Persistent Systems Limited interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - 1
Persistent Systems Limited
3 rounds | 10 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 4 Months
Topics: Data Structures, Algorithms, System Design, Aptitude, OOPS
Tip
Tip 1 : Must do Previously asked Interview as well as Online Test Questions.
Tip 2 : Go through all the previous interview experiences from Codestudio and Leetcode.
Tip 3 : Do at-least 2 good projects and you must know every bit of them.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: Above 7 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Have at-least 2 good projects explained in short with all important points covered.
Tip 2 : Every skill must be mentioned.
Tip 3 : Focus on skills, projects and experiences more.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Easy
Online Coding Test
Duration45 Minutes
Interview date17 Aug 2016
Coding problem2
This was an online coding round where we had 2 questions to solve under 45 minutes. The questions were more on the easier side and can be solved if one has practised DSA questions well.
1. Cycle Detection in a Singly Linked List
Moderate
15m average time
80% success
0/80
Asked in companies



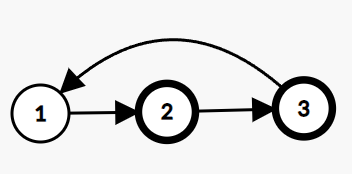
You are given a Singly Linked List of integers. Return true if it has a cycle, else return false.
A cycle occurs when a node's next points back to a previous node in the list.
Example:
In the given linked list, there is a cycle, hence we return true.
Problem approach
1) Initialize slow and fast at the beginning.
2) Start moving slow to every next node and moving fast 2 jumps, while making sure that fast and its next is not null.
3) If after adjusting slow and fast, if they are referring to the same node, there is a cycle otherwise repeat the process
4) If fast reaches the end or null then the execution stops and we can conclude that no cycle exists.
TC : O(N), where N=total number of nodes
SC : O(1)
2. First non repeating character
Easy
15m average time
80% success
0/40
Asked in companies



Ninja is now bored with numbers and is now playing with characters but hates when he gets repeated characters. Ninja is provided a string, and he wants to return the first unique character in the string.The string will contain characters only from the English alphabet set, i.e., ('A' - 'Z') and ('a' - 'z'). If there is no non-repeating character, print the first character of the string. If there is no non-repeating character, return the first character of the string.
Problem approach
1) We initialize a hash map ‘frequencyOfCharacters’ to store the frequency of each element.
2) We will iterate over the length of the string ‘S’, i.e., i = 0 to i = N - 1:
2.1) We will store the frequency of a character at position i in ‘frequencyOfCharacters’.
2.2) If the element already exists in ‘frequencyOfCharacters’, then increment ‘frequencyOfCharacters’ for that character.
3) We will iterate over the length of the string, i.e., i = 0 to i = N - 1:
4) If frequencyOfCharacters[S[i]] is 1 then we return the value of S[i] as the final answer.
5) We will return the first character of the string as the final answer.
TC : O(N), where N=length of the string
SC : O(N)
02
Round
Medium
Face to Face
Duration60 Minutes
Interview date17 Aug 2016
Coding problem6
This round had 1 question of DSA followed by questions from OS and OOPS.
1. LCA In A BST
Moderate
15m average time
85% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given a binary search tree of integers with N nodes. You are also given references to two nodes 'P' and 'Q' from this BST.
Your task is to find the lowest common ancestor(LCA) of these two given nodes.
The lowest common ancestor for two nodes P and Q is defined as the lowest node that has both P and Q as descendants (where we allow a node to be a descendant of itself)
A binary search tree (BST) is a binary tree data structure which has the following properties.
• The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with data less than the node’s data.
• The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with data greater than the node’s data.
• Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
For example:
'P' = 1, 'Q' = 3
tree = 2 1 4 -1 -1 3 -1 -1 -1,
The BST corresponding will be-
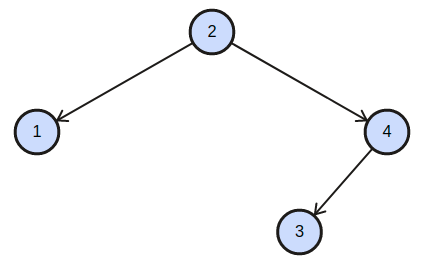
Here, we can clearly see that LCA of node 1 and node 3 is 2.
Problem approach
Approach :
1) Let the current node in the iteration be ‘currNode’.
2) While currNode is not equal to NULL:
2.1) If currNode -> data is less than P -> data and Q -> data, then LCA would be in the right subtree.
2.2) If currNode -> data is greater than P -> data and Q -> data, then LCA would be in the left subtree.
2.3) Else, currNode would be the LCA.
TC : O(N)
SC : O(1)
2. OOPS Question
Difference between Abstract class and Interface.
Problem approach
The differences between Abstract Class and Interface are as follows:
Abstract Class:
1) Abstract classes have a default constructor and it is called whenever the concrete subclass is instantiated.
2) It contains Abstract methods as well as Non-Abstract methods.
3) The class which extends the Abstract class shouldn’t require the implementation of all the methods, only Abstract methods need to be implemented in the concrete sub-class.
4) Abstract class contains instance variables.
Interface:
1 )It doesn’t have any constructor and couldn’t be instantiated.
2) The abstract method alone should be declared.
3) Classes that implement the interface should provide the implementation for all the methods.
4) The interface contains only constants.
