PayU interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
Associate Software Engineer
PayU
4 rounds | 9 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Journey
My journey toward cracking the PayU interview was a mix of consistent preparation, real-world exposure, and learning from past mistakes. I’m a final-year student at Jaypee Institute of Information Technology, Noida, and before PayU, I interned as a backend developer at a UK-based startup (KED UK), where I worked with Spring Boot, REST APIs, and real-world project architecture. This hands-on experience helped me build confidence and develop a deeper understanding of backend concepts.
In parallel, I prepared for technical interviews by focusing on DSA using Striver’s DSA Sheet and regularly solving problems on coding platforms. I also revised core CS subjects like DBMS, OOP, and Operating Systems through YouTube videos and handwritten notes. I had already built a few full-stack projects, which further strengthened my understanding and provided practical points to discuss during interviews.
When I got shortlisted for PayU, I knew the competition would be tough. I went through three interview rounds that tested my problem-solving skills, backend knowledge, and thought process. Each round boosted my confidence, as I had prepared for both the practical and theoretical aspects. Cracking the interview was a fulfilling moment—not just because I got selected, but because I could see how months of effort had finally paid off.
Application story
It was an on-campus hiring process, so I applied there.
The 1st round was an online assessment with two coding questions.
The 2nd round was Technical Interview 1, which lasted for approximately 2 hours.
The 3rd round was a Technical + Managerial round, which lasted for 1 hour.
The 4th round was the HR round.
Why selected/rejected for the role?
I was selected for the role at PayU because of my strong foundation in backend development, hands-on experience from my internship at a UK-based startup (KED UK), and my ability to explain projects and concepts clearly during the interviews. I had also consistently practiced DSA and revised core subjects like DBMS and OOP, which helped me perform confidently in all three interview rounds. My practical experience, clear communication, and structured problem-solving approach made a positive impression on the interviewers.
Also, my interviewers were very friendly and supportive—they helped me whenever I got stuck.
Preparation
Duration: 12 Months
Topics: Data Structures and Algorithms, Spring Boot, DBMS, Java, OOPs
Tip
Tip 1: Practice at least 2–3 easy to medium-level DSA questions daily.
Tip 2: Build 3–4 full-stack projects.
Tip 3: Study core subjects every weekend (DBMS, OOPs, Networking, etc.).
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: 7 CGPA, (Salary Package: 12-15 LPA)
Resume tip
Tip 1: Make a one-page resume.
Tip 2: Only add skills that you actually know.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Medium
Online Coding Interview
Duration80 minutes
Interview date24 Apr 2025
Coding problem2
Duration: 2 hours
Time: It was held in the evening.
Format:
16 MCQ questions
1 DSA question (a dynamic programming problem of easy to medium difficulty)
1 SQL query
1. Rod cutting problem
Moderate
40m average time
75% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Given a rod of length ‘N’ units. The rod can be cut into different sizes and each size has a cost associated with it. Determine the maximum cost obtained by cutting the rod and selling its pieces.
Note:
1. The sizes will range from 1 to ‘N’ and will be integers.
2. The sum of the pieces cut should be equal to ‘N’.
3. Consider 1-based indexing.
Problem approach
As soon as I saw the problem, I realized it was a DP question, and I already knew the approach.
The idea is to fill the DP table from bottom to top. For each rod of length i, starting from i = 1 to i = n, find the maximum value that can be obtained by cutting it into two pieces of lengths j and (i - j).
2. SQL query
There was one SQL query. Tables were given, and we had to solve it.
You are given a table of employee data. Each employee has an ID, name, salary, and an optional manager. Write an SQL query to find the names of employees who earn more than their respective managers.
Problem approach
The question was related to subqueries and joins.
Step 1: Understand the relationships
Each row represents an employee and contains a reference to their manager using manager_id.
To compare an employee's salary with their manager’s, we need two rows from the same table — one for the employee and one for the manager.
Step 2: Use a SELF JOIN
We join the Employees table to itself:
One alias represents the employee (E1)
The other represents the manager (E2)
Join condition: E1.manager_id = E2.emp_id
Step 3: Compare salaries
Condition: E1.salary > E2.salary
Step 4: Write the query
Select the names of employees who earn more than their manager.
02
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration120 minutes
Interview date28 Apr 2025
Coding problem3
It started with my introduction. When I mentioned my internship as a backend developer, he asked me to open a compiler and gave me a coding question related to trees. The interviewer was very friendly and made me feel comfortable.
1. Construct Binary Tree From Inorder and Preorder Traversal
Easy
10m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You have been given the preorder and inorder traversal of a binary tree. Your task is to construct a binary tree using the given inorder and preorder traversals.
Note:
You may assume that duplicates do not exist in the given traversals.
