Oges interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - 1
Oges
2 rounds | 4 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Journey
Since I am from mechanical engineering background it was time taking for me to get accepted for the test itself despite from being an NITian. I did a lot of DSA, front and backend projects, SQL, mong etc and I had to do it in 10 months because I left a good paying mechanical engineering job in a very big company. My startup that I did in my college was the best eyeopener for me and I fell in love with software. I started with preparing DSA then frond-end and then backend mostly in JAVA and I think that 10 months dedication helped me cracked OGES
Application story
I applied in flipkart via reffral from my friend and it took around 1 month to schedule the technical coding test followed by two interview rounds. Interviewer were in general very helpful and continously making it sure that I am going in the right direction and making sure that the proper communicaton is been made and making it sure that I am not going too nervous
Why selected/rejected for the role?
I think the way I communicate while solving the problem is the main reason, i try to think aloud while solving I think this is very important as interviewer will sure that you are not cheating and how you are approaching the proble, this helped mee too as whever I was on the wrong path interview was able to give me hints to get back on the track.
Preparation
Duration: 10 months
Topics: DSA, OOPS, DMS, REACT for front end, Spring boot for backend
Tip
Tip 1 : Start with basics, solve problems by doing dry run, even if you have seen the solution, do the dry run for that approach, this way you will learn a lot and would solve another 2-3 problems within the same question
Tip 2 : Don't try to get arond the buzz words, never jumps concepts like DP, trees, heaps etc unless you are good with arrays and string and all the basics.
Tip 3 : Try to understand time complexities and space complexities and why something took O(n) and same thing can took O(1) using different apprach, this will help to understand datastructures and why they are used
Application process
Where: Referral
Eligibility: CGPA 7 or above
Resume tip
Tip 1: Be very crisp and clear and use more numbers to show metrics becuse number are understood better by humans
Tip 2: Don't be vague and don't add project you haven't worked on sincerely as here you can loose your integrity.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Easy
Online Coding Interview
Duration60 mins
Interview date4 Oct 2022
Coding problem1
Round had a flexible window of 8 hours within 12pm to 8 pm , copypasting was not allowed, I had to write the variables name again and again. I had to clear all the cases to get my question accepted
1. Merge Sort
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



Given a sequence of numbers ‘ARR’. Your task is to return a sorted sequence of ‘ARR’ in non-descending order with help of the merge sort algorithm.
Example :
Merge Sort Algorithm -
Merge sort is a Divide and Conquer based Algorithm. It divides the input array into two-parts, until the size of the input array is not ‘1’. In the return part, it will merge two sorted arrays a return a whole merged sorted array.
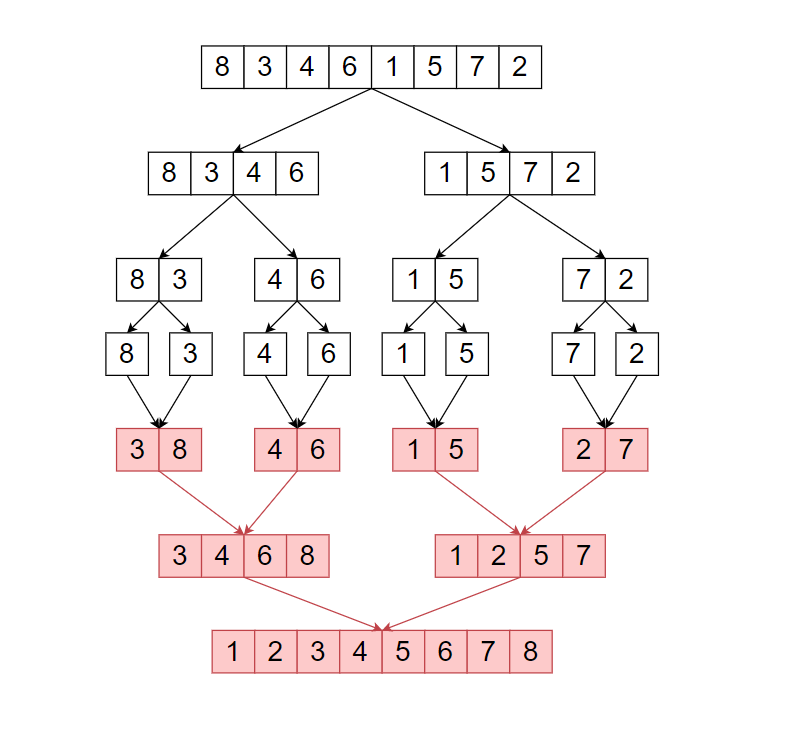
The above illustrates shows how merge sort works.
