Myntra pvt ltd interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
Software Developer
Myntra pvt ltd
3 rounds | 5 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 6 months
Topics: Data Structures, Algorithms, System Design, Aptitude, OOPS
Tip
Tip 1 : Must do Previously asked Interview as well as Online Test Questions.
Tip 2 : Go through all the previous interview experiences from Codestudio.
Tip 3 : Do at-least 2 good projects and you must know every bit of them.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: Above 7 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Have at-least 2 good projects explained in short with all important points covered.
Tip 2 : Every skill must be mentioned.
Tip 3 : Focus on skills, projects and experiences more.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Easy
Online Coding Interview
Duration120 minutes
Interview date10 Sep 2020
Coding problem2
This was a 2 hour round consisting of 5 mcqs and 2 codes. The mcqs were pretty much simple based on DS, DBMS, OS, OOP, and C language.
1. Convert A Given Binary Tree To Doubly Linked List
Moderate
15m average time
80% success
0/80
Asked in companies


Given a Binary Tree, convert this binary tree to a Doubly Linked List.
A Binary Tree (BT) is a data structure in which each node has at most two children.
A Doubly Linked List contains a previous pointer, along with the next pointer and data.
The order of nodes in Doubly Linked List must be the same as Inorder of the given Binary Tree.
The doubly linked list should be returned by taking the next pointer as right and the previous pointer as left.
You need to return the head of the Doubly Linked List.
For the given binary tree :
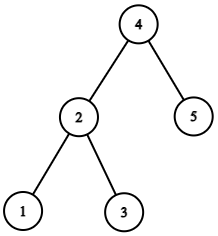
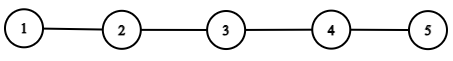
You need to return the head to the doubly linked list.
The doubly linked list would be: 1 2 3 4 5 and can be represented as:
Problem approach
If the left subtree exists, recursively convert the left subtree to Doubly Linked List.
If the right subtree exists, recursively convert the right subtree to Doubly Linked List.
When in the left subtree, find the inorder predecessor of the root, make this as the previous of the root and its next as the root.
Similarly, when in the right subtree, find the inorder successor of the root, make this as the next of the root and its previous as the root
Finally, return the leftmost node and return it since this would be the head of the Doubly Linked List.
2. Validate BST
Moderate
25m average time
70% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Given a binary tree with N number of nodes, check if that input tree is Partial BST (Binary Search Tree) or not. If yes, return true, return false otherwise.
A binary search tree (BST) is said to be a Partial BST if it follows the following properties.
• The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with data less than and equal to the node’s data.
• The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with data greater than and equal to the node’s data.
• Both the left and right subtrees must also be partial binary search trees.
Example:
Input:
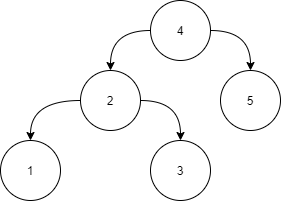
Answer:
Level 1:
All the nodes in the left subtree of 4 (2, 1, 3) are smaller
than 4, all the nodes in the right subtree of the 4 (5) are
larger than 4.
Level 2 :
For node 2:
All the nodes in the left subtree of 2 (1) are smaller than
2, all the nodes in the right subtree of the 2 (3) are larger than 2.
For node 5:
The left and right subtree for node 5 is empty.
Level 3:
For node 1:
The left and right subtree for node 1 are empty.
For node 3:
The left and right subtree for node 3 are empty.
Because all the nodes follow the property of a Partial binary
search tree, the above tree is a Partial binary search tree.
Problem approach
A simple O(N) approach for this question would be :
1. Do an inorder traversal of the tree and store all the values in a temporary array.
2. Next, check if the array is sorted in ascending order or not.
3. If it is sorted, the given tree is a BST.
The above approach uses an auxiliary array. In order to avoid using auxiliary array :
1. Maintain track of the previously visited node in a variable prev.
2. Next, do an inorder traversal of the tree and store the value of the previously visited node in prev.
3. If the value of the current node is less than prev, then the given tree is not a BST.
02
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date12 Sep 2020
Coding problem3
3 coding questions were asked in this round.
1. Sort an array in wave form
Easy
10m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You have been given an unsorted array ‘ARR’.
Your task is to sort the array in such a way that the array looks like a wave array.
Example:
If the given sequence ‘ARR’ has ‘N’ elements then the sorted wave array looks like -
‘ARR[0] >= ARR[1]’ and ‘ARR[1] <= ARR[2]’
‘ARR[2] >= ARR[3]’ and ‘ARR[3] <= ARR[4]’
‘ARR[4] >= ARR[5]’ and ‘ARR[5] <= ARR[6]’ And so on.
Note:
1. ‘ARR[0]’ must be greater than or equal to ‘ARR[1]’.
2. There can be multiple arrays that look like a wave array but you have to return only one.
3. We have an internal function that will check your solution and return 'True' in case your array is one of the solutions otherwise return 'False'.
Explanation
The given array ‘ ARR = { 4, 3, 5, 2, 3, 1, 2 } ’
The below figure is a visual representation of the given ‘ARR’ and you can see we can express ‘ARR’ in a waveform array because
4>3 and 3<5
5>2 and 2<3
3>1 and 1<2
And it follows the condition of wave array.
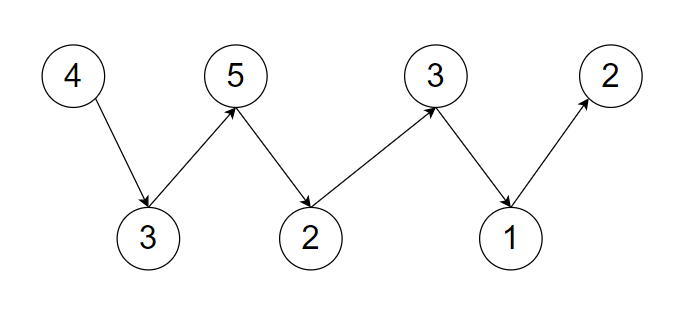
Follow up:
Try to solve this problem in linear time complexity.
Problem approach
This question can be solved using any sorting algorithm.
1. Sort the array first so that all the elements are arranged in increasing order.
A[0]<=A[1]<=A[2]<=A[3]…. A[n-1]
2. Next, pick the elements in pairs from the start and swap the adjacent elements. This will arrange the array in the wave form.
The time complexity of this approach would be O(nlogn).
For a more optimized approach, On observing the output pattern carefully, if the values at all even positions are greater than the value at the odd positions, then the wave form can be obtained.
1. So, run a loop incrementing by two to Iterate over even positioned
elements.
2. If the current element is smaller than the last odd element, then swap the
current element with the last element.
if(i > 0 && A[i-1] > A[i])
swap(A[i], A[i-1])
3. If the current element is smaller than the next odd element, then swap the
current element with the last element.
if(i < n-1 && A[i] < A[i+1])
swap(A[i], A[i+1])
2. Search In Rotated Sorted Array
Moderate
30m average time
65% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Aahad and Harshit always have fun by solving problems. Harshit took a sorted array consisting of distinct integers and rotated it clockwise by an unknown amount. For example, he took a sorted array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] and if he rotates it by 2, then the array becomes: [4, 5, 1, 2, 3].
After rotating a sorted array, Aahad needs to answer Q queries asked by Harshit, each of them is described by one integer Q[i]. which Harshit wanted him to search in the array. For each query, if he found it, he had to shout the index of the number, otherwise, he had to shout -1.
For each query, you have to complete the given method where 'key' denotes Q[i]. If the key exists in the array, return the index of the 'key', otherwise, return -1.
Note:
Can you solve each query in O(logN) ?
Problem approach
This question could be solved using Binary search which would have a time complexity of O(log n).
The approach would be:
1.Find the mid = (low + high)/2
2.If key is present at middle point, return mid.
3. If arr[low….mid] is sorted
a) If key to be searched lies in range from arr[low] to arr[mid], apply binary search for arr[low..mid].
b) Else apply for arr[mid+1..high]
4. Else (arr[mid+1..high] must be sorted)
a) If key to be searched lies in range from arr[mid+1]
to arr[high], apply binary search for arr[mid+1..high].
b) Else recur for arr[low..mid]
3. Running Median
Hard
46m average time
50% success
0/120
Asked in companies



