NCR Corporation interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
Software Engineer Intern
NCR Corporation
3 rounds | 9 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 3 months
Topics: Data Structures, Algorithms, Aptitude, OOPS, OS
Tip
Tip 1 : Must do Previously asked Interview as well as Online Test Questions.
Tip 2 : Go through all the previous interview experiences from Codestudio and Leetcode.
Tip 3 : Do at-least 2 good projects and you must know every bit of them.
Application process
Where: Company Website
Eligibility: Above 7 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Have at-least 2 good projects explained in short with all important points covered.
Tip 2 : Every skill must be mentioned.
Tip 3 : Focus on skills, projects and experiences more.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date14 Sep 2020
Coding problem3
Technical Interview round with questions on DSA and DBMS.
1. Merge Sort
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



Given a sequence of numbers ‘ARR’. Your task is to return a sorted sequence of ‘ARR’ in non-descending order with help of the merge sort algorithm.
Example :
Merge Sort Algorithm -
Merge sort is a Divide and Conquer based Algorithm. It divides the input array into two-parts, until the size of the input array is not ‘1’. In the return part, it will merge two sorted arrays a return a whole merged sorted array.
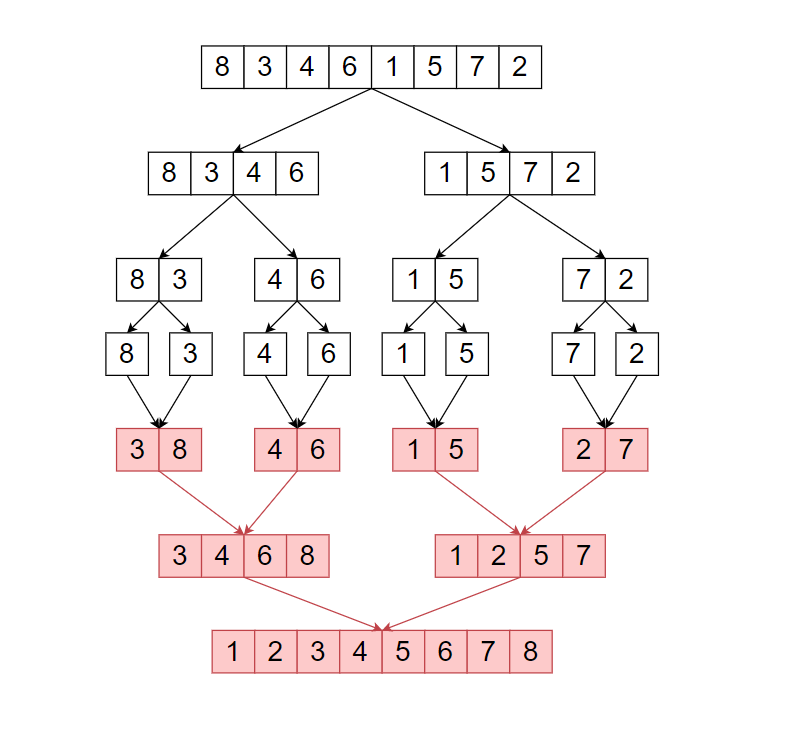
The above illustrates shows how merge sort works.
Note :
It is compulsory to use the ‘Merge Sort’ algorithm.
Problem approach
It works on the principle of Divide and Conquer. Merge sort repeatedly divides the array into several arrays until each array consists of a single element and merging those arrays in a manner that results into a sorted array.
Pseudocode :
MergeSort(A, p, r):
if p > r
return
q = (p+r)/2
mergeSort(A, p, q)
mergeSort(A, q+1, r)
merge(A, p, q, r)
Merge function : The task is to merge two subarrays A[p..q] and A[q+1..r] to create a sorted array A[p..r].
Steps :
Create copies of the subarrays L ← A[p..q] and M ← A[q+1..r].
Create three pointers i, j and k
i indicates current index of L, starting at 1
j indicates current index of M, starting at 1
k indicates the current index of A[p..q], starting at p.
