NetApp India Pvt Ltd interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
Software Developer
NetApp India Pvt Ltd
3 rounds | 9 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 5 months
Topics: Data Structures, Algorithms, OS, DBMS, Networking, Aptitude, OOPS
Tip
Tip 1 : Must do Previously asked Interview as well as Online Test Questions.
Tip 2 : Go through all the previous interview experiences from Codestudio and Leetcode.
Tip 3 : Do at-least 2 good projects and you must know every bit of them.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: Above 7 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Have at-least 2 good projects explained in short with all important points covered.
Tip 2 : Every skill must be mentioned.
Tip 3 : Focus on skills, projects and experiences more.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Easy
Face to Face
Duration60 minutes
Interview date20 May 2015
Coding problem4
This was the first technical round.
1. Reverse Linked List
Moderate
15m average time
85% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Given a singly linked list of integers. Your task is to return the head of the reversed linked list.
For example:
The given linked list is 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4-> NULL. Then the reverse linked list is 4 -> 3 -> 2 -> 1 -> NULL and the head of the reversed linked list will be 4.
Follow Up :
Can you solve this problem in O(N) time and O(1) space complexity?
Problem approach
This can be solved both: recursively and iteratively.
The recursive approach is more intuitive. First reverse all the nodes after head. Then we need to set head to be the final node in the reversed list. We simply set its next node in the original list (head -> next) to point to it and sets its next to NULL. The recursive approach has a O(N) time complexity and auxiliary space complexity.
For solving the question is constant auxiliary space, iterative approach can be used. We maintain 3 pointers, current, next and previous, abbreviated as cur, n and prev respectively. All the events occur in a chain.
1. Assign prev=NULL, cur=head .
2. Next, repeat the below steps until no node is left to reverse:
2.1) Initialize n to be the node after cur. i.e. (n=cur->next)
2.2) Then make cur->next point to prev (next node pointer).
2.3) Then make prev now point to the cur node.
2.4) At last move cur also one node ahead to n.
The prev pointer will be the last non null node and hence the answer.
2. LCA of Binary Tree
Moderate
10m average time
90% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You have been given a Binary Tree of distinct integers and two nodes ‘X’ and ‘Y’. You are supposed to return the LCA (Lowest Common Ancestor) of ‘X’ and ‘Y’.
The LCA of ‘X’ and ‘Y’ in the binary tree is the shared ancestor of ‘X’ and ‘Y’ that is located farthest from the root.
Note :
You may assume that given ‘X’ and ‘Y’ definitely exist in the given binary tree.
For example :
For the given binary tree
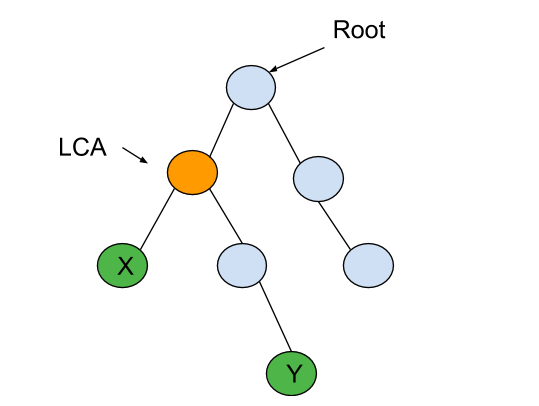
LCA of ‘X’ and ‘Y’ is highlighted in yellow colour.
Problem approach
The recursive approach is to traverse the tree in a depth-first manner. The moment you encounter either of the nodes node1 or node2, return the node. The least common ancestor would then be the node for which both the subtree recursions return a non-NULL node. It can also be the node which itself is one of node1 or node2 and for which one of the subtree recursions returns that particular node.
Pseudo code :
LowestCommonAncestor(root, node1, node2)
{
if(not root)
return NULL
if (root == node1 or root == node2)
return root
left = LowestCommonAncestor(root.left, node1, node2)
right = LowestCommonAncestor(root.right, node1, node2)
if(not left)
return right
else if(not right)
return left
else
return root
}3. Computer Organization and Architecture Question
What is internal fragmentation?
Problem approach
Internal fragmentation happens when the memory is split into mounted-sized blocks. Whenever a method is requested for the memory, the mounted-sized block is allotted to the method. just in case the memory allotted to the method is somewhat larger than the memory requested, then the distinction between allotted and requested memory is that the internal fragmentation.
4. CS Fundamentals Question
Which part of memory stores uninitialized static and global variables?
Problem approach
The uninitialized data segment is also known as a . bss segment that stores all the uninitialized global, local and external variables. If the global, static and external variables are not initialized, they are assigned with zero value by default.
02
Round
Easy
Face to Face
Duration60 minutes
Interview date20 May 2015
Coding problem4
Technical Interview round with questions on DSA, OS, OOPS etc.
