Persistent Systems Limited interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - 1
Persistent Systems Limited
3 rounds | 10 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 4 Months
Topics: Data Structures, Algorithms, System Design, Aptitude, OOPS
Tip
Tip 1 : Must do Previously asked Interview as well as Online Test Questions.
Tip 2 : Go through all the previous interview experiences from Codestudio and Leetcode.
Tip 3 : Do at-least 2 good projects and you must know every bit of them.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: Above 7 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Have at-least 2 good projects explained in short with all important points covered.
Tip 2 : Every skill must be mentioned.
Tip 3 : Focus on skills, projects and experiences more.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Medium
Online Coding Test
Duration60 Minutes
Interview date22 Aug 2019
Coding problem2
This was an online coding round where we had 2 questions and some Technical MCQ's to solve. The coding questions were supposed to be solved under 1 hour and the questions were not so tough as such.
1. Next Greater Element
Easy
10m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given an array 'a' of size 'n'.
Print the Next Greater Element(NGE) for every element.
The Next Greater Element for an element 'x' is the first element on the right side of 'x' in the array, which is greater than 'x'.
If no greater elements exist to the right of 'x', consider the next greater element as -1.
For example:
Input: 'a' = [7, 12, 1, 20]
Output: NGE = [12, 20, 20, -1]
Explanation: For the given array,
- The next greater element for 7 is 12.
- The next greater element for 12 is 20.
- The next greater element for 1 is 20.
- There is no greater element for 20 on the right side. So we consider NGE as -1.
Problem approach
Approach :
1) Initialize an array ‘ANS’ of integer type and the same size as the input array to store the Next Greater Elements.
2) Declare a stack ‘S’ of integer type that will have Next Greater Element as its top element.
3) Iterate the array in reverse order. (say, iterator = ‘i’)
4) Pop from ‘S’ until the stack ‘S’ is not empty and the current element is greater than the top element of the stack
5) Update ‘ANS[i]’ with the top element of ‘S’.
6) If the stack is empty then update ‘ANS[i]’ with -1.
7) Push the current element onto the stack ‘S’.
8) Return ‘ANS’.
TC : O(N), where N=number of elements in the array
SC : O(N)
2. Arranging Array
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies

You are given an array of N integers. Your task is to rearrange the elements of the array such that the total XOR sum of all adjacent elements is maximized.
The XOR sum is defined as follows. For an array a of size N, compute:
F = (a[1] ⊕ a[0]) + (a[2] ⊕ a[1]) + ... + (a[N-1] ⊕ a[N-2]) where ⊕ denotes the bitwise XOR operator.
Your goal is to output a permutation of the original array that results in the maximum possible value of F.
Note :
You do not need to print anything; it has already been taken care of. Just implement the given function.
Problem approach
Approach :
1) Sort the array in descending order.
2) Print all the ones, if present.
3) From the remaining array print it in descending order making sure not to reprint the ones again.
TC : O(N * log(N)), where N=size of the array.
SC : O(1)
02
Round
Medium
Face to Face
Duration60 Minutes
Interview date22 Aug 2019
Coding problem7
The interviewer asked 2 coding problems in this round and then the rest of the questions were preety much revolving around Computer Networks and Operating System.
1. Detect and Remove Loop
Moderate
10m average time
90% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Given a singly linked list, you have to detect the loop and remove the loop from the linked list, if present. You have to make changes in the given linked list itself and return the updated linked list.
Expected Complexity: Try doing it in O(n) time complexity and O(1) space complexity. Here, n is the number of nodes in the linked list.
Problem approach
Approach :
Finding the cycle :
1) Initialize slow and fast at the beginning.
2) Start moving slow to every next node and move fast 2 jumps, while making sure that fast and its next is not null.
3) If slow and fast refer to the same node anytime during the process, there is a cycle, otherwise, repeat the process.
4) If fast reaches the end or NULL, then the execution stops and we can conclude that no cycle exists.
Removing the cycle :
1) Find the length of the cycle, let’s say ‘L’.
2) We will take two pointers ‘ptr1’ and ‘ptr2’, initially ‘ptr1’ points to head and ‘ptr2’ points to Lth node from the head.
3) We will move the pointers until they meet at the same node.
4) To remove the cycle we have to find the previous node of the ‘ptr2’ and change its ‘next’ values to NULL.
TC : O(N), where N=number of nodes in the Linked List
SC : O(1)
2. Matrix Is Symmetric
Easy
10m average time
80% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given a square matrix, return true if the matrix is symmetric otherwise return false.
A symmetric matrix is that matrix whose transpose is equal to the matrix itself.