Until we reach the end of either L or M, pick the larger among the elements from L and M and place them in the correct position at A[p..q]
When we run out of elements in either L or M, pick up the remaining elements and put in A[p..q]
Time complexity : O(nlogn)
2. Search In Rotated Sorted Array
Easy
12m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You have been given a sorted array/list 'arr' consisting of ‘n’ elements. You are also given an integer ‘k’.
Now the array is rotated at some pivot point unknown to you.
For example, if 'arr' = [ 1, 3, 5, 7, 8], then after rotating 'arr' at index 3, the array will be 'arr' = [7, 8, 1, 3, 5].
Now, your task is to find the index at which ‘k’ is present in 'arr'.
Note :
1. If ‘k’ is not present in 'arr', then print -1.
2. There are no duplicate elements present in 'arr'.
3. 'arr' can be rotated only in the right direction.
Example:
Input: 'arr' = [12, 15, 18, 2, 4] , 'k' = 2
Output: 3
Explanation:
If 'arr' = [12, 15, 18, 2, 4] and 'k' = 2, then the position at which 'k' is present in the array is 3 (0-indexed).
Problem approach
This was a pretty standard Binary Search Question and I had solved this question before on platforms like LeetCode and CodeStudio . I was asked this question to test my implementation skills and how well do I handle Edge Cases .
Approach :
1) The idea is to find the pivot point, divide the array in two sub-arrays and perform binary search.
2) The main idea for finding pivot is – for a sorted (in increasing order) and pivoted array, pivot element is the only element for which next element to it is smaller than it.
3) Using the above statement and binary search pivot can be found.
4) After the pivot is found out divide the array in two sub-arrays.
5) Now the individual sub – arrays are sorted so the element can be searched using Binary Search.
TC : O(Log(N))
SC : O(1)
3. DBMS Question
Query to find Nth highest Salary
Problem approach
TOP keyword can be used to find the nth highest salary. By default ORDER BY clause print rows in ascending order, since we need the highest salary at the top, we have used ORDER BY DESC, which will display salaries in descending order. Again DISTINCT is used to remove duplicates. The outer query will then pick the topmost salary, which would be your Nth highest salary.
SQL query :
SELECT TOP 1 salary
FROM (
SELECT DISTINCT TOP N salary
FROM #Employee
ORDER BY salary DESC
) AS temp
ORDER BY salary
02
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date14 Sep 2020
Coding problem5
Questions based on OOPS and Software Lifecycle were asked in this round.
1. Java Question
Explain the OOPS concepts.
Problem approach
A class is a user defined blueprint or prototype from which objects are created. It represents the set of properties or methods that are common to all objects of one type. In general, class declarations can include these components, in order:
1. Modifiers: A class can be public or has default access (Refer this for details).
2. Class name: The name should begin with a initial letter (capitalized by convention).
3. Superclass(if any): The name of the class’s parent (superclass), if any, preceded by the keyword extends. A class can only extend (subclass) one parent.
4. Interfaces(if any): A comma-separated list of interfaces implemented by the class, if any, preceded by the keyword implements. A class can implement more than one interface.
5. Body: The class body surrounded by braces, { }.
Object is a basic unit of Object Oriented Programming and represents the real life entities. A typical Java program creates many objects, which as you know, interact by invoking methods. An object consists of:
1. State : It is represented by attributes of an object. It also reflects the properties of an object.
2. Behavior : It is represented by methods of an object. It also reflects the response of an object with other objects.
3. Identity : It gives a unique name to an object and enables one object to interact with other objects.
4. Method: A method is a collection of statements that perform some specific task and return result to the caller. A method can perform some specific task without returning anything. Methods allow us to reuse the code without retyping the code. In Java, every method must be part of some class which is different from languages like C, C++ and Python.
The 4 pillars of OOPS are :
Pillar 1: Abstraction
Data Abstraction is the property by virtue of which only the essential details are displayed to the user. The trivial or the non-essentials units are not displayed to the user.
Data Abstraction may also be defined as the process of identifying only the required characteristics of an object ignoring the irrelevant details. The properties and behaviors of an object differentiate it from other objects of similar type and also help in classifying/grouping the objects.
