Myntra pvt ltd interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
Software Developer
Myntra pvt ltd
3 rounds | 9 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 3 months
Topics: Data Structures, Algorithms, System Design, Aptitude, OOPS, Databases
Tip
Tip 1 : Must do Previously asked Interview as well as Online Test Questions.
Tip 2 : Go through all the previous interview experiences from Codestudio and Leetcode.
Tip 3 : Do at-least 2 good projects and you must know every bit of them.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: Above 7 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Have at-least 2 good projects explained in short with all important points covered.
Tip 2 : Every skill must be mentioned.
Tip 3 : Focus on skills, projects and experiences more.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date4 Aug 2020
Coding problem2
It was a 60 minute online coding interview where programming questions were discussed.
1. Reverse Linked List
Moderate
15m average time
85% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Given a singly linked list of integers. Your task is to return the head of the reversed linked list.
For example:
The given linked list is 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4-> NULL. Then the reverse linked list is 4 -> 3 -> 2 -> 1 -> NULL and the head of the reversed linked list will be 4.
Follow Up :
Can you solve this problem in O(N) time and O(1) space complexity?
Problem approach
This can be solved both: recursively and iteratively.
The recursive approach is more intuitive. First reverse all the nodes after head. Then we need to set head to be the final node in the reversed list. We simply set its next node in the original list (head -> next) to point to it and sets its next to NULL. The recursive approach has a O(N) time complexity and auxiliary space complexity.
For solving the question is constant auxiliary space, iterative approach can be used. We maintain 3 pointers, current, next and previous, abbreviated as cur, n and prev respectively. Steps :
1. Assign prev=NULL, cur=head .
2. Next, repeat the below steps until no node is left to reverse:
1. Initialize n to be the node after cur. i.e(n=cur->next)
2. Then make cur->next point to prev (next node pointer).
3. Then make prev now point to the cur node.
4. At last move cur also one node ahead to n.
The prev pointer will be the last non null node and hence the answer.
2. Move All Negative Numbers To Beginning And Positive To End
Easy
10m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given an array 'ARR' consisting of 'N' integers. You need to rearrange the array elements such that all negative numbers appear before all positive numbers.
Note:
The order of elements in the resulting array is not important.
Example:
Let the array be [1, 2, -3, 4, -4, -5]. On rearranging the array such that all negative numbers appear before all positive numbers we get the resulting array [-3, -5, -4, 2, 4, 1].
Problem approach
The naive approach would be to use an auxiliary array. Copy all elements to that array. Copy all negative elements first to the original array and then all positive elements. This approach would have a time complexity of O(N) but also uses O(N) auxiliary space.
For constant space, we first count total negative numbers.
Then till all negative numbers are moved to the beginning, traverse the array. Swap the positions of negative and positive elements and move negative numbers one by one to correct position.
02
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date5 Aug 2020
Coding problem4
Questions based on data structures , OOPS , Java and operating systems were discussed.
1. Convert a binary tree to its sum tree
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



Given a binary tree of integers, you are supposed to modify the given binary tree to a sum tree where each node value is replaced by the sum of the values of both left and right subtrees in the given tree. The value of leaf nodes is changed to zero.
Example:
Below is the example showing the input tree and its sum tree.
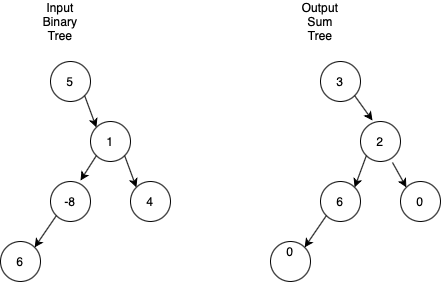
Problem approach
The question can be solved recursively in O(N) time complexity and O(N) auxiliary space complexity.
Store the initial value of the node in a variable.
Next, Recursively call for left and right subtrees and change the value of the current node as sum of the values returned by the two recursive calls.
At last, return the sum of new value and the initial value.
2. Java Question
String pool and how garbage collection functionality works?
Problem approach
String Pool in java is a pool of Strings stored in Java Heap Memory. String pool helps in saving a lot of space for Java Runtime although it takes more time to create the String. String Pool is possible only because String is immutable in Java and its implementation of String interning concept. String pool is also an example of Flyweight design pattern.
3. Java Question
Singleton pattern, observer pattern?
Problem approach
Singleton is a creational design pattern which ensures that a class has only one instance, while providing a global access point to this instance.
The Observer Pattern defines a one to many dependency between objects so that one object changes state, all of its dependents are notified and updated automatically.
4. Java Question
How to synchronize HashMap in Java?
Problem approach
HashMap is a non-synchronized collection class. So, we need to explicitly synchronise them. HashMap can be synchronized using the Collections.synchronizedMap() method. It returns a thread-safe map backed up by the specified HashMap. In order to guarantee serial access, it is critical that all access to the backing map is accomplished through the returned map.
Syntax: public static Map synchronizedMap(Map m)
Parameters: This method takes the map as a parameter to be “wrapped” in a synchronized map.
Return Value: This method returns a synchronized view of the specified map.
03
Round
Medium
HR Round
Duration45 minutes
Interview date5 Aug 2020
Coding problem3
This was CTO round, if you make this round…you are doing pretty good.
He asked a lot on what I worked on and asked questions relevant to that. Process thread, stacks heaps. A minor system design on component in their system. How they are shared between and trade-off. We discussed about scalability and challenge.
1. System Design Question
Design a website where after user request. A bunch of processes need to be executed and then a mail is sent to user with the result. Take care of scalability etc?
2. DBMS Questions
Design with one-one mapping, one-many mapping…some basic questions
3. OS Question
Difference between process and thread
Problem approach
A process is an instance of a program that is being executed. Thread is a lightweight process that is managed by the scheduler independently. For Eg : Opening a new browser is a process while opening multiple tabs in a browser is thread.
Processes are independent of each other while threads are interdependent and share memory.
Each process is treated as a new process by the operating system while with threads. the OS takes all the user-level threads as a single process.
If one process gets blocked by the operating system, then the other process can continue the execution. But if any user-level thread gets blocked, all of its peer threads also get blocked because OS takes all of them as a single process.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
Software Developer
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Myntra pvt ltd
1943 views
1 comments
0 upvotes
Software Developer
3 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Myntra pvt ltd
2055 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Software Developer
4 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Myntra pvt ltd
1289 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Software Developer
4 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Myntra pvt ltd
1765 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
Software Developer
5 rounds | 14 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
3986 views
1 comments
0 upvotes
Software Developer
6 rounds | 12 problems
Interviewed by SAP Labs
2872 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Software Developer
3 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
1202 views
0 comments
0 upvotes






