NetApp India Pvt Ltd interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - 1
NetApp India Pvt Ltd
3 rounds | 10 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 5 months
Topics: Data Structures, Algorithms, Networking, OS, DBMS, Aptitude, OOPS
Tip
Tip 1 : Must do Previously asked Interview as well as Online Test Questions.
Tip 2 : Go through all the previous interview experiences from Codestudio and Leetcode.
Tip 3 : Do at-least 2 good projects and you must know every bit of them.
Application process
Where: Referral
Eligibility: Above 7 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Have at-least 2 good projects explained in short with all important points covered.
Tip 2 : Every skill must be mentioned.
Tip 3 : Focus on skills, projects and experiences more.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Easy
Face to Face
Duration60 minutes
Interview date16 Feb 2015
Coding problem5
Technical Interview round with questions on DSA, Programming and OOPS.
1. Implement strstr() function in C
Moderate
25m average time
70% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given two strings A and B. Find the index of the first occurrence of A in B. If A is not present in B, then return -1.
For Example:
A = “bc”, B = “abcddbc”.
String “A” is present at index 1, and 5(0-based index), but we will return 1 as it is the first occurrence of “A” in string “B”.
Follow Up:
Can you solve this in linear time and space complexity?
Problem approach
Iterative implementation of strstr(): It returns a pointer to the first occurrence of Y in X or a null pointer if Y is not part of X. The time complexity of this solution is O(m.n) where m and n are the length of String X and Y, respectively.
// returns true if `X` and `Y` are the same
int compare(const char *X, const char *Y)
{
while (*X && *Y)
{
if (*X != *Y) {
return 0;
}
X++;
Y++;
}
return (*Y == '\0');
}
// Function to implement `strstr()` function
const char* strstr(const char* X, const char* Y)
{
while (*X != '\0')
{
if ((*X == *Y) && compare(X, Y)) {
return X;
}
X++;
}
return NULL;
}2. C Question
What happens when we try to access a null pointer in C?
Problem approach
The standard says that accessing a NULL ptr is “undefined behavior”. Undefined behavior can be anything, including:
Nothing at all - continue running the program as if nothing happened
Crashing the application
Corrupting application data
3. Compiler Design Question
What are the phases of a compiler?
Problem approach
Phase 1: Lexical Analysis
Lexical Analysis is the first phase when compiler scans the source code. This process can be left to right, character by character, and group these characters into tokens.
Here, the character stream from the source program is grouped in meaningful sequences by identifying the tokens. It makes the entry of the corresponding tickets into the symbol table and passes that token to next phase.
Phase 2: Syntax Analysis
Syntax analysis is all about discovering structure in code. It determines whether or not a text follows the expected format. The main aim of this phase is to make sure that the source code was written by the programmer is correct or not. Syntax analysis is based on the rules based on the specific programing language by constructing the parse tree with the help of tokens. It also determines the structure of source language and grammar or syntax of the language.
Phase 3: Semantic Analysis
Semantic analysis checks the semantic consistency of the code. It uses the syntax tree of the previous phase along with the symbol table to verify that the given source code is semantically consistent. It also checks whether the code is conveying an appropriate meaning. Semantic Analyzer will check for Type mismatches, incompatible operands, a function called with improper arguments, an undeclared variable, etc.
Phase 4: Intermediate Code Generation
Once the semantic analysis phase is over the compiler, generates intermediate code for the target machine. It represents a program for some abstract machine. Intermediate code is between the high-level and machine level language. This intermediate code needs to be generated in such a manner that makes it easy to translate it into the target machine code.
Phase 5: Code Optimization
The next phase of is code optimization or Intermediate code. This phase removes unnecessary code line and arranges the sequence of statements to speed up the execution of the program without wasting resources. The main goal of this phase is to improve on the intermediate code to generate a code that runs faster and occupies less space.
Phase 6: Code Generation
Code generation is the last and final phase of a compiler. It gets inputs from code optimization phases and produces the page code or object code as a result. The objective of this phase is to allocate storage and generate relocatable machine code. It also allocates memory locations for the variable. The instructions in the intermediate code are converted into machine instructions. This phase coverts the optimize or intermediate code into the target language.
4. Operating System Question
What is a system stack?
Problem approach
The system stack (a.k.a. call stack or just "the stack") is a place in memory for things that the heap doesn't cover. The system stack is more organized than the heap since it uses the stack data structure, where order matters. Also, the address of the next allocation is known at all times because of this organization. Allocated items are pushed on to the stack in a particular order and popped off when needed. Most importantly, the system stack is used to store information about subroutine calls (where it gets the name "call stack"). The stack stores parameters for the function and a return address where the program should pick up when the function is finished. It also reserves a space for a return value to be popped by the system on return. The piece of stack used by a subprogram is called a stack frame.
5. Count Set Bits In A Number
Easy
25m average time
70% success
0/40
Asked in companies


Ninja was given an integer ‘N’. For each number from ‘0’ to ‘N’, he must print the number of set bits present in its binary representation.
For example:
The binary representation of ‘5’ is 101. Therefore the number of set bits is 2.
Problem approach
The direct approach would be to loop through all bits in an integer, check if a bit is set and if it is, then increment the set bit count.
Time Complexity: Θ(logn) (Theta of logn)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Brian Kernighan’s Algorithm can also be used here.
This algorithm is based on the idea that subtracting 1 from a decimal number flips all the bits after the rightmost set bit(which is 1) including the rightmost set bit.
For example :
10 in binary is 00001010
9 in binary is 00001001
8 in binary is 00001000
So if we subtract a number by 1 and do it bitwise & with itself (n & (n-1)), we unset the rightmost set bit. If we do n & (n-1) in a loop and count the number of times the loop executes, we get the set bit count.