Pillar 2: Encapsulation
It is defined as the wrapping up of data under a single unit. It is the mechanism that binds together code and the data it manipulates. Another way to think about encapsulation is, it is a protective shield that prevents the data from being accessed by the code outside this shield. Technically in encapsulation, the variables or data of a class is hidden from any other class and can be accessed only through any member function of own class in which they are declared.
As in encapsulation, the data in a class is hidden from other classes, so it is also known as data-hiding.
Encapsulation can be achieved by Declaring all the variables in the class as private and writing public methods in the class to set and get the values of variables.
Pillar 3: Inheritance
Inheritance is an important pillar of OOP(Object Oriented Programming). It is the mechanism in java by which one class is allow to inherit the features(fields and methods) of another class.
Pillar 4: Polymorphism
It refers to the ability of OOPs programming languages to differentiate between entities with the same name efficiently. This is done by Java with the help of the signature and declaration of these entities.
Polymorphism in Java are mainly of 2 types:
Overloading
Overriding
2. Java Question
Access modifiers in Java
Problem approach
There are four types of Java access modifiers:
Private: The access level of a private modifier is only within the class. It cannot be accessed from outside the class.
Default: The access level of a default modifier is only within the package. It cannot be accessed from outside the package. If you do not specify any access level, it will be the default.
Protected: The access level of a protected modifier is within the package and outside the package through child class. If you do not make the child class, it cannot be accessed from outside the package.
Public: The access level of a public modifier is everywhere. It can be accessed from within the class, outside the class, within the package and outside the package.
3. Software Engineering Question
What is SDLC? What are its phases?
Problem approach
Software Development Life Cycle is the application of standard business practices to building software applications. It’s typically divided into six to eight steps: Planning, Requirements, Design, Build, Document, Test, Deploy, Maintain. Some project managers will combine, split, or omit steps, depending on the project’s scope. These are the core components recommended for all software development projects.
The seven phases of SDLC are :
1. Planning
In the Planning phase, project leaders evaluate the terms of the project. This includes calculating labor and material costs, creating a timetable with target goals, and creating the project’s teams and leadership structure.
Planning can also include feedback from stakeholders. Stakeholders are anyone who stands to benefit from the application. Try to get feedback from potential customers, developers, subject matter experts, and sales reps.
2. Define Requirements
Defining requirements is considered part of planning to determine what the application is supposed to do and its requirements. For example, a social media application would require the ability to connect with a friend. An inventory program might require a search feature.
Requirements also include defining the resources needed to build the project.
3. Design and Prototyping
The Design phase models the way a software application will work. Some aspects of the design include:
Architecture – Specifies programming language, industry practices, overall design, and use of any templates or boilerplate
User Interface – Defines the ways customers interact with the software, and how the software responds to input
Platforms – Defines the platforms on which the software will run, such as Apple, Android, Windows version, Linux, or even gaming consoles
Programming – Not just the programming language, but including methods of solving problems and performing tasks in the application
Communications – Defines the methods that the application can communicate with other assets, such as a central server or other instances of the application
Security – Defines the measures taken to secure the application, and may include SSL traffic encryption, password protection, and secure storage of user credentials
Prototyping can be a part of the Design phase. A prototype is like one of the early versions of software in the Iterative software development model. It demonstrates a basic idea of how the application looks and works. This “hands-on” design can be shown to stakeholders. Use feedback o improve the application. It’s less expensive to change the Prototype phase than to rewrite code to make a change in the Development phase.
4. Software Development
This is the actual writing of the program. A small project might be written by a single developer, while a large project might be broken up and worked by several teams. Use an Access Control or Source Code Management application in this phase. These systems help developers track changes to the code. They also help ensure compatibility between different team projects and to make sure target goals are being met.
The coding process includes many other tasks. Many developers need to brush up on skills or work as a team. Finding and fixing errors and glitches is critical. Tasks often hold up the development process, such as waiting for test results or compiling code so an application can run. SDLC can anticipate these delays so that developers can be tasked with other duties.
