PhonePe interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - 1
PhonePe
4 rounds | 7 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 3 Months
Topics: Data Structures, OOPS, Algorithms, Dynamic Programming, OS, DBMS
Tip
Tip 1 : Don't be afraid to ask for a hint
Tip 2 : Focus on problem solving.
Application process
Where: Referral
Eligibility: No criteria
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Don't lie on your resume
Tip 2 : Try to mention what was your part in the projects mentioned
Interview rounds
01
Round
Medium
Online Coding Interview
Duration90 Minutes
Interview date15 Nov 2021
Coding problem2
1. Sort 0 1 2
Easy
22m average time
0/40
Asked in companies



You have been given an integer array/list(ARR) of size 'N'. It only contains 0s, 1s and 2s. Write a solution to sort this array/list.
Note :
Try to solve the problem in 'Single Scan'. ' Single Scan' refers to iterating over the array/list just once or to put it in other words, you will be visiting each element in the array/list just once.
2. Count Ways To Reach The N-th Stairs
Moderate
30m average time
80% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You have been given a number of stairs. Initially, you are at the 0th stair, and you need to reach the Nth stair.
Each time, you can climb either one step or two steps.
You are supposed to return the number of distinct ways you can climb from the 0th step to the Nth step.
Note:
Note: Since the number of ways can be very large, return the answer modulo 1000000007.
Example :
N=3
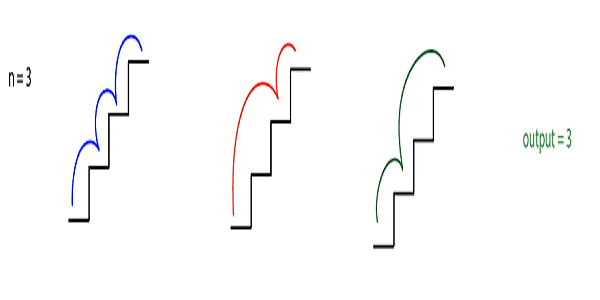
We can climb one step at a time i.e. {(0, 1) ,(1, 2),(2,3)} or we can climb the first two-step and then one step i.e. {(0,2),(1, 3)} or we can climb first one step and then two step i.e. {(0,1), (1,3)}.
02
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration60 Minutes
Interview date14 Jan 2022
Coding problem2
The interviewer was on time.
1. Diameter Of Binary Tree
Easy
10m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given a Binary Tree.
Return the length of the diameter of the tree.
Note :
The diameter of a binary tree is the length of the longest path between any two end nodes in a tree.
The number of edges between two nodes represents the length of the path between them.
Example :
Input: Consider the given binary tree:
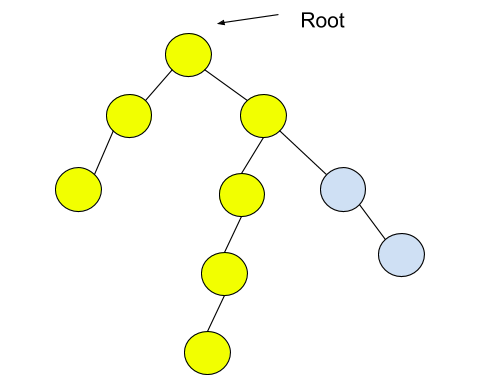
Output: 6
Explanation:
Nodes in the diameter are highlighted. The length of the diameter, i.e., the path length, is 6.
Problem approach
Applied DFS traversal and a hasmap to store distance
2. Find The Repeating And Missing Number
Easy
10m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given an array 'nums' consisting of first N positive integers. But from the N integers, one of the integers occurs twice in the array, and one of the integers is missing. You need to determine the repeating and the missing integer.
Example:
Let the array be [1, 2, 3, 4, 4, 5]. In the given array ‘4’ occurs twice and the number ‘6’ is missing.
Problem approach
The expected time complexity was N*Log(N). The approach I used was the Binary Search on answer.
03
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date21 Jan 2022
Coding problem2
1. Largest subarray with equal number of 0s and 1s
Moderate
10m average time
85% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given an array consisting of 0s and 1s. You need to find the length of the largest subarray with an equal number of 0s and 1s.
For example:
If the given array is: [0, 0, 1, 0, 1] The largest subarray would be: [0, 1, 0, 1] (last 4 elements) having length 4.
2. Pairs with difference K
Moderate
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given with an array of integers and an integer K. You have to find and print the count of all such pairs which have difference K.
Note: Take absolute difference between the elements of the array.
Problem approach
Binary search on answer concept was used in this question as well
04
Round
Medium
HR Round
Duration40 minutes
Interview date12 Feb 2022
Coding problem1
It was HM round. An engineering manager took this round
1. Project based question
This round was primarily focused on the projects mentioned in the resume.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by PhonePe
4288 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
5 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by PhonePe
2788 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by PhonePe
0 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by PhonePe
2184 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
5 rounds | 12 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
114869 views
24 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
58031 views
5 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
35057 views
7 comments
0 upvotes






