PhonePe interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - 1
PhonePe
4 rounds | 6 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 7 months
Topics: Data Structures and Algorithms, OOPS, Web Development, Operating Systems, Database Management System, Automata theory.
Tip
Tip 1 : Practice as many questions as possible from any of the good coding platform.
Tip 2 : Core CS fundamentals should be strong and can't be neglected before interview.
Tip 3 : Some hands-on dev projects are really good to have as companies nowadays(mostly startups) look some good hands-on experience even in freshers.
Application process
Where: Other
Eligibility: No criteria
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Should be single page, to the point and precise resume.
Tip 2 : Only put truth on the resume.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Medium
Online Coding Test
Duration60 Minutes
Interview date15 Mar 2021
Coding problem3
1. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock
Hard
20m average time
80% success
0/120
Asked in companies



You have been given an array 'PRICES' consisting of 'N' integers where PRICES[i] denotes the price of a given stock on the i-th day. You are also given an integer 'K' denoting the number of possible transactions you can make.
Your task is to find the maximum profit in at most K transactions. A valid transaction involves buying a stock and then selling it.
Note
You can’t engage in multiple transactions simultaneously, i.e. you must sell the stock before rebuying it.
For Example
Input: N = 6 , PRICES = [3, 2, 6, 5, 0, 3] and K = 2.
Output: 7
Explanation : The optimal way to get maximum profit is to buy the stock on day 2(price = 2) and sell it on day 3(price = 6) and rebuy it on day 5(price = 0) and sell it on day 6(price = 3). The maximum profit will be (6 - 2) + (3 - 0) = 7.
Problem approach
We must know the concept of stock market that we must buy stocks at low price and sell it in high price. In this problem we use two pointer approach where left pointer will take care about buying and right is for selling the stocks.
Time Complexity: O(n) we just traverse the array 1 time for 1 transaction
Space Complexity: O(1) , extra space not required
2. Maximum Sum Rectangle
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given a matrix ‘ARR’ with ‘N’ rows and ‘M’ columns. Your task is to find the maximum sum rectangle in the matrix.
Maximum sum rectangle is a rectangle with the maximum value for the sum of integers present within its boundary, considering all the rectangles that can be formed from the elements of that matrix.
For Example
Consider following matrix:
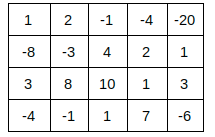
The rectangle (1,1) to (3,3) is the rectangle with the maximum sum, i.e. 29.
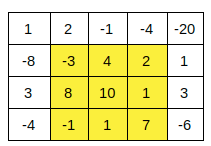
Problem approach
The idea behind this algorithm is to fix the left and right columns and try to find the sum of the element from the left column to right column for each row, and store it temporarily.
We will try to find top and bottom row numbers. After getting the temporary array, we can apply the Kadane’s Algorithm to get maximum sum sub-array. With it, the total rectangle will be formed.
Sample I/P :
1 2 -1 -4 -20
-8 -3 4 2 1
3 8 10 1 3
-4 -1 1 7 -6
Output :
The top left point and bottom right point of the submatrix, and the total sum of the submatrix.
(Top, Left) (1, 1)
(Bottom, Right) (3, 3)
The max sum is : 29
3. Snake and Ladder
Moderate
30m average time
60% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You have been given a Snake and Ladder Board with 'N' rows and 'N' columns with the numbers written from 1 to (N*N) starting from the bottom left of the board, and alternating direction each row.
For example
For a (6 x 6) board, the numbers are written as follows:
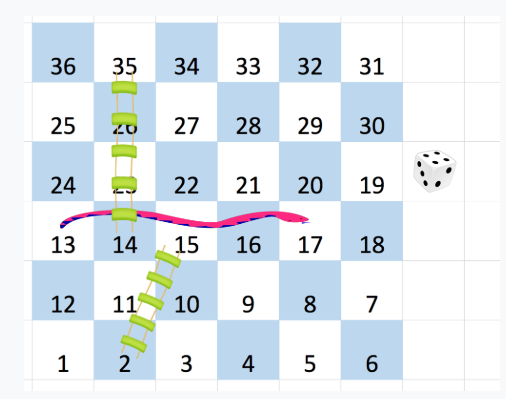
You start from square 1 of the board (which is always in the last row and first column). On each square say 'X', you can throw a dice which can have six outcomes and you have total control over the outcome of dice throw and you want to find out the minimum number of throws required to reach the last cell.
Some of the squares contain Snakes and Ladders, and these are possibilities of a throw at square 'X':
You choose a destination square 'S' with number 'X+1', 'X+2', 'X+3', 'X+4', 'X+5', or 'X+6', provided this number is <= N*N.
If 'S' has a snake or ladder, you move to the destination of that snake or ladder. Otherwise, you move to S.
A board square on row 'i' and column 'j' has a "Snake or Ladder" if board[i][j] != -1. The destination of that snake or ladder is board[i][j].
Note :
You can only take a snake or ladder at most once per move: if the destination to a snake or ladder is the start of another snake or ladder, you do not continue moving - you have to ignore the snake or ladder present on that square.
For example, if the board is:
-1 1 -1
-1 -1 9
-1 4 -1
Let's say on the first move your destination square is 2 [at row 2, column 1], then you finish your first move at 4 [at row 1, column 2] because you do not continue moving to 9 [at row 0, column 0] by taking the ladder from 4.
A square can also have a Snake or Ladder which will end at the same cell.
For example, if the board is:
-1 3 -1
-1 5 -1
-1 -1 9
Here we can see Snake/Ladder on square 5 [at row 1, column 1] will end on the same square 5.
Problem approach
The primary motive in this question is to find out the least amount of dice throws to reach the end from the source or a custom start point. The user has complete control over the outcome of the dice. This problem can be solved using DFS (Depth First Search), BFS (Breadth-First Search) or Dijkstra’s Algorithm.
02
Round
Medium
Face to Face
Duration70 Minutes
Interview date14 May 2021
Coding problem2
1. Longest Increasing Subsequence
Moderate
30m average time
65% success
0/80
Asked in companies