The number of times it loops is equal to the number of set bits in a given integer.
Algorithm :
1) Initialize count: = 0
2) If integer n is not zero
(a) Do bitwise & with (n-1) and assign the value back to n
n: = n&(n-1)
(b) Increment count by 1
(c) go to step 2
3)Else return count
02
Round
Easy
Face to Face
Duration60 minutes
Interview date16 Feb 2015
Coding problem4
Technical Interview round with questions on DSA, Programming and OOPS.
1. Inorder Traversal of tree without recursion
Easy
32m average time
0/40
Asked in companies



You have been given a Binary Tree of 'n' nodes, where the nodes have integer values. Your task is to return the In-Order traversal of the given binary tree.
For example :
For the given binary tree:
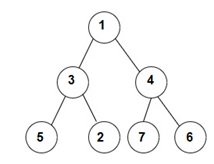
The Inorder traversal will be [5, 3, 2, 1, 7, 4, 6].
Problem approach
Inorder traversal requires that we print the leftmost node first and the right most node at the end.
So basically for each node we need to go as far as down and left as possible and then we need to come back and go right. So the steps would be :
1. Start with the root node.
2. Push the node in the stack and visit it's left child.
3. Repeat step 2 while node is not NULL, if it's NULL then pop the topmost node from the stack and print it.
4. Now move to node's right child and repeat step 1
5. Repeat the above steps while node is not NULL and stack is not empty
2. Detect loop in singly linked list
Moderate
15m average time
80% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given a Singly Linked List of integers. Return true if it has a cycle, else return false.
A cycle occurs when a node's next points back to a previous node in the list.
Example:
In the given linked list, there is a cycle, hence we return true.
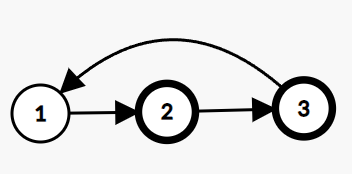
Problem approach
Floyd's algorithm can be used to solve this question.
Define two pointers slow and fast. Both point to the head node, fast is twice as fast as slow. There will be no cycle if it reaches the end. Otherwise, it will eventually catch up to the slow pointer somewhere in the cycle.
Let X be the distance from the first node to the node where the cycle begins, and let X+Y be the distance the slow pointer travels. To catch up, the fast pointer must travel 2X + 2Y. L is the cycle size. The total distance that the fast pointer has travelled over the slow pointer at the meeting point is what we call the full cycle.
X+Y+L = 2X+2Y
L=X+Y
Based on our calculation, slow pointer had already traveled one full cycle when it met fast pointer, and since it had originally travelled A before the cycle began, it had to travel A to reach the cycle's beginning!
After the two pointers meet, fast pointer can be made to point to head. And both slow and fast pointers are moved till they meet at a node. The node at which both the pointers meet is the beginning of the loop.
Pseudocode :
detectCycle(Node *head)
{
Node *slow=head,*fast=head;
while(slow!=NULL && fast!=NULL && fast->next!=NULL)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
if(slow==fast)
{
fast = head;
while(slow!=fast)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast=fast->next;
}
return slow;
}
}
return NULL;
}3. Microprocessor Question
What is an interrupt?
Problem approach
An interrupt is a special type of condition that occurs during the working of a microprocessor.
Microprocessor services the interrupt by executing a subroutine called interrupt service routine (ISR).
The interrupt can be given to the processor by the external signal(i.e. on external pins of a Microprocessor) or as a software interrupt or by the condition produced by the program.
4. Computer Network Question
What is CSMA protocol?
Problem approach
Carrier Sense Multiple Access (CSMA) is a network protocol for carriertransmission that operates in the Medium Access Control (MAC) layer. It senses or listens whether the shared channel for transmission is busy or not, and transmits if the channel is not busy. Using CMSA protocols, more than one users or nodes send and receive data through a shared medium that may be a single cable or optical fiber connecting multiple nodes, or a portion of the wireless spectrum.
Working Principle
When a station has frames to transmit, it attempts to detect presence of the carrier signal from the other nodes connected to the shared channel. If a carrier signal is detected, it implies that a transmission is in progress. The station waits till the ongoing transmission executes to completion, and then initiates its own transmission. Generally, transmissions by the node are received by all other nodes connected to the channel.
Since, the nodes detect for a transmission before sending their own frames,collision of frames is reduced. However, if two nodes detect an idle channel at the same time, they may simultaneously initiate transmission. This would cause the frames to garble resulting in a collision.
03
Round
Easy
HR Round
Duration30 minutes
Interview date16 Feb 2015
Coding problem1
Typical Managerial round.
1. Basic HR Questions
1. Tell me a question which I should ask you?
2. Why should we hire you?
3. How do u cope up with your team?
4. Are you confident of getting into Net App ?
5.Will you be disappointed if u r not selected?
6. Would you relocate to Bangalore if u get into the company?
Questions I asked the interviewer:
1. What would be my position in your company hierarchy?
2. How would you evaluate my performance?
Problem approach
Tip 1 : The cross questioning can go intense some time, think before you speak.
Tip 2 : Be open minded and answer whatever you are thinking, in these rounds I feel it is important to have opinion.
Tip 3 : Context of questions can be switched, pay attention to the details. It is okay to ask questions in these round, like what are the projects currently the company is investing, which team you are mentoring. How all is the work environment etc.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
Software Developer
3 rounds | 9 problems
Interviewed by NetApp India Pvt Ltd
1546 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by OYO
4782 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Meesho
6543 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 9 problems
Interviewed by Salesforce
3567 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
5 rounds | 12 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
114869 views
24 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
58031 views
5 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
35057 views
7 comments
0 upvotes








