Nagarro Software interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - 1
Nagarro Software
3 rounds | 9 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 4 Months
Topics: Data Structures, Algorithms, System Design, Aptitude, OOPS
Tip
Tip 1 : Must do Previously asked Interview as well as Online Test Questions.
Tip 2 : Go through all the previous interview experiences from Codestudio.
Tip 3 : Do at-least 2 good projects and you must know every bit of them.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: Above 7 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Have at-least 2 good projects explained in short with all important points covered.
Tip 2 : Every skill must be mentioned.
Tip 3 : Focus on skills, projects and experiences more.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Medium
Online Coding Interview
Duration150 Minutes
Interview date14 Jul 2021
Coding problem3
It was an Aptitude test and Technical objective test of 60 minutes followed by a Coding test of 90 minutes.There was a 1 hour gap b/w the two tests.
1. Count Ways To Reach The N-th Stairs
Moderate
30m average time
80% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You have been given a number of stairs. Initially, you are at the 0th stair, and you need to reach the Nth stair.
Each time, you can climb either one step or two steps.
You are supposed to return the number of distinct ways you can climb from the 0th step to the Nth step.
Note:
Note: Since the number of ways can be very large, return the answer modulo 1000000007.
Example :
N=3
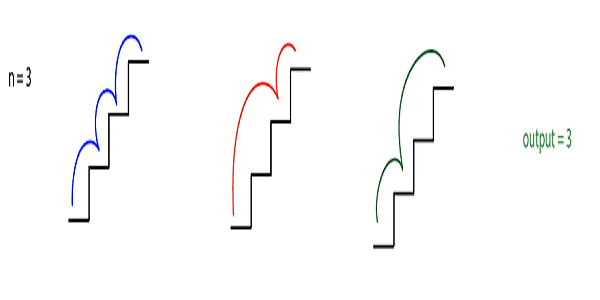
We can climb one step at a time i.e. {(0, 1) ,(1, 2),(2,3)} or we can climb the first two-step and then one step i.e. {(0,2),(1, 3)} or we can climb first one step and then two step i.e. {(0,1), (1,3)}.
Problem approach
Approach (Using DP) :
Our intuition is:
How can we reach “currStep” step in taking one step or two steps:
1) We can take the one-step from (currStep-1)th step or,
We can take the two steps from (currStep-2)th step.
2) So the total number of ways to reach “currStep” will be the sum of the total number of ways to reach at (currStep-1)th and the total number of ways to reach (currStep-2)th step.
Let dp[currStep] define the total number of ways to reach “currStep” from the 0th. So,
dp[ currStep ] = dp[ currStep-1 ] + dp[ currStep-2 ]
3) The base case will be, If we have 0 stairs to climb then the number of distinct ways to climb will be one (we are already at Nth stair that’s the way) and if we have only one stair to climb then the number of distinct ways to climb will be one, i.e. one step from the beginning.
TC : O(N), where ‘N’ is the number of stairs.
SC : O(N)
2. Equilibrium Index
Easy
0/40
Asked in companies


You are given an array Arr consisting of N integers. You need to find the equilibrium index of the array.
An index is considered as an equilibrium index if the sum of elements of the array to the left of that index is equal to the sum of elements to the right of it.
Note:
1. The array follows 0-based indexing, so you need to return the 0-based index of the element.
2. Note that the element at the equilibrium index won’t be considered for either left sum or right sum.
3. If there are multiple indices which satisfy the given condition, then return the left-most index i.e if there are indices i,j,k…. which are equilibrium indices, return the minimum among them
4. If no such index is present in the array, return -1.
Problem approach
Approach :
1) Let prefSum[] be the array which stores the prefix sum, where prefSum[i] will be the sum of elements of the array up to the index i i.e prefSum[i] = arr[0] + arr[1] + …. + arr[i]
2) So if we are at index i, the sum of elements to the left of index i is stored at leftSum = prefSum[i - 1], given that i-1 is a valid array index.
3) Let arraySum denote the sum of the complete array.
4) Now to find the sum of elements to the right of the index i, rightSum = total sum - (sum of elements to the left of i )+ arr[i](because we need to exclude the element at index i)
5) The above statement can be simplified to rightSum = arraySum - prefSum[i - 1] + arr[i]. Thus we can say that rightSum = arraySum - prefSum[i] (since prefSum[i - 1] + arr[i] = prefSum[i]).
