PayPal interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
Software Engineer
PayPal
3 rounds | 6 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 6 months
Topics: Data Structures, Algorithms, System Design, Aptitude, OOPS
Tip
Tip 1 : Must do Previously asked Interview as well as Online Test Questions.
Tip 2 : Go through all the previous interview experiences from Codestudio and Leetcode.
Tip 3 : Do at-least 2 good projects and you must know every bit of them.
Application process
Where: Company Website
Eligibility: Above 7 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Have at-least 2 good projects explained in short with all important points covered.
Tip 2 : Every skill must be mentioned.
Tip 3 : Focus on skills, projects and experiences more.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date6 Oct 2020
Coding problem2
Technical interview round where the Interviewer asked me questions based on data structures and algorithms.
1. Implementation: HashMap
Easy
30m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



Design a data structure that stores a mapping of a key to a given value and supports the following operations in constant time.
1. INSERT(key, value): Inserts an integer value to the data structure against a string type key if not already present. If already present, it updates the value of the key with the new one. This function will not return anything.
2. DELETE(key): Removes the key from the data structure if present. It doesn't return anything.
3. SEARCH(key): It searches for the key in the data structure. In case it is present, return true. Otherwise, return false.
4. GET(key): It returns the integer value stored against the given key. If the key is not present, return -1.
5. GET_SIZE(): It returns an integer value denoting the size of the data structure.
6. IS_EMPTY(): It returns a boolean value, denoting whether the data structure is empty or not.
Note :
1. Key is always a string value.
2. Value can never be -1.
Operations Performed :
First(Denoted by integer value 1): Insertion to the Data Structure. It is done in a pair of (key, value).
Second(Denoted by integer value 2): Deletion of a key from the Data Structure.
Third(Denoted by integer value 3): Search a given key in the Data Structure.
Fourth(Denoted by integer value 4): Retrieve the value for a given key from the Data Structure.
Fifth(Denoted by integer value 5): Retrieve the size of the Data Structure.
Sixth(Denoted by integer value 6): Retrieve whether the Data Structure is empty or not.
Problem approach
An array of linked lists can be used to implement a hashmap.
To transform the key into an index, we look to a hashing function. We can use a hashing function to convert the key into an integer within the bounds of our hash map array's index range. In an ideal situation, that would allow us to reduce the size of the hash map array to the maximum number of entries.
For the get() method , we just hash() our key, access the corresponding bucket in our hashmap array (data), and navigate through the linked list (if necessary) and return the correct value, or -1 if the key is not found.
For the put() method, we should first remove() any earlier instance of that key to avoid chaining multiple versions of a key definition in our linked list. Then we simply form a new node at the head of the proper hash map bucket, pushing any others back.
The remove() method will be similar to the get() method, except that we need to find and stitch together the nodes on either side of the node that matches the key, removing it from the linked list entirely.
2. Integer To Roman Numeral
Easy
10m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