For example :
For the preorder sequence = [1, 2, 4, 7, 3] and the inorder sequence = [4, 2, 7, 1, 3], we get the following binary tree.
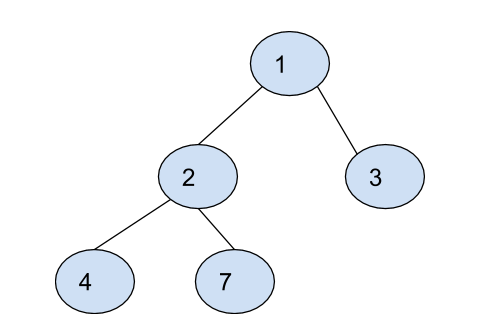
Problem approach
I solved the problem, but then he modified the question — for example, he asked me to add postorder traversal as well.
Approach:
Start with Preorder Traversal:
The first element in the preorder array is always the root of the tree (or subtree).
Find Root in Inorder:
Locate the root element (from preorder) in the inorder array. This divides the inorder array into:
Left part → Left Subtree
Right part → Right Subtree
Recursive Construction:
Recursively build the left subtree using the left part of the inorder array and the corresponding elements in the preorder array.
Recursively build the right subtree using the right part of the inorder array and the corresponding elements in the preorder array.
Use Indexing:
Maintain a global or reference index for preorder traversal (starting at 0).
Each time you pick an element from preorder, increment this index.
Optimize Inorder Lookup:
Use a hash map to store the index of each element in the inorder array for O(1) lookup.
Base Condition:
When start > end in the inorder range, return NULL.
2. DBMS
You are given a table Student(id, name, age, grades). Write an SQL query to return only the name and grade of all students.
3. DBMS
You are given a table Student(id, name, age, grades). Write a query to return the names of students who are 14 years old or older.
03
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration45 minutes
Interview date30 Jun 2025
Coding problem3
This was the Technical + Managerial round.
He seemed a bit strict, and I was also nervous.
He asked me many questions related to databases only.
Along with the approach to one array/list question.
1. DBMS
What is normalization in DBMS? Explain its different normal forms (1NF, 2NF, 3NF) with brief examples. (Learn)
Problem approach
Start by defining Normalization: a process used to remove redundancy and ensure data integrity.
- 1NF (First Normal Form): Ensure that each cell contains atomic (indivisible) values.
- 2NF (Second Normal Form): Ensure the table is in 1NF, and all non-key attributes are fully functionally dependent on the primary key.
- 3NF (Third Normal Form): Ensure the table is in 2NF, and there are no transitive dependencies.
2. DBMS
Explain the key differences between SQL and NoSQL databases. In which scenarios would you prefer one over the other? (Learn)
Problem approach
Define both:
SQL: Structured data, relational schema, supports JOINs (e.g., MySQL, PostgreSQL).
NoSQL: Unstructured or semi-structured data, schema-less (e.g., MongoDB, Cassandra).
Use cases:
SQL: Banking systems, ERP applications.
NoSQL: Real-time analytics, social media platforms, IoT applications.
3. First Missing Positive
Moderate
18m average time
84% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given an array 'ARR' of integers of length N. Your task is to find the first missing positive integer in linear time and constant space. In other words, find the lowest positive integer that does not exist in the array. The array can have negative numbers as well.
For example, the input [3, 4, -1, 1] should give output 2 because it is the smallest positive number that is missing in the input array.
Problem approach
Ignore negative numbers and zeros.
Try to place each number at its correct index (value x at index x - 1) using in-place swaps.
After rearranging, iterate through the array:
The first index where arr[i] != i + 1 gives the answer as i + 1.
If all positions are correct, return n + 1.
The problem is solved in O(n) time and O(1) space.
04
Round
Easy
HR Round
Duration30 minutes
Interview date1 Jun 2025
Coding problem1
The HR round mainly focused on my location, work hours, and she explained everything about my role and the company.
She also asked about my location preference.
1. HR Insights
The HR round was quite smooth — it was more of an informative session where the HR explained the company, team structure, and role expectations. I believe my confidence, clear communication, and genuine interest in the role helped me stand out as a good fit for the team.
Problem approach
Tip 1: Be confident.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by PayU
1812 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by PayU
2248 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 9 problems
Interviewed by Salesforce
3566 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by PayU
290 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
Associate Software Engineer
3 rounds | 10 problems
Interviewed by Amdocs
2391 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Associate Software Engineer
3 rounds | 2 problems
Interviewed by Ernst & Young (EY)
2728 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Associate Software Engineer
3 rounds | 15 problems
Interviewed by Ernst & Young (EY)
2383 views
0 comments
0 upvotes