Note :
It is compulsory to use the ‘Merge Sort’ algorithm.
Problem approach
Step I: I explained them major 4 sorting algos including insertion sort, merge sort, bubble sort and quick sort
step 2: I explained thier time complexities which was not asked but I still find it valuable to share
step3: I did the merge sort implementation
02
Round
Medium
Face to Face
Duration90 mins
Interview date15 Oct 2022
Coding problem3
In this round they asked my about my Jee rank, and few physics and mathematics concepts, then some statistics. Environment was a bit serious and they were two interiewers.
After this I was asked few theory question on my DSA and SQL fundamentals
I was then presented a case for which I needed to code the solution
1. Technical Question
Why we need time complexities and why we care about them?
Problem approach
Tip 1:Before jumping to answer try to interpret the tone of the interviewer, it will show you how deep he wants you to go in the topic
Tip 2: Be confident about your answers but if you came across the case you don't know, just say it, it will show your honesty and integrity
Tip 3: Try to ask more questions on top of what interview have asked you, it will make things more clear to you
2. DBMS Question
Difference between sql and no sql platforms and why we need them both
Problem approach
Tip 1: DBMS questions are mostly conceptual and they have well established answers try to be technical and crisp about the asnwers.
Tip 2: Give examples to strengthen your case and answers
Tip 3: Learn DBMS concepts well from know is the only way to answer these questions correctly, you can't made things up
3. Implementation: HashMap
Easy
30m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



Design a data structure that stores a mapping of a key to a given value and supports the following operations in constant time.
1. INSERT(key, value): Inserts an integer value to the data structure against a string type key if not already present. If already present, it updates the value of the key with the new one. This function will not return anything.
2. DELETE(key): Removes the key from the data structure if present. It doesn't return anything.
3. SEARCH(key): It searches for the key in the data structure. In case it is present, return true. Otherwise, return false.
4. GET(key): It returns the integer value stored against the given key. If the key is not present, return -1.
5. GET_SIZE(): It returns an integer value denoting the size of the data structure.
6. IS_EMPTY(): It returns a boolean value, denoting whether the data structure is empty or not.
Note :
1. Key is always a string value.
2. Value can never be -1.
Operations Performed :
First(Denoted by integer value 1): Insertion to the Data Structure. It is done in a pair of (key, value).
Second(Denoted by integer value 2): Deletion of a key from the Data Structure.
Third(Denoted by integer value 3): Search a given key in the Data Structure.
Fourth(Denoted by integer value 4): Retrieve the value for a given key from the Data Structure.
Fifth(Denoted by integer value 5): Retrieve the size of the Data Structure.
Sixth(Denoted by integer value 6): Retrieve whether the Data Structure is empty or not.
Problem approach
Step 1: Design the data structure: Create an array of fixed size to serve as the underlying storage for the key-value pairs. Each index in the array represents a bucket that can hold multiple key-value pairs.
Step 2: Define the hash function: Implement a hash function that takes a key as input and calculates a hash code. The hash code is used to determine the index of the bucket where the key-value pair will be stored.
Step 3: Handle collisions: If two or more keys produce the same hash code (collisions), you need to handle them. Common techniques include separate chaining and open addressing. In separate chaining, each bucket contains a linked list or other data structure to store multiple key-value pairs. In open addressing, the hashmap searches for the next available bucket in case of collisions.
Step 4: Implement basic operations: Provide methods for the basic hashmap operations:
put(key, value): Insert the key-value pair into the hashmap. Hash the key to find the appropriate bucket and store the pair there.
get(key): Retrieve the value associated with a given key. Hash the key to find the bucket, then search for the key-value pair within the bucket.
remove(key): Remove the key-value pair associated with the given key. Hash the key to find the bucket, then delete the pair if found.
Step 5: Resize the hashmap (optional): To handle dynamic resizing, you can implement a mechanism to resize the hashmap when the number of elements exceeds a certain threshold. This involves creating a new larger array and rehashing all existing key-value pairs into the new array.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is recursion?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by OYO
4656 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
2 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
960 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Meesho
6450 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 9 problems
Interviewed by Salesforce
3451 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
5 rounds | 12 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
114578 views
24 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
57824 views
5 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
34960 views
7 comments
0 upvotes