Example of symmetric matrix :
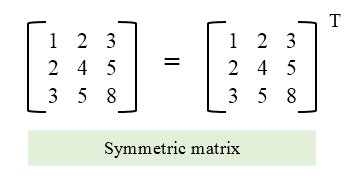
Problem approach
Approach :
1) Traverse the matrix element by element and compare ‘MATRIX' ( i, j) with 'MATRIX" ( j, i).
2) And if anywhere there inequality exists between them simply return false from that point else continue.
3) In the end, if not returned previously from anywhere else just return true, as ‘MATRIX’ is symmetric.
TC : O(N^2), where N=size of the square matrix
SC : O(1)
3. DBMS Question
What is meant by normalization and denormalization?
Problem approach
NORMALIZATION :
1) Normalization is a process of reducing redundancy by organizing the data into multiple tables.
2) Normalization leads to better usage of disk spaces and makes it easier to maintain the integrity of the database.
DENORMALIZATION :
1) Denormalization is the reverse process of normalization as it combines the tables which have been normalized into a single table so that data retrieval becomes faster.
2) JOIN operation allows us to create a denormalized form of the data by reversing the normalization.
4. Networking Question
Describe the OSI Reference Model
Problem approach
Open System Interconnections (OSI) is a network architecture model based on the ISO standards. It is called the OSI model as it deals with connecting the systems that are open for communication with other systems.
The OSI model has seven layers. The principles used to arrive at the seven layers can be summarized briefly as below :
1) Create a new layer if a different abstraction is needed.
2) Each layer should have a well-defined function.
3) The function of each layer is chosen based on internationally standardized protocols.
5. Networking Question
What is the difference between anycast, unicast, and multicast?
Problem approach
Unicast : The unicast addressing method indicates that communication through a network involves a unique sender (source) and a single receiver (destination). Making an analogy, we can see unicast communication as a particular conversation with a single person (unicast) at a party with many people (network).
Multicast : A multicast address can be used to deliver a package to a group of destinations. Any packet sent to a multicast address, will be delivered to every host that has joined that particular group.Since IPv6 has no support for the broadcast address, any function that used to rely on broadcasts will now be using multicast addresses.Multicast addresses are in the range of FF00::/8.
Anycast : The anycast address is very similar to the multicast address, but packets will be delivered to only one random host, instead of the entire group.Anycast address don’t have a specific range, as they are exactly the same as regular unicast addresses. This means that a hosts has no way to distinguish a unicast from an anycast address when it sends a packet.
6. OS Question
What is thrashing in OS?
Problem approach
It is generally a situation where the CPU performs less productive work and more swapping or paging work. It spends more time swapping or paging activities rather than its execution. By evaluating the level of CPU utilization, a system can detect thrashing. It occurs when the process does not have enough pages due to which the page-fault rate is increased. It inhibits much application-level processing that causes computer performance to degrade or collapse.
7. OS Question
What is a deadlock in OS? What are the necessary conditions for a deadlock?
Problem approach
Deadlock is generally a situation where a set of processes are blocked as each process is holding resources and waits to acquire resources held by another process. In this situation, two or more processes simply try to execute simultaneously and wait for each to finish their execution because they are dependent on each other. We can see a hand problem in our system whenever a deadlock occurs in a program. It is one of the common problems you can see in multiprocessing.
Necessary Conditions for Deadlock
There are basically four necessary conditions for deadlock as given below:
1) Mutual Exclusion
2) Hold and Wait
3) No Pre-emption
4) Circular Wait or Resource Wait
03
Round
Easy
HR Round
Duration30 Minutes
Interview date22 Aug 2019
Coding problem1
This was a typical HR round with some standard Behavioral questions.
1. Basic HR Question
Tell me something not there in your resume.
Problem approach
If you get this question, it's an opportunity to choose the most compelling information to share that is not obvious from your resume.
Example :
Strength -> I believe that my greatest strength is the ability to solve problems quickly and efficiently, which makes me unique from others.
Abillity to Handle Pressure -> I enjoy working under pressure because I believe it helps me grow and become more efficient .
Tip : Emphasize why you were inspired to apply for the job. You can also explain that you are willing to invest a great deal of energy if hired.
These are generally very open ended questions and are asked to test how quick wit a candidate is. So there is nothing to worry about if you have a good command over your communication skills and you are able to propagate your thoughts well to the interviewer

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 10 problems
Interviewed by Persistent Systems Limited
1059 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Analyst
3 rounds | 13 problems
Interviewed by Persistent Systems Limited
913 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Persistent Systems Limited
959 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 8 problems
Interviewed by Persistent Systems Limited
298 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by BNY Mellon
6315 views
3 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by BNY Mellon
0 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by CIS - Cyber Infrastructure
2179 views
0 comments
0 upvotes