You are given a stream of 'N' integers. For every 'i-th' integer added to the running list of integers, print the resulting median.
Print only the integer part of the median.
Problem approach
To solve this question, the concept of heaps can be used. Two heaps can be maintained: a max heap for storing lower half of the numbers and a min heap for storing greater half of the numbers.
Process each element one by one.
1. To add an element to one of the heaps:
Check if next item is smaller than maxHeap root add it to maxHeap, else add it to minHeap
2: Balance the heaps (after this step heaps will be either balanced or one of them will contain 1 more item)
Condition : If number of elements in one of the heaps is greater than the other by more than 1, remove the root element from the one containing more elements and add to the other one
3. Now to calculate median:
If the heaps contain equal amount of elements;
median = (root of maxHeap + root of minHeap)/2
Else
median = root of the heap with more elements
The time complexity of this approach would be O(nlogn) and auxiliary space complexity is O(n).
03
Round
Easy
HR Round
Duration30 minutes
Interview date15 Sep 2020
Coding problem0
This was a HR round. A number of questions were asked.
Q1. My info & work
Q2. What are my favorite tasks & contribution?
Q3. What are technical challenges that you solved?
Q4. Where do you want to work & what interests you?
I also asked the interviewer some questions which include :
Q1. What is your role?
Q2. Where did you work before?
Q3. What are +ve & -ve’s of myntra, you think?
Q4. Why you left your previous job?
Q5. How is work life at myntra?

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
Software Developer
3 rounds | 9 problems
Interviewed by Myntra pvt ltd
2265 views
1 comments
0 upvotes
Software Developer
3 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Myntra pvt ltd
2055 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Software Developer
4 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Myntra pvt ltd
1289 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Software Developer
4 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Myntra pvt ltd
1765 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
Software Developer
5 rounds | 14 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
3987 views
1 comments
0 upvotes
Software Developer
6 rounds | 12 problems
Interviewed by SAP Labs
2872 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Software Developer
3 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
1202 views
0 comments
0 upvotes