6) If we get leftSum = rightSum at any index, return that index.
7) After for loop ends return -1, since there is no valid index.
TC : O(N), where N=size of the array
SC : O(N)
3. Closest Perfect Square
Easy
15m average time
80% success
0/40
Asked in company

You are given a positive integer ‘N’. You are required to print the perfect square number closest to the ‘N’ and the number of steps required to reach that number.
For Example:
N = 21
The perfect square closest to 21 is 25, and the distance is 4.
Problem approach
Approach :
1) Declare a variable ‘X’ of type int to store the square root of ‘N’.
2) Compare the Distance between the square of ‘X’ and ‘N’ and the square of ‘X + 1’ and ‘N’.
3) If the distance of ‘N’ from the square of ‘X’ is less than the distance of ‘N’ from the square of ‘X + 1’ then return X and abs(N - (X * X)).
4) Otherwise return ‘X+1’and abs( N - (X+1) * (X + 1)).
TC : O(sqrt(N)), where N=given integer
SC : O(1)
02
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration45 Minutes
Interview date14 Jul 2021
Coding problem2
This round had 2 questions where I had to first explain my approach with proper complexity analysis and then write the pseudo code for the same.
1. Longest Palindromic Substring
Moderate
35m average time
65% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Given a string ’S’ consisting of lower case English letters, you are supposed to return the longest palindromic substring of ‘S’.
Note that in case of more than one longest palindromic substrings with the same length you need to return the rightmost substring in the given string. For example in string “bbbab”, there are two possible longest palindromic substrings i.e. “bbb” and “bab”, and since you are supposed to return the rightmost substring, so you need to return “bab” as the answer.
Note:
A substring is a contiguous sequence of elements within a string (for example, “bcd” is a substring of “abcde” while “bce” is not).
A string is said to be palindrome if the reverse of the string is the same as the actual string. For example, “abba” is a palindrome, but “abbc” is not a palindrome.
Problem approach
Approach :
1) Create a 2-D dp boolean vector(with all false initially) where dp[i][j] states whether s[i...j] is a palindrome or not and initilialise a variable ans=1 which will store the final answer.
2) Base Case : For every i from 0 to n-1 fill dp[i][i]=1 ( as a single character is always a palindrome ).
3) Now, run 2 loops first one from i=n-1 to i=0 (i.e., tarverse from the back of the string) and the second one from j=i+1 to n.
4) For every s[i]==s[j] , check if(j-i==1 i.e., if s[i] and s[ j] are two consecutive same letters) or if(dp[i+1][j-1]==1 or not i.e., if the string s[i+1,....j-1] is palindrome or not.
5) Because if the string s[i+1,....j-1] is a palindrome and s[i]==s[j] then s[i] and s[j] can be appended at the starting and the ending position of s[i+1,...j-1] and s[i...j] will then be a palindrome , so mark dp[i][j]=1 and update the answer as ans=max(ans , j-i+1).
6) Finally return the ans
TC : O(N^2) where N=length of the string s
SC : O(N^2)
2. Validate BST
Moderate
25m average time
70% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Given a binary tree with N number of nodes, check if that input tree is Partial BST (Binary Search Tree) or not. If yes, return true, return false otherwise.
A binary search tree (BST) is said to be a Partial BST if it follows the following properties.
• The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with data less than and equal to the node’s data.
• The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with data greater than and equal to the node’s data.
• Both the left and right subtrees must also be partial binary search trees.
Example:
Input:
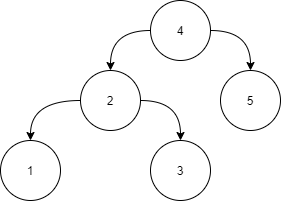
Answer:
Level 1:
All the nodes in the left subtree of 4 (2, 1, 3) are smaller
than 4, all the nodes in the right subtree of the 4 (5) are
larger than 4.
Level 2 :
For node 2:
All the nodes in the left subtree of 2 (1) are smaller than
2, all the nodes in the right subtree of the 2 (3) are larger than 2.
For node 5:
The left and right subtree for node 5 is empty.
Level 3:
For node 1:
The left and right subtree for node 1 are empty.
For node 3:
The left and right subtree for node 3 are empty.
Because all the nodes follow the property of a Partial binary
search tree, the above tree is a Partial binary search tree.
Problem approach
Approach :
1) Take a stack of TreeNodes and a TreeNode prev with its initial value as NULL.