1. Find square root of an integer
Easy
15m average time
80% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given a positive integer ‘n’.
Your task is to find and return its square root. If ‘n’ is not a perfect square, then return the floor value of sqrt(n).
Example:
Input: ‘n’ = 7
Output: 2
Explanation:
The square root of the number 7 lies between 2 and 3, so the floor value is 2.
Problem approach
The Simple Approach is to find the floor of the square root, try with all-natural numbers starting from 1. Continue incrementing the number until the square of that number is greater than the given number.
Algorithm:
1. Create a variable (counter) i and take care of some base cases, i.e when the given number is 0 or 1.
2. Run a loop until i*i <= n , where n is the given number. Increment i by 1.
3. The floor of the square root of the number is i – 1
Time Complexity: O(√ n).
The Better Approach would be to use Binary Search. The idea is to find the largest integer i whose square is less than or equal to the given number. The values of i * i is monotonically increasing, so the problem can be solved using binary search.
Algorithm:
1. Take care of some base cases, i.e when the given number is 0 or 1.
2. Create some variables, lowerbound l = 0, upperbound r = n, where n is the given number, mid and ans to store the answer.
3. Run a loop until l <= r , the search space vanishes
4. Check if the square of mid (mid = (l + r)/2 ) is less than or equal to n, If yes then search for a larger value in second half of search space, i.e l = mid + 1, update ans = mid
5. Else if the square of mid is more than n then search for a smaller value in first half of search space, i.e r = mid – 1
6. Print the value of answer.
Time Complexity : O(logn)
2. Operating System Question
In a unix or linux file system, how file path resolved? For example : /root/home/ooo/abc.c
Problem approach
given path of file: /root/home/ooo/abc.c how does an os finds where abc.c
The system locates the root directory of the file system. A pointer to this is kept in memory since the partition is mounted. The pointer to this top-level inode includes pointers to the data blocks of the top-level directory.
The system reads the dents (directory entries) there searching for the one for “root”. Once the dent is found, it also includes an inode pointer to the directory.
Using the inode for “root”, it finds the data blocks for that directory.
The system reads the dents in the “root” directory, searching for the one for “home”, and picking up the inode pointer for the “home” directory.
Using the inode for “home”, it finds the data blocks for that directory.
The system reads the dents in the “home” directory, searching for the one for “ooo”, and picking up the inode pointer for the “ooo” directory.
Using the inode for “ooo”, it finds the data blocks for that directory.
The system reads the dents in the “ooo” directory, searching for the one for “abc.c”, and picking up the inode pointer for the “abc.c” file.
At this point, the open(“/root/home/ooo/abc.c”,”r”) syscall completes.
When the program does a read() syscall, the system uses the inode for “abc.c”, and finds the data blocks for that file.
Data blocks are transferred to the program. read() completes.
3. Operating System Question
Where does the returned value for 'main' function go?
Problem approach
In UNIX systems it looks something like this:
When you compile a program with gcc, it wraps a startup routine around your main() function. This routine calls your main() function and saves its return value. It then calls the exit() function (which your program might call as well), that does some general clean up. This function then again calls _exit(), which is a system call that tells the OS to save the returned value of your main() function in the process table (where meta information about your process is saved). As soon as another process calls wait() on your process id (PID), your returned value is given to the calling process and your process is removed from the table.
4. CS Fundamentals Question
What is segmentation fault?
Problem approach
Segmentation fault is a specific kind of error caused by accessing memory that “does not belong to you.”
When a piece of code tries to do read and write operation in a read only location in memory or freed block of memory, it is known as core dump. It is an error indicating memory corruption.
03
Round
Easy
HR Round
Duration30 minutes
Interview date20 May 2015
Coding problem1
This was a typical managerial round.
1. Basic HR Questions
1) What is your experience of the whole day?
2) What part did you like best in our ppt?
3) Are you clear about your role in netApp?
4) What subjects did u like the best in college? why?
5) Extra curricular activities in college?
6) Any queries about our company or the compensation package etc.
Problem approach
Tip 1 : The cross questioning can go intense some time, think before you speak.
Tip 2 : Be open minded and answer whatever you are thinking, in these rounds I feel it is important to have opinion.
Tip 3 : Context of questions can be switched, pay attention to the details. It is okay to ask questions in these round, like what are the projects currently the company is investing, which team you are mentoring. How all is the work environment etc.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 10 problems
Interviewed by NetApp India Pvt Ltd
3499 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by OYO
4782 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Meesho
6543 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 9 problems
Interviewed by Salesforce
3567 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
Software Developer
5 rounds | 14 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
3986 views
1 comments
0 upvotes
Software Developer
6 rounds | 12 problems
Interviewed by SAP Labs
2872 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Software Developer
3 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
1202 views
0 comments
0 upvotes









