Nosh technologies interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - 1
Nosh technologies
2 rounds | 4 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Journey
I joined my BTech program after taking the JEE exam. At first, I was unaware of coding, but after two years, my seniors told me it was the only way to get into big companies. Then, I started practising coding on different websites.
Application story
This company visited our campus for placement. It allowed the first round to be an online assessment, and based on the results of this assessment, they made their selections.
Why selected/rejected for the role?
Regrettably, I was unsuccessful in the interview due to my inability to solve the final question in the second round. Despite my sincere efforts, I struggled to find the correct solution within the allotted time, resulting in an unfavourable outcome.
Preparation
Duration: 6 months
Topics: Data Structures, Pointers, Object-Oriented Programming (OOP), System Design, Algorithms, Dynamic Programming, Operating Systems, Databases, Networking, Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC), System Architecture, Web Technologies
Tip
Tip 1: Review Core Concepts: Refresh your knowledge of fundamental computer science concepts, including data structures, algorithms, and object-oriented programming. Focus on understanding how these concepts work, their time and space complexities, and when to use them in different scenarios.
Tip 2: Practice Coding Problems: Solve coding problems regularly to improve your problem-solving skills and familiarity with standard algorithms and data structures. Leverage online platforms, coding challenges, and interview preparation websites to practice coding under time constraints.
Tip 3: Brush Up on System Design: Understand the principles of system design and scalability. Study different system architectures like client-server, microservices, and distributed systems. Practice designing scalable and efficient systems while considering factors like performance, fault tolerance, and data storage.
Tip 4: Study Your Resume and Projects: Review your resume thoroughly and be prepared to discuss your previous projects, including the technologies used, challenges faced, and solutions implemented. Be able to explain your role and contributions in detail and highlight any unique or notable aspects of your work.
Tip 5: Mock Interviews and Communication Skills: Practice mock interviews with friends or colleagues, or use online platforms that offer interview simulations. Work on your communication skills, as clear and concise communication is essential during technical interviews. Practice explaining your thought process, sharing your approach to problem-solving, and asking clarifying questions.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: Above 7 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1: Clear and Concise Format: Maintain a well-organized and easily readable resume format. Utilize clear headings and bullet points to emphasize crucial details. Ensure consistency by using a professional font throughout the document. Limit your resume to one or two pages, focusing on presenting the most pertinent and impactful information.
Tip 2: Tailor Your Resume for Each Application: Customize your resume to suit the requirements of each job application. Carefully analyze the job description and integrate relevant keywords and skills into your resume. Highlight your relevant experiences, accomplishments, and skills that align closely with the specific role you're applying for.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date20 Apr 2023
Coding problem2
The round began with the interviewer posing questions related to core concepts such as data structures, algorithms, and object-oriented programming. They expect me to demonstrate a solid understanding of these fundamental topics, including their implementation, time complexity analysis, and practical applications.
1. Colorful Knapsack
Hard
45m average time
0/120
Asked in companies



You are given 'N' stones labeled from 1 to 'N'. The 'i-th' stone has the weight W[i]. There are 'M' colors labeled by integers from 1 to 'M'. The 'i-th' stone has the color C[i] which is an integer between 1 to 'M', both inclusive.
You have been required to fill a Knapsack with these stones. The Knapsack can hold a total weight of 'X'.
You are required to select exactly 'M' stones; one of each color. The sum of the weights of the stones must not exceed 'X'. Since you paid a premium for a Knapsack with capacity 'X', you are required to fill the Knapsack as much as possible.
Write a program to calculate the best way to fill the Knapsack - that is, the unused capacity should be minimized.
Problem approach
This was solved by me through dynamic programming. Let dp[i][j] denote the maximum possible weight you can fill in the bag with a total capacity of j using exactly one stone of each colour from 1 to i. Now you can club all same-colored stones in a vector. Then this problem is the same as the classical knapsack problem and I passed all test cases and selected for the next round.
2. Longest Increasing Subsequence
Moderate
30m average time
65% success
0/80
Asked in companies