2) Run a loop till stack is not empty or root != NULL.
3) While pushing a root to the stack, push all its left descendants into the stack untill root != NULL.
4) Take current = stack.top() and pop it from the stack
5) Check if prev is NOT NULL and if prev->val >= curr->val , if this cond. is met simply return false.
6) Update prev with current.
7) Update root with root->right.
TC : O(N) where N=number of nodes in the binary tree
SC : O(N)
03
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration50 Minutes
Interview date14 Jul 2021
Coding problem4
This round also had 2 questions from DS/Algo which were followed by some questions from DBMS and SQL.
1. Nearest numbers with the same number of set bits
Easy
10m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



Given a positive integer ‘n’, your task is to find the next smallest integer and the previous largest integer having the exact number of ‘1’ bits set in their binary representation as ‘n’.
Example:
‘n = 6’
The binary representation of 6 = ‘0110’, which has two ‘1’ bits set.
Next smallest integer = 9 = ‘1001’, the smallest integer greater than 6 having two ‘1’ bits set.
Previous largest integer = 5 = ‘0101’, largest integer smaller than 6 having two ‘1’ bits set.
Therefore, the answer is {9, 5}.
Note:
1. ‘n’ is a positive integer greater than one.
2. For any given integer ‘n’, there is always a positive integer smaller than ‘n’ having the exact number of ‘1’ bits set.
3. Don’t print anything. Just implement the function and return the answer.
4. ‘n’ can have a max of ‘30’ bits.
Problem approach
Approach :
When we observe the binary sequence from 0 to 2n – 1 (n is no. of bits), right most bits (least significant) vary rapidly than left most bits. The idea is to find right most string of 1’s in x, and shift the pattern to right extreme, except the left most bit in the pattern. Shift the left most bit in the pattern (omitted bit) to left part of x by one position.
//Pseudo Code :
int findNextGreaterNum(int n)
{
int ct=0 , subt=0, idx=0;
for(int i=0; i<32; i++)
{
while(n&(1<0)
{
idx=i; //idx-1 will hold the position of the leftmost one in the rightmost 1's pattern
break;
}
}
int add=(1< int ans=n-subt+add;
cout< return ans;
}
2. Find Duplicates In Array
Easy
15m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given an array/list 'ARR' consisting of N integers, which contains elements only in the range 0 to N - 1. Some of the elements may be repeated in 'ARR'. Your task is to find all such duplicate elements.
Note:
1. All the elements are in the range 0 to N - 1.
2. The elements may not be in sorted order.
3. You can return the duplicate elements in any order.
4. If there are no duplicates present then return an empty array.
Problem approach
Approach :
1) There is another mathematical approach by which we can solve this problem in linear time and constant space.
2) For every element ARR[i], increment the ARR[i]%N’th element by n i.e. ARR[ARR[i] % N] += N.
3) Now again traverse the array and print the indices where ARR[i]/N is greater than 1. It guarantees that the number N has been added to that index.
4) All these indices will be the repetitive elements because all the elements in the array are in the range 0 to N - 1 and ARR[i] will be greater than N if and only if ‘i’ has occurred more than once in the array.
TC : O(N)
SC : O(1)
3. DBMS Question
Advantages of using Views.
Problem approach
The advantages of using a view in the table are :
1) It is a subset of the data in table.
2) It store complex queries.
3) It can simplify multiple tables into one.
4) It occupies very little space.
5) It presents the data from different perspectives.
4. DBMS Question
What are Constraints in SQL?
Problem approach
Constraints are used to specify the rules concerning data in the table. It can be applied for single or multiple fields in an SQL table during the creation of the table or after creating using the ALTER TABLE command. The constraints are:
1) NOT NULL - Restricts NULL value from being inserted into a column.
2) CHECK - Verifies that all values in a field satisfy a condition.
3) DEFAULT - Automatically assigns a default value if no value has been specified for the field.
4) UNIQUE - Ensures unique values to be inserted into the field.
5) INDEX - Indexes a field providing faster retrieval of records.
6) PRIMARY KEY - Uniquely identifies each record in a table.
7) FOREIGN KEY - Ensures referential integrity for a record in another table.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Nagarro Software
0 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Nagarro Software
917 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Nagarro Software
1208 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Nagarro Software
748 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
5 rounds | 12 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
114869 views
24 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
58031 views
5 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
35057 views
7 comments
0 upvotes





