Nagarro interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
Trainee Software Engineer
Nagarro
4 rounds | 5 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Journey
I was in the final year of college when I applied to Nagarro in 2021. I later appeared for two online assessments followed by two interviews. Entering Nagarro as a trainee software professional in my final year of college marked the beginning of a transformative journey.
Application story
Entering the recruitment process at Nagarro through my college's training and placement cell, I swiftly progressed through the stages. A week after applying, I was greeted with an online assessment featuring theoretical objective questions. Upon success, I encountered a second round the next day. The second round was a coding round with three easy-level DSA questions. Although I could only solve two out of the three questions, I received confirmation that I had cleared the coding round. Then I received an invite for a technical interview.
Within five days, I prepared for the interview, but I did not hear from them for a month. After a month, HR emailed me to ask for available time slots for the managerial and HR rounds. I provided the details, and my final round was scheduled. Within a week of the final round, I received my offer letter, with my joining date set for 20 days later.
Why selected/rejected for the role?
My core subject knowledge was beyond expectations as I was preparing for the GATE exam. This helped me in the selection process.
Preparation
Duration: 3 months
Topics: Arrays, String, LinkedList, Sorting algorithms, OOPS fundamentals, DBMS
Tip
Tip 1: Fundamentals must be clear.
Tip 2: Practice speaking while writing code during the interview.
Tip 3: Be calm while answering questions and listen properly to the question.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: 7 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1: Be confident while you answer.
Tip 2: Prepare your core CSE fundamentals thoroughly.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Easy
Online Coding Interview
Duration30 minutes
Interview date8 Apr 2021
Coding problem0
DBMS, SQL and DSA.
02
Round
Medium
Online Coding Interview
Duration60 minutes
Interview date9 Apr 2021
Coding problem3
1. Array
Moderate
15m average time
85% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given an array consisting of 'N' positive integers where each integer is either 0 or 1 or 2. Your task is to sort the given array in non-decreasing order.
Note :
1. The array consists of only 3 distinct integers 0, 1, 2.
2. The array is non-empty.
2. Reverse Stack Using Recursion
Easy
21m average time
80% success
0/40
Asked in companies


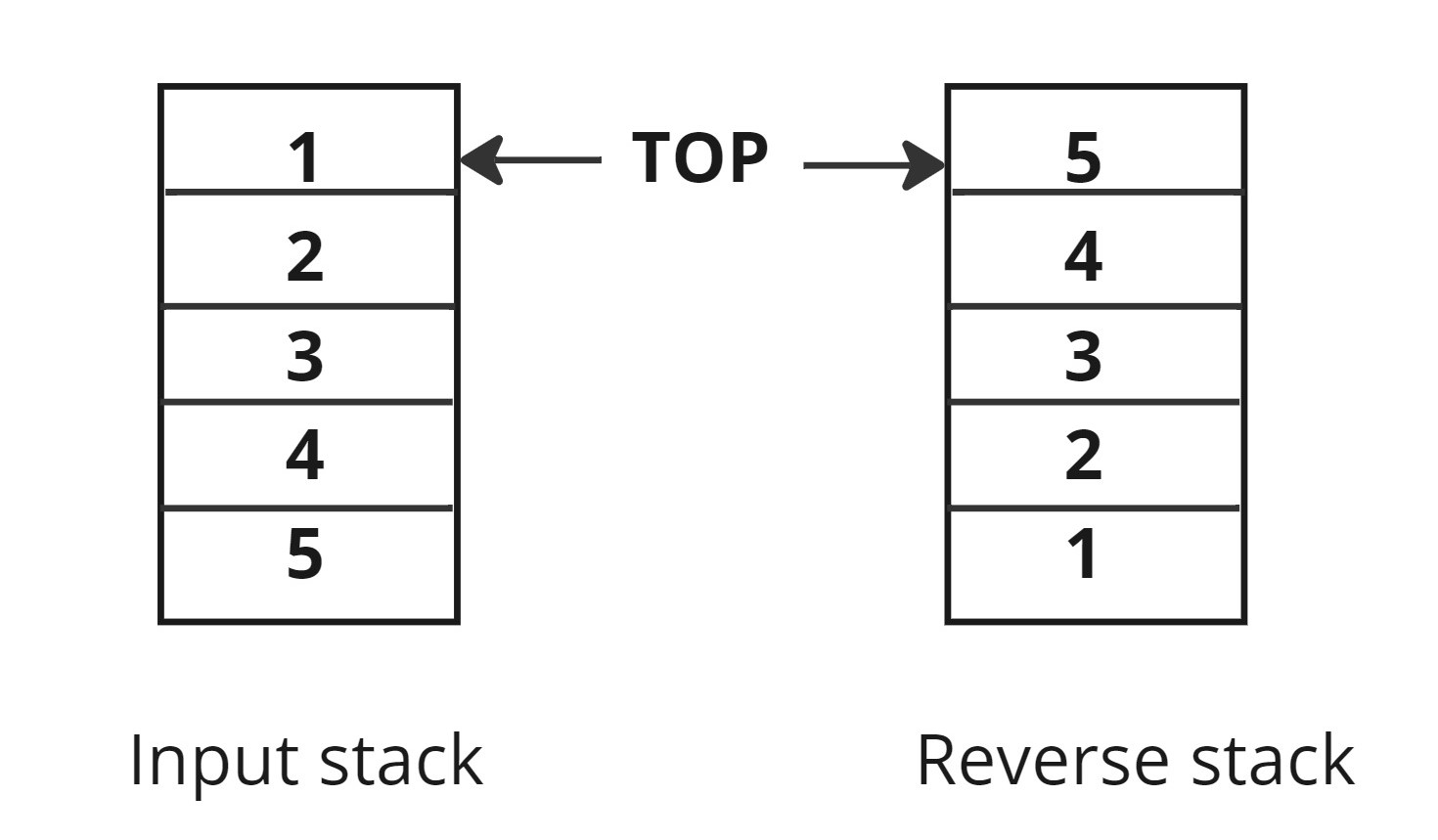
Reverse a given stack of 'N' integers using recursion. You are required to make changes in the input parameter itself.
Note: You are not allowed to use any extra space other than the internal stack space used due to recursion.
Example:
Input: [1,2,3,4,5]
Output: [5,4,3,2,1]
3. Hashing
Easy
25m average time
65% success
0/40
Asked in companies



