Myntra pvt ltd interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
Software Developer
Myntra pvt ltd
4 rounds | 5 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 6 months
Topics: Data Structures, Algorithms, System Design, Aptitude, OOPS
Tip
Tip 1 : Be thorough with Data Structures and Algorithms and also with your resume.
Tip 2 : Must do Previously asked Interview as well as Online Test Questions.
Tip 3 : Go through all the previous interview experiences from Codestudio and Leetcode.
Tip 4 : Do at-least 2 good projects and you must know every bit of them.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: Above 7 CGPA, Eligible branches : Computer Science & Engineering, Mathematics & Computing, Electrical Engineering and Electronics & Communication Engineering.
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Have at-least 2 good projects explained in short with all important points covered.
Tip 2 : Every skill must be mentioned.
Tip 3 : Focus on skills, projects and experiences more.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Easy
Online Coding Test
Duration90 minutes
Interview date12 Jan 2015
Coding problem1
Myntra had conducted a coding test on campus before the start of the placement season with 2 questions, one on stack and other on DP.
Tips : For the test, the DP question asked was pretty standard, on Longest Common Subsequence. The question on stacks, I don't remember what it was but it was also pretty straight forward. For the test, I would recommend to solve problem from GFG. If they do come to resume shortlisting, they are looking for people who have done good projects and internships.
1. Longest Common Subsequence
Moderate
0/80
Asked in companies



You have been given two Strings “STR1” and “STR2” of characters. Your task is to find the length of the longest common subsequence.
A String ‘a’ is a subsequence of a String ‘b’ if ‘a’ can be obtained from ‘b’ by deletion of several (possibly, zero or all) characters. A common subsequence of two Strings is a subsequence that is common to both Strings.
Problem approach
This problem can be solved using recursion. In this approach, we will start form last element of both the strings. If elements at the last matches then we will decrement length of both the string else we will decrement the length of either of the string.
lcs(s1, s2, n, m):
if n == 0 or m == 0:
return 0
if s1[n-1] == s2[m - 1]:
return 1 + lcs(s1, s2, n-1, m-1)
else:
return max(lcs(s1, s2, n-1, m), lcs(s1, s2, n, m-1))
But this approach would result in TLE for longer test cases. It can be optimized using dynamic programming.
In the top down approach, we make a table of size [m+1][n+1] where m and n are the length of the strings. The intermediate row and column of the table indicates what will be the value of the longest common subsequence if its called for the smaller inputs.
if s1[i - 1] == s2[j - 1]:
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1
else:
dp[i][j] = max(dp[i][j - 1], dp[i - 1][j])
02
Round
Easy
Face to Face
Duration60 minutes
Interview date14 Jan 2015
Coding problem1
The interview started off with questions on my general interest in Software Development. The first round had two coding questions, I was supposed to write the code on paper.
For the questions, they asked me to code the solution first. And then gave a specific input and asked me to demonstrate step by step in my code, how it would lead to the correct answer.
Tips: It's ok if you can't code a general solution, if you can write a code which works for the particular input they have given then also it's ok with them. But be thorough with Data structures.
1. Add two number as linked lists
Moderate
10m average time
80% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You have been given two singly Linked Lists, where each of them represents a positive number without any leading zeros.
Your task is to add these two numbers and print the summation in the form of a linked list.
Example:
If the first linked list is 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 -> NULL and the second linked list is 4 -> 5 -> NULL.
The two numbers represented by these two lists are 12345 and 45, respectively. So, adding these two numbers gives 12390.
So, the linked list representation of this number is 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 9 -> 0 -> NULL.
Problem approach
This is a simple elementary addition problem.
Approach:
1. Traverse the two linked lists.
2. In each iteration, add the numbers in the nodes of the linked lists
3. If the sum of two digits is greater than 9, then we will have to find out the “carry ” : sum%10 to be added in the next iteration.
4. If the lists are unequal, then the smaller one will end before the longer. In this case, we will put only the remaining nodes of the longer list in the resultant list
The time complexity will be O(m+n) since we are iterating both the lists only once.
03
Round
Medium
Face to Face
Duration60 minutes
Interview date14 Jan 2015
Coding problem3
I wasn't asked to write any code in this interview. They asked me some questions on Machine Learning, because of my projects in them. Then they asked me if I knew graph algorithms. Since I knew BFS and DFS, I told them. They asked the difference between the two. Then they asked me if I knew how to find the shortest distance between two points in a graph. I didn't know Dijkstra's properly but I knew it worked on the greedy approach so was able to tell that. Then they asked me how would I find the second shortest path. I tried to answer it with the same greedy approach, but couldn't arrive at the complete solution.
Tips: They ask a tough theoretical question. It's ok if you don't know the answer, they only look for your approach.
1. BFS in Graph
Easy
10m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