For a given array with N elements, you need to find the length of the longest subsequence from the array such that all the elements of the subsequence are sorted in strictly increasing order.
Strictly Increasing Sequence is when each term in the sequence is larger than the preceding term.
For example:
[1, 2, 3, 4] is a strictly increasing array, while [2, 1, 4, 3] is not.
Problem approach
Firstly I gave a recursion approach but then the interviewer asked me to optimize that so I gave him a standard DP approach for the longest increasing subsequences by storing the results and using them for future calculations of bigger problems.
02
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date20 Apr 2023
Coding problem2
The environment during the round was likely professional and focused.
1. Top View Of Binary Tree
Moderate
25m average time
70% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given a Binary Tree of 'n' nodes.
The Top view of the binary tree is the set of nodes visible when we see the tree from the top.
Find the top view of the given binary tree, from left to right.
Example :
Input: Let the binary tree be:
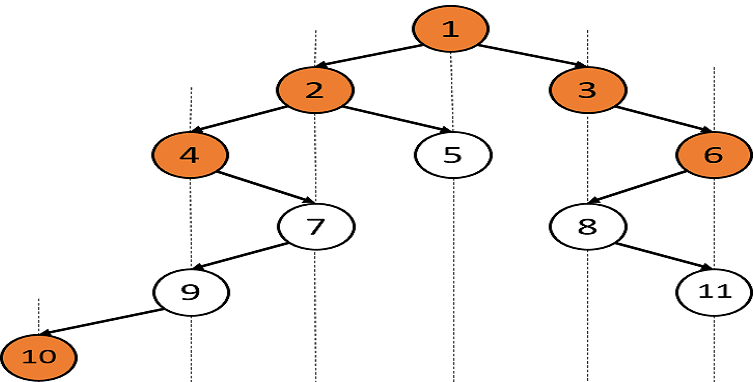
Output: [10, 4, 2, 1, 3, 6]
Explanation: Consider the vertical lines in the figure. The top view contains the topmost node from each vertical line.
Problem approach
I simply used level-order traversal and the concept of horizontal distance. Whenever we encounter the first node for a particular horizontal distance then we store that in the map and at last in the map we have a tree top view. The interviewer asked me to write its code and I wrote a clean and commented code for it and he was satisfied.
2. Merge Point Of Two Linked Lists
Moderate
0/80
Asked in companies



Given two singly linked lists, 'FIRST_HEAD' and 'SECOND_HEAD'. Your task is to find the 'MERGING POINT' i.e. the data of the node at which merging starts. If there is no merging, return -1.
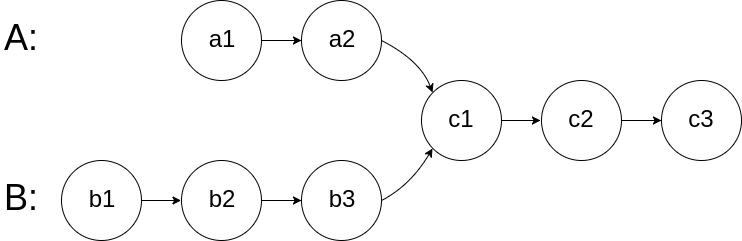
For example:-
The given Linked Lists are merging at node c1.
In this case, c1 is 'MERGING POINT'.
Problem approach
At first, I gave the interviewer a complete brute force by considering each element of the first list and comparing it with each element of another list but that was inefficient. So I gave the interviewer the optimal approach by finding the difference in lengths of the linked list and then traversing the bigger linked list to the difference. Now start traversing both linked lists till we find the common element. This solution impressed the interviewer.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by Nosh technologies
367 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Nosh technologies
467 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by Nosh technologies
351 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by Nosh technologies
363 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
5 rounds | 12 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
114869 views
24 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
58031 views
5 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
35057 views
7 comments
0 upvotes