Given an integer ‘N’, the task is to find its corresponding Roman numeral.
Roman numerals are represented by seven different symbols: I, V, X, L, C, D and M.
Symbol Value
I 1
V 5
X 10
L 50
C 100
D 500
M 1000
Example :
2 is written as II in the roman numeral, just two one’s added together.
12 is written as XII, which is simply X(ten) + II(one+one).
The number 27 is written as XXVII, which is XX + V + II.
Roman numerals are usually written largest to smallest from left to right.
However, the numeral for four is not IIII. Instead, the number four is written as IV. Because the one is before the five we subtract it making four.
The same principle applies to the number nine, which is written as IX.
There are six instances where subtraction is used:
I can be placed before V (5) and X (10) to make 4 and 9.
X can be placed before L (50) and C (100) to make 40 and 90.
C can be placed before D (500) and M (1000) to make 400 and 900.
Problem approach
A lookup table can be used to map the digit with its corresponding Roman numeral. Next, traverse the lookup table in descending order of the keys and keep inserting the appropriate numeral as many times till the target number is greater than the corresponding key. Keep reducing the target number by the same amount.
02
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date6 Oct 2020
Coding problem2
Technical interview round where the Interviewer asked me questions based on data structures and algorithms.
1. Total area of overlapping rectangles
Easy
10m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given two arbitrary rectangles on a 2-D coordinate plane, which may have an intersecting area. You have to find the net area covered by both the rectangles on the cartesian plane.
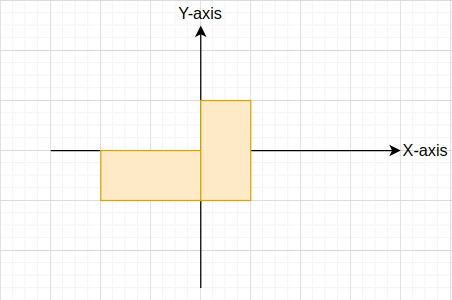
The orange area depicted in the above figure is the net area covered by both rectangles on the cartesian plane.
Note:
1. For a rectangle, its top left and bottom right coordinates are given.
2. Coordinates of the rectangles are integer values.
3. Edges of the given rectangles will always be parallel to the X and Y coordinate axes of the cartesian plane.
4. It is guaranteed that both the rectangles will have at least a unit area.
Problem approach
The idea behind the approach would be that If the rectangles do not overlap, then rectangle 1 must either be higher, lower, to the left, or to the right of rectangle 2.
Consider a 1D overlap :
[(x1,y1)(x2,y1)] and [(x3,y2),(x4,y2)]
For an overlap to occur necessary condition is: x1 < x3 < x2 && x3 < x2 < x4
Now, for a 2D case we use 1D conditions for both X and Y axes
Case-1: Rec2 intersects with Rec1 on top right corner
Case-2: Rec2 intersects with Rec1 on top left corner.
Case-3: Rec2 intersects with Rec1 on bottom left corner
Case-4: Rec2 intersects with Rec1 on bottom right corner
bool case1 = (x1 < x4 && x3 < x2 && y1 < y4 && y3 < y2); //top right intersection
bool case2 = (x3 < x2 && x1 < x4 && y1 < y4 && y3 < y2); //top left intersection
bool case3 = (x3 < x2 && x1 < x4 && y3 < y2 && y4 < y1); //bottom left intersection
bool case4 = (x1 < x4 && x3 < x2 && y3 < y2 && y4 < y1); //bottom right intersection
2. Longest Repeating Subsequence
Moderate
15m average time
85% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given a string ‘st’, Your task is to find the length of the longest repeating subsequence such that two subsequences don’t have the same character at the same position.
For Example :
The given string st = AABCBDC.
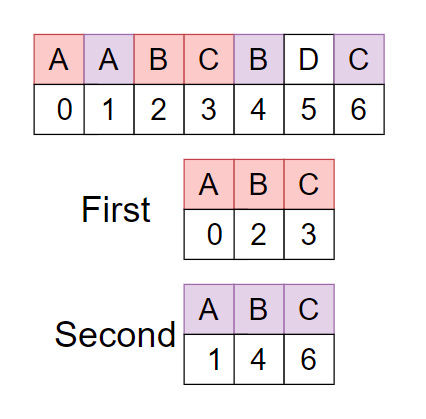
As you can see there are two repeating longest subsequences “ABC” with the same character but different position. Therefore the required answer is ‘3’ as the length of “ABC” is 3.
Problem approach
The naive approach is to find all substrings in O(n2) and checking it with the substrings of the remaining string in O(n). The time complexity of this solution would be O(N^3).
The solution can be optimized to O(N^2) using the concept of dynamic programming.
The idea is to look for every same character and save its index. Check whether difference between index is less than longest repeating and non-overlapping substring size.
Here, dp[i][j] stores length of the matching and non-overlapping substrings ending with i'th and j'th characters.
If the characters at (i-1)th and (j-1)th position matches dp[i-1][j-1] is less than the length of the considered substring (j-1) then maximum value of dp[i][j] and the maximum index i till this point is updated. The length of the longest repeating and non-overlapping substring can be found by the maximum value of dp[i][j] and the substring itself can be found using the length and the ending index which is the finishing index of the suffix.
Recursive Relation :
LCSRe(i, j) stores length of the matching and non-overlapping substrings ending with i'th and j'th characters.
If str[i-1] == str[j-1] && (j-i) > LCSRe(i-1, j-1)
LCSRe(i, j) = LCSRe(i-1, j-1) + 1,
Else
LCSRe(i, j) = 0
Where i varies from 1 to n and j varies from i+1 to n
03
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date6 Oct 2020
Coding problem2
This was a system design round.
1. System Design Question
Design a Rate Limiter.
Problem approach
A rate limiter is a tool that monitors the number of requests per a window time a service agrees to allow. If the request count exceeds the number agreed by the service owner and the user (in a decided window time), the rate limiter blocks all the excess calls(say by throwing exceptions). Rate limiters can be implemented using different designs :
Fixed window counters
Sliding window counters
Sliding window logs
2. System Design Questions
1. Merchant Onboarding Design
2. Restaurant Design
Problem approach
Tip 1: Firstly, remember that the system design round is extremely open-ended and there’s no such thing as a standard answer. Even for the same question, you’ll have a totally different discussion with different interviewers.
Tip 2:Before you jump into the solution always clarify all the assumptions you’re making at the beginning of the interview. Ask questions to identify the scope of the system. This will clear the initial doubt, and you will get to know what are the specific detail interviewer wants to consider in this service.
Tip 3 : Design your structure and functions according to the requirements and try to convey your thoughts properly to the interviewer so that you do not mess up while implementing the idea .

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
Software Engineer
2 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by PayPal
3192 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Software Engineer
4 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by PayPal
1436 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Software Engineer
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by PayPal
3754 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Software Engineer
3 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by PayPal
6421 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
Software Engineer
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Optum
7922 views
1 comments
0 upvotes
Software Engineer
5 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
10070 views
1 comments
0 upvotes
Software Engineer
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
4395 views
1 comments
0 upvotes