Given an adjacency list representation of a directed graph with ‘n’ vertices and ‘m’ edges. Your task is to return a list consisting of Breadth-First Traversal (BFS) starting from vertex 0.
In this traversal, one can move from vertex 'u' to vertex 'v' only if there is an edge from 'u' to 'v'. The BFS traversal should include all nodes directly or indirectly connected to vertex 0.
Note:
The traversal should proceed from left to right according to the input adjacency list.
Example:
Adjacency list: { {1,2,3},{4}, {5}, {},{},{}}
The interpretation of this adjacency list is as follows:
Vertex 0 has directed edges towards vertices 1, 2, and 3.
Vertex 1 has a directed edge towards vertex 4.
Vertex 2 has a directed edge towards vertex 5.
Vertices 3, 4, and 5 have no outgoing edges.
We can also see this in the diagram below.
BFS traversal: 0 1 2 3 4 5

Problem approach
BFS is a traversing algorithm we start traversing from a selected node (starting node) and traverse the graph layer wise thus exploring the neighbor nodes (nodes which are directly connected to source node). And then move towards the next-level neighbor nodes.
Pseudocode :
BFS (G, s)
Q.push( s ) //Inserting s in queue Q until all its neighbor vertices are marked.
mark s as visited.
while ( Q is not empty)
//Removing that vertex from queue, whose neighbor will be visited now
u = Q.pop( )
//processing all the neighbors of u
for all neighbors v of u in Graph G
if v is not visited
Q.push( v ) //Stores v in Q to further visit its neighbor
mark w as visited.
2. DFS Traversal
Moderate
35m average time
65% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Given an undirected and disconnected graph G(V, E), containing 'V' vertices and 'E' edges, the information about edges is given using 'GRAPH' matrix, where i-th edge is between GRAPH[i][0] and GRAPH[i][1]. print its DFS traversal.
V is the number of vertices present in graph G and vertices are numbered from 0 to V-1.
E is the number of edges present in graph G.
Note :
The Graph may not be connected i.e there may exist multiple components in a graph.
Problem approach
The DFS algorithm is a recursive algorithm based on the idea of backtracking. It starts with the initial node of the graph G, and then goes to deeper and deeper until we find the goal node or the node which has no children.
Pseudocode :
DFS(G, s):
mark s as visited
for all neighbors v of s in Graph G:
if v is not visited:
DFS-recursive(G, v)
3. Dijkstra's shortest path
Moderate
25m average time
65% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You have been given an undirected graph of ‘V’ vertices (labeled 0,1,..., V-1) and ‘E’ edges. Each edge connecting two nodes (‘X’,’Y’) will have a weight denoting the distance between node ‘X’ and node ‘Y’.
Your task is to find the shortest path distance from the source node, which is the node labeled as 0, to all vertices given in the graph.
Example:
Input:
4 5
0 1 5
0 2 8
1 2 9
1 3 2
2 3 6
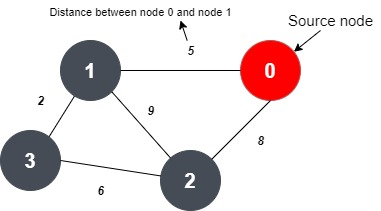
In the given input, the number of vertices is 4, and the number of edges is 5.
In the input, following the number of vertices and edges, three numbers are given. The first number denotes node ‘X’, the second number denotes node ‘Y’ and the third number denotes the distance between node ‘X’ and ‘Y’.
As per the input, there is an edge between node 0 and node 1 and the distance between them is 5.
The vertices 0 and 2 have an edge between them and the distance between them is 8.
The vertices 1 and 2 have an edge between them and the distance between them is 9.
The vertices 1 and 3 have an edge between them and the distance between them is 2.
The vertices 2 and 3 have an edge between them and the distance between them is 6.
Note:
1. There are no self-loops(an edge connecting the vertex to itself) in the given graph.
2. There can be parallel edges i.e. two vertices can be directly connected by more than 1 edge.
Problem approach
Dijkstra's Algorithm basically starts at the source node and it analyzes the graph to find the shortest path between that node and all the other nodes in the graph.
The algorithm keeps track of the currently known shortest distance from each node to the source node and it updates these values if it finds a shorter path.
Once the shortest path between the source node and another node is found, that node is marked as "visited" and added to the path.
The process continues until all the nodes in the graph have been added to the path. This way, we have a path that connects the source node to all other nodes following the shortest path possible to reach each node.
To implement Dijkstra, priority queue can be used.
04
Round
Easy
HR Round
Duration30 minutes
Interview date15 Jan 2015
Coding problem0
They asked me to code one question which was on stacks, I don't remember the question, but it was also not difficult, and I wrote the code for that. Then they started to drill me on my resume, on every project that I had done, every miniscule detail.
Tips: Be very thorough with your resume. It's a clear red flag for them if you can't explain something you have written on your resume.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
Software Developer
3 rounds | 9 problems
Interviewed by Myntra pvt ltd
2265 views
1 comments
0 upvotes
Software Developer
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Myntra pvt ltd
1944 views
1 comments
0 upvotes
Software Developer
3 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Myntra pvt ltd
2056 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Software Developer
4 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Myntra pvt ltd
1290 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
Software Developer
5 rounds | 14 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
3987 views
1 comments
0 upvotes
Software Developer
6 rounds | 12 problems
Interviewed by SAP Labs
2872 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Software Developer
3 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
1202 views
0 comments
0 upvotes