5. Testing
It’s critical to test an application before making it available to users. Much of the testing can be automated, like security testing. Other testing can only be done in a specific environment – consider creating a simulated production environment for complex deployments. Testing should ensure that each function works correctly. Different parts of the application should also be tested to work seamlessly together—performance test, to reduce any hangs or lags in processing. The testing phase helps reduce the number of bugs and glitches that users encounter. This leads to a higher user satisfaction and a better usage rate.
6. Deployment
In the deployment phase, the application is made available to users. Many companies prefer to automate the deployment phase. This can be as simple as a payment portal and download link on the company website. It could also be downloading an application on a smartphone..
7. Operations and Maintenance
At this point, the development cycle is almost finished. The application is done and being used in the field. The Operation and Maintenance phase is still important, though. In this phase, users discover bugs that weren’t found during testing. These errors need to be resolved, which can spawn new development cycles.
In addition to bug fixes, models like Iterative development plan additional features in future releases. For each new release, a new Development Cycle can be launched.
4. Software Engineering Question
What is scrum methodology?
Problem approach
Scrum is an agile development methodology used in the development of Software based on an iterative and incremental processes. Scrum is adaptable, fast, flexible and effective agile framework that is designed to deliver value to the customer throughout the development of the project. The primary objective of Scrum is to satisfy the customer’s need through an environment of transparency in communication, collective responsibility and continuous progress. The development starts from a general idea of what needs to be built, elaborating a list of characteristics ordered by priority (product backlog) that the owner of the product wants to obtain.
5. Software Engineering Question
What is waterfall model? What are its phases?
Problem approach
he waterfall model is a sequential design process in which progress is seen as flowing steadily downwards (like a waterfall) through the phases of Conception, Initiation, Analysis, Design, Construction, Testing, Production/Implementation, and Maintenance.
The phases of waterfall model are :
1. Requirements: The first phase involves understanding what needs to design and what is its function, purpose, etc. Here, the specifications of the input and output or the final product are studied and marked.
2. System Design: The requirement specifications from the first phase are studied in this phase and system design is prepared. System Design helps in specifying hardware and system requirements and also helps in defining overall system architecture. The software code to be written in the next stage is created now.
3. Implementation: With inputs from system design, the system is first developed in small programs called units, which are integrated into the next phase. Each unit is developed and tested for its functionality which is referred to as Unit Testing.
4. Integration and Testing: All the units developed in the implementation phase are integrated into a system after testing of each unit. The software designed, needs to go through constant software testing to find out if there are any flaws or errors. Testing is done so that the client does not face any problem during the installation of the software.
5. Deployment of System: Once the functional and non-functional testing is done, the product is deployed in the customer environment or released into the market.
6. Maintenance: This step occurs after installation, and involves making modifications to the system or an individual component to alter attributes or improve performance. These modifications arise either due to change requests initiated by the customer, or defects uncovered during live use of the system. The client is provided with regular maintenance and support for the developed software.
03
Round
Easy
HR Round
Duration30 minutes
Interview date14 Sep 2020
Coding problem1
The last round was managerial round.
1. Basic HR Questions
1. Where do you see yourself after 5 years ?
2. Why NCR ?
3. Why should we hire you ?
4. Some questions on the projects that I have done.
5. Some situation based questions were asked.
Problem approach
Tip 1 : The cross questioning can go intense some time, think before you speak.
Tip 2 : Be open minded and answer whatever you are thinking, in these rounds I feel it is important to have opinion.
Tip 3 : Context of questions can be switched, pay attention to the details. It is okay to ask questions in these round, like what are the projects currently the company is investing, which team you are mentoring. How all is the work environment etc.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - Intern
4 rounds | 8 problems
Interviewed by NCR Corporation
2276 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
5 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by NCR Corporation
1207 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
4 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by NCR Corporation
1208 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Associate Software Engineer
4 rounds | 9 problems
Interviewed by NCR Corporation
1503 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
Software Engineer Intern
2 rounds | 2 problems
Interviewed by CIS - Cyber Infrastructure
606 views
1 comments
0 upvotes