3. OOPS Question
What is the static keyword in Java?
Problem approach
1) The static keyword in Java is mainly used for memory management.
2) The static keyword in Java is used to share the same variable or method of a given class.
3) The users can apply static keywords with variables, methods, blocks, and nested classes.
4) The static keyword belongs to the class than an instance of the class.
5) The static keyword is used for a constant variable or a method that is the same for every instance of a class.
4. OS Question
Explain deadlock. How would you handle a deadlock?
Problem approach
Deadlock : Deadlock is a situation where a set of processes are blocked because each process is holding a resource and waiting for another resource acquired by some other process.
Consider an example when two trains are coming toward each other on the same track and there is only one track, none of the trains can move once they are in front of each other. A similar situation occurs in operating systems when there are two or more processes that hold some resources and wait for resources held by other(s).
Deadlock can arise if the following four conditions hold simultaneously (Necessary Conditions) :
1) Mutual Exclusion : One or more than one resource are non-shareable (Only one process can use at a time)
2) Hold and Wait : A process is holding at least one resource and waiting for resources.
3) No Preemption : A resource cannot be taken from a process unless the process releases the resource.
4) Circular Wait : A set of processes are waiting for each other in circular form.
Methods for handling deadlock :
There are three ways to handle deadlock
1) Deadlock prevention or avoidance : The idea is to not let the system into a deadlock state.
One can zoom into each category individually, Prevention is done by negating one of above mentioned necessary conditions for deadlock.
Avoidance is kind of futuristic in nature. By using strategy of “Avoidance”, we have to make an assumption. We need to ensure that all information about resources which process will need are known to us prior to execution of the process. We use Banker’s algorithm in order to avoid deadlock.
2) Deadlock detection and recovery : Let deadlock occur, then do preemption to handle it once occurred.
3) Ignore the problem altogether : If deadlock is very rare, then let it happen and reboot the system. This is the approach that both Windows and UNIX take.
5. OS Question
Difference between Process and Thread
Problem approach
Process : A process is the execution of a program that allows us to perform the appropriate actions specified in a program. It can be defined as an execution unit where a program runs. The OS helps us to create, schedule, and terminates the processes which is used by CPU. The other processes created by the main process are called child process.
Thread : Thread is an execution unit that is part of a process. A process can have multiple threads, all executing at the same time. It is a unit of execution in concurrent programming. A thread is lightweight and can be managed independently by a scheduler. It helps us to improve the application performance using parallelism.
Major Differences b/w Process and Thread :
1) Process means a program is in execution, whereas thread means a segment of a process.
2) A Process is not Lightweight, whereas Threads are Lightweight.
3) A Process takes more time to terminate, and the thread takes less time to terminate.
4) Process takes more time for creation, whereas Thread takes less time for creation.
5) Process likely takes more time for context switching whereas as Threads takes less time for context switching.
6) A Process is mostly isolated, whereas Threads share memory.
7) Process does not share data, and Threads share data with each other.
6. OS Question
Explain Static and Dynamic Linking in OS
Problem approach
Static Linking : Static linking is the result of the linker copying all library routines used in the program into the executable image. This may require more disk space and memory than dynamic linking, but is both faster and more portable, since it does not require the presence of the library on the system where it is run.
Dynamic Linking : Dynamic linking is accomplished by placing the name of a sharable library in the executable image. Actual linking with the library routines does not occur until the image is run, when both the executable and the library are placed in memory. An advantage of dynamic linking is that multiple programs can share a single copy of the library.
03
Round
Easy
HR Round
Duration30 Minutes
Interview date17 Aug 2016
Coding problem2
This is a cultural fitment testing round. HR was very frank and asked standard questions. Then we discussed about my role.
1. Basic HR Question
Tell me something not there in your resume.
Problem approach
If you get this question, it's an opportunity to choose the most compelling information to share that is not obvious from your resume.
Example :
Strength -> I believe that my greatest strength is the ability to solve problems quickly and efficiently, which makes me unique from others.
Ability to handle Pressure -> I enjoy working under pressure because I believe it helps me grow and become more efficient.
Tip : Emphasize why you were inspired to apply for the job. You can also explain that you are willing to invest a great deal of energy if hired.
These are generally very open ended questions and are asked to test how quick wit a candidate is. So there is nothing to worry about if you have a good command over your communication skills and you are able to propagate your thoughts well to the interviewer.
2. Basic HR Question
Why should we hire you ?
Problem approach
Tip 1 : The cross questioning can go intense some time, think before you speak.
Tip 2 : Be open minded and answer whatever you are thinking, in these rounds I feel it is important to have opinion.
Tip 3 : Context of questions can be switched, pay attention to the details. It is okay to ask questions in these round, like what are the projects currently the company is investing, which team you are mentoring. How all is the work environment etc.
Tip 4 : Since everybody in the interview panel is from tech background, here too you can expect some technical questions. No coding in most of the cases but some discussions over the design can surely happen.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
Analyst
3 rounds | 13 problems
Interviewed by Persistent Systems Limited
912 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 10 problems
Interviewed by Persistent Systems Limited
1360 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Persistent Systems Limited
959 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 8 problems
Interviewed by Persistent Systems Limited
298 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by BNY Mellon
6315 views
3 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by BNY Mellon
0 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by CIS - Cyber Infrastructure
2179 views
0 comments
0 upvotes