‘Hashing’ is a technique in which a large non-negative integer is mapped with a smaller non-negative integer using a function called ‘hash function’ and this smaller integer is used as an index of an array called ‘hash table’.
We define ‘Collision’ as a situation when a large integer is mapped to the index in a hash table that is already mapped with some other integer.
‘Quadratic Probing’ is a collision handling technique in which we take the original hash value and successively add ‘i*i’ in ‘ith’ iteration until an unmapped index is found in the hash table. This technique works as follows:
Let ‘x’ be a larger integer, ‘n’ be the size of the hash table, and ‘h(x) = x mod n’ be a hash function. Then in Quadratic Probing -:
1. If we find that the index h(x), is already mapped to some other integer in the hashtable, then we try for index (h(x) + 1 * 1) mod n.
2. If the index (h(x) + 1*1) mod n, is also already mapped to some other integer in the hashtable, then we try for index (h(x) + 2 * 2) mod n.
3. If the index (h(x) + 2*2) mod n, is also already mapped to some other integer in the hashtable, then we try for index ‘(h(x) + 3 * 3) mod n.
4. We repeat this process until an unmapped index is found in the hashtable or index values start repeating.
In Quadratic probing, sometimes, it is possible that we cannot map an integer with any index in the hashtable.
Given an array ‘keys’ consisting of ‘n’ non-negative integers. Let's consider the hash function h(x) = x mod n. Assume that you are traversing the array ‘keys’ from left to right and you need to insert all these keys in the hash table. For each element of the array ‘keys’, your task is to determine the index by which this element is mapped in the hash table if ‘Quadratic Probing’ technique is used to handle the collision. Return an array ‘hashTable’ of size ‘n’ where the element at index ‘i’ is the element from the given array ‘keys’ that is mapped to that index or -1 if no element is mapped to that index.
For Example -: Consider, array ‘keys’ = {50, 49, 76, 85, 92, 73, 18}, ‘n’ = 7 and the hash function h(x) = x mod 7. Then -:
1. h(50) = 50 mod 7 = 1, thus it will be mapped to index ‘1’ in the hashtable.
2. h(49) = 49 mod 7 = 0, thus it will be mapped to index ‘0’ in hashtable.
3. h(76) = 76 mod 7 = 6, thus it will be mapped to index ‘6’ in the hashtable.
4. h(85) = 85 mod 7 = 1, thus it should be mapped to index ‘1’ in the hashtable, but index ‘1’is already mapped with 50, so we try for index (h(85) + 1*1) mod 7 = ‘2’, as index ‘2’ is not mapped previously, thus it will be mapped to index ‘2’ in hashtable’.
5. h(92) = 92 mod 7 = 1, thus it should be mapped to index ‘1’ in the hashtable, but index ‘1’ is already mapped with 50, so we try for index (h(92) + 1*1) mod 7 = 2, but index ‘2’ is also occupied so we try for index (h(92) + 2*2) mod 7 = ‘5’, as index ‘5’ is not mapped previously, thus it will be mapped to index ‘5’ in hashtable
6. h(73) = 73 mod 7 = 3, thus it will be mapped to index ‘3’ in the hashtable.
7. h(18) = 18 mod 7 = 4, thus it will be mapped to index ‘4’ in the hashtable.
Thus the resultant array ‘hashTable’ should be {49, 50, 85, 73, 18, 92, 76}.

Note:
1. Consider ‘0’ based indexing.
2. Don’t print anything, just return the integer array ‘hashTable’.
03
Round
Medium
Face to Face
Duration40 minutes
Interview date15 Apr 2021
Coding problem1
1. DSA, Time complexity, space complexity, projects, internship etc.
Asked for an introduction and then asked about my internship and final-year project.
After that, they asked me about OOP pillars.
What is time complexity and space complexity? (Learn)
Merge sort and Quick sort their time complexity and which one is better and why?
Followed by 1 linked-list question for which they asked my to share screen and write pseudo code.
04
Round
Easy
HR Round
Duration20 minutes
Interview date15 Jul 2021
Coding problem1
1. HR Questions
Personality and behavioural questions.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
Which SQL clause is used to specify the conditions in a query?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by OYO
4355 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 9 problems
Interviewed by Salesforce
3265 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
System Engineer
2 rounds | 2 problems
Interviewed by Tata Consultancy Services (TCS)
2809 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Associate Software Engineer
3 rounds | 2 problems
Interviewed by Nagarro
389 views
0 comments
0 upvotes






