to Face
Duration30 minutes
Interview date19 Jun 2024
Coding problem1
1. System Design
So the interviewer gave me a really interesting real-world simulation problem.
They said:
"Imagine a situation where you're designing a parking lot system. It's a single-lane parking area — think of it like a stack: the first car to enter is at the bottom, and the last car to enter is at the top. Now, cars can arrive and depart at any time, but here's the catch — if a car that's not on the top wants to leave, you need to temporarily remove the cars above it, let the target car exit, and then put the others back in the same order. Also, if the parking lot is full, incoming cars should wait outside in a queue. Your task is to simulate this system using appropriate data structures."
They asked me to implement three operations:
arrive(plate_number): When a car arrives, either park it (if space is available) or add it to the waiting queue.
depart(plate_number): When a car wants to leave, remove it from the parking lot or the queue. If it's in the lot but not on top, temporarily move the cars above it.
status(): Print the list of currently parked cars and the waiting queue.
So basically, I had to figure out how to use:
a stack for the parking lot,
a queue for the waiting line, and
possibly a hash map to keep track of each car’s position for faster lookup.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - Intern
3 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Morgan Stanley
1775 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Morgan Stanley
2234 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
3 rounds | 10 problems
Interviewed by Morgan Stanley
0 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Morgan Stanley
1205 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - Intern
3 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
15556 views
4 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
4 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
15417 views
1 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
10179 views
2 comments
0 upvotes





