Paytm (One97 Communications Limited) interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - 1
Paytm (One97 Communications Limited)
3 rounds | 5 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Journey
I started my preparation in the early days of my college when I started practicing the leetcode and the code studio problems. In the end, I have done more than 300 questions on the leetcode platform.
Application story
I applied to this company throw the on-campus opportunity as my college is a tier 1 college this company always visit my college for hire.
Why selected/rejected for the role?
I was rejected because I was not able to explain all the concept with the correct accuracy.
Preparation
Duration: 4 months
Topics: Data Structures, Pointers, OOPS, System Design, Algorithms, Dynamic Programming
Tip
Regarding DSA preparation, I have a theory. 20 percent of the questions will be asked in 80 percent of the interview and 80 percent of the questions will be asked in 20 percent of the interviews. In short, some questions have a very high chance of coming up during the interviews and some have very low chance. We should focus more on the questions that have more chance of coming up in the interview. You can find these questions on Striver SDE Sheet, InterviewBit, Leetcode 100 most liked, Leetcode 100 most important.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: Above 7 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Make Sure that your resume is simple and also try to fit all the information on only one page.
Tip 2 : Have at least 2 projects with the latest technologies, Github link of projects should be provided
Interview rounds
01
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date9 Dec 2022
Coding problem2
1. 3Sum
Moderate
15m average time
85% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given an array/list ARR consisting of N integers. Your task is to find all the distinct triplets present in the array which adds up to a given number K.
An array is said to have a triplet {ARR[i], ARR[j], ARR[k]} with sum = 'K' if there exists three indices i, j and k such that i!=j, j!=k and i!=j and ARR[i] + ARR[j] + ARR[k] = 'K'.
Note:
1. You can return the list of values in any order. For example, if a valid triplet is {1, 2, -3}, then {2, -3, 1}, {-3, 2, 1} etc is also valid triplet. Also, the ordering of different triplets can be random i.e if there are more than one valid triplets, you can return them in any order.
2. The elements in the array need not be distinct.
3. If no such triplet is present in the array, then return an empty list, and the output printed for such a test case will be "-1".
Problem approach
You are given an array/list ARR consisting of N integers. Your task is to find all the distinct triplets present in the array which adds up to a given number K.
An array is said to have a triplet {ARR[i], ARR[j], ARR[k]} with sum = 'K' if there exists three indices i, j and k such that i!=j, j!=k and i!=j and ARR[i] + ARR[j] + ARR[k] = 'K'.
2. Top View Of Binary Tree
Moderate
25m average time
70% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given a Binary Tree of 'n' nodes.
The Top view of the binary tree is the set of nodes visible when we see the tree from the top.
Find the top view of the given binary tree, from left to right.
Example :
Input: Let the binary tree be:
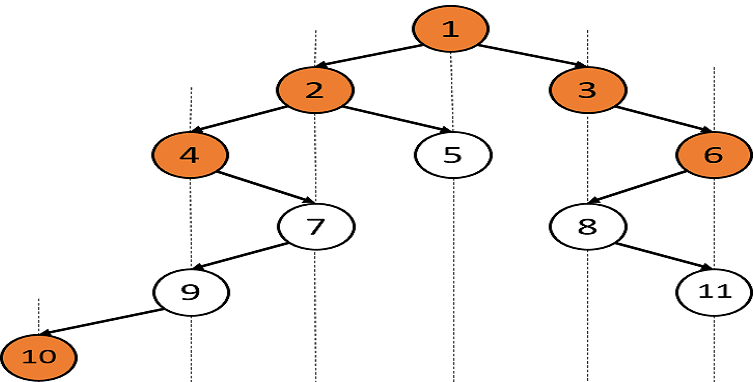
Output: [10, 4, 2, 1, 3, 6]
Explanation: Consider the vertical lines in the figure. The top view contains the topmost node from each vertical line.
Problem approach
You are given a Binary Tree of integers. You are supposed to return the top view of the given binary tree. The Top view of the binary tree is the set of nodes that are visible when we see the tree from the top.
02
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date9 Dec 2022
Coding problem2
1. Copy List with Random Pointer
Easy
10m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



Given a linked list having two pointers in each node. The first one points to the next node of the list, however, the other pointer is random and can point to any node of the list or null. The task is to create a deep copy of the given linked list and return its head. We will validate whether the linked list is a copy of the original linked list or not.
A deep copy of a Linked List means we do not copy the references of the nodes of the original Linked List rather for each node in the original Linked List, a new node is created.
For example,
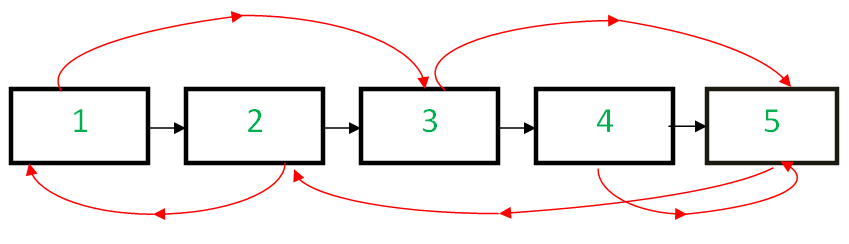
Random pointers are shown in red and next pointers in black.
Problem approach
Given a linked list having two pointers in each node. The first one points to the next node of the list, however, the other pointer is random and can point to any node of the list or null. The task is to create a deep copy of the given linked list and return its head. We will validate whether the linked list is a copy of the original linked list or not.
A deep copy of a Linked List means we do not copy the references of the nodes of the original Linked List rather for each node in the original Linked List, a new node is created.
2. Intersection of Two Linked Lists
Easy
25m average time
73% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given two Singly Linked Lists of integers, which may have an intersection point.
Your task is to return the first intersection node. If there is no intersection, return NULL.
Example:-
The Linked Lists, where a1, a2, c1, c2, c3 is the first linked list and b1, b2, b3, c1, c2, c3 is the second linked list, merging at node c1.

Problem approach
You are given two Singly Linked List of integers, which are merging at some node of a third linked list.
Your task is to find the data of the node at which merging starts. If there is no merging, return -1.
03
Round
Easy
HR Round
Duration30 minutes
Interview date9 Dec 2022
Coding problem1
1. Basic HR Questions
What is the difference between confidence and over confidence?
What is the difference between hard work and smart work?
How do you feel about working nights and weekends?

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
To make an AI less repetitive in a long paragraph, you should increase:
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Paytm (One97 Communications Limited)
923 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Paytm (One97 Communications Limited)
716 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 10 problems
Interviewed by Paytm (One97 Communications Limited)
541 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 8 problems
Interviewed by Paytm (One97 Communications Limited)
522 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
5 rounds | 12 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
114453 views
24 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
57719 views
5 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
34914 views
7 comments
0 upvotes





