OYO interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - 1
OYO
2 rounds | 4 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 3 months
Topics: OOPS, Core Java, DBMS, SQL & PL/SQL, Data Structures and Algorithms, UI (HTML, JS), SDLC, Java 8 concepts, UML diagrams, Collections, Multithreading, Exception Handling, Hashing, Recursion problems.
Tip
Tip 1 : Practice more problem-solving questions
Tip 2 : Understand the concepts in depth
Tip 3 : Try to work on one or two hands on projects to get more experience in that stack.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: Above 7 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Have some projects on your resume.
Tip 2 : Do not put false things on your resume.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration45 minutes
Interview date5 Sep 2022
Coding problem2
1. Kth largest element in the unsorted array
Moderate
10m average time
90% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given an array consisting of 'N' distinct positive integers and a number 'K'. Your task is to find the kth largest element in the array.
Example:
Consider the array {2,1,5,6,3,8} and 'K' = 3, the sorted array will be {8, 6, 5, 3, 2, 1}, and the 3rd largest element will be 5.
Note:
1) Kth largest element in an array is the kth element of the array when sorted in non-increasing order.
2) All the elements of the array are pairwise distinct.
Problem approach
I gave the max-heap based approach, in which I told him to insert every item into the max-heap, and then return the top K. For this, he asked the time Complexity, I answered O(Klog(K*N)). He told me to optimize it further. This time I gave a pointer based approach, i.e., to set a pointer at every category and then check for max among them, then increment count for the pointer of the category in which max was found, and do it till we have found K elements. For this, he asked the time Complexity, I answered O(K*N). He told me to optimize it further by combining the above two approaches, I did it and gave the Time Complexity as O(Klog(N)).
2. DBMS Questions
Draw E-R Diagram for Ola.
Problem approach
Tip 1 : Revise ER diagrams and practice them
Tip 2 : List all entities and their relationships involved with the app.
Tip 3 : After drawing tables apply normalization to reduce redundancy.
02
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration45 minutes
Interview date5 Sep 2022
Coding problem2
1. Maximum sum path from the leaf to root
Easy
10m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given a binary tree of 'N' nodes.
Your task is to find the path from the leaf node to the root node which has the maximum path sum among all the root to leaf paths.
For Example:
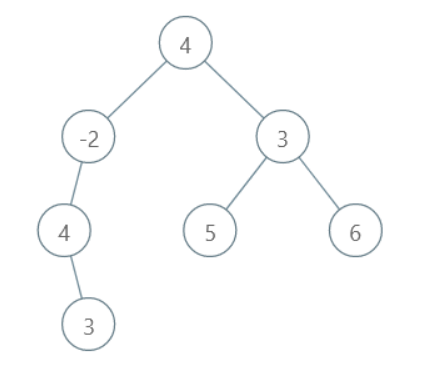
All the possible root to leaf paths are:
3, 4, -2, 4 with sum 9
5, 3, 4 with sum 12
6, 3, 4 with sum 13
Here, the maximum sum is 13. Thus, the output path will be 6, 3, 4.
Note:
There will be only 1 path with max sum.
Problem approach
For each node there can be four ways that the max path goes through the node:
1. Node only
2. Max path through Left Child + Node
3. Max path through Right Child + Node
4. Max path through Left Child + Node + Max path through Right Child
The idea is to keep trace of four paths and pick up the max one in the end. An important thing to note is, root of every subtree need to return maximum path sum such that at most one child of root is involved. This is needed for parent function call. In below code, this sum is stored in ‘max_single’ and returned by the recursive function.
2. Sort A Partial Sorted Array
Easy
10m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in company

Ninja has been given an arbitrary array of integers of size ‘N'. You can think of the array as the concatenation of two individually sorted arrays in non-decreasing order. Ninja needs to sort the entire array in ascending order.
Can you help Ninja to sort the array?
Note :
Both the partitions need not be of the same size.
Problem approach
I didn't knew the solution so I thought of this as given n arrays having m nos in each array and we need to sort all arrays with space cmplexity of the order O(nlogm) but definitely not O(m*n) due to memory constraints.
So this is a common Priority Queue Problem for which I told the approach.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by OYO
4782 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 9 problems
Interviewed by OYO
0 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by OYO
1057 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by OYO
824 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
5 rounds | 12 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
114869 views
24 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
58030 views
5 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
35057 views
7 comments
0 upvotes