For a given array with N elements, you need to find the length of the longest subsequence from the array such that all the elements of the subsequence are sorted in strictly increasing order.
Strictly Increasing Sequence is when each term in the sequence is larger than the preceding term.
For example:
[1, 2, 3, 4] is a strictly increasing array, while [2, 1, 4, 3] is not.
Problem approach
- Number itself is a increasing subsequence so initialize as 1.
- If right index greater than left, then dp[left] + 1 and dp[i] whichever is greater then asign to dp[i].
- Finally iterate the dp array to get the greatest.
2. Longest Increasing Path In A 2D Matrix
Hard
10m average time
90% success
0/120
Asked in companies



You have been given a MATRIX of non-negative integers of size N x M where 'N' and 'M' denote the number of rows and columns, respectively.
Your task is to find the length of the longest increasing path when you can move to either four directions: left, right, up or down from each cell. Moving diagonally or outside the boundary is not allowed.
Note: A sequence of integers is said to form an increasing path in the matrix if the integers when traversed along the allowed directions can be arranged in strictly increasing order. The length of an increasing path is the number of integers in that path.
For example :
3 2 2
5 6 6
9 5 11
In the given matrix, 3 → 5 → 6 and 3 → 5 → 9 form increasing paths of length 3 each.
Problem approach
1) Build an inital graph given the input matrix, each edge will be a->b so that matrix[i][j] < matrix[i'][j'] for i' and j' 4-neighbor of i,j.
2) After that, run Kahn's algorithm for topological sorting, keep removing vertices and add its neighbors which in-degree equals 0.
3) Count how many times a new vertex is added to the Queue (this means that a new vertex has been discovered so our final answer should be incremented by 1).
4) Keep removing verfices until no more vertices are available and return the final answer.
03
Round
Medium
Face to Face
Duration45 Minutes
Interview date26 May 2021
Coding problem1
1. Search in Rotated Sorted Array
Easy
12m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You have been given a sorted array/list 'arr' consisting of ‘n’ elements. You are also given an integer ‘k’.
Now the array is rotated at some pivot point unknown to you.
For example, if 'arr' = [ 1, 3, 5, 7, 8], then after rotating 'arr' at index 3, the array will be 'arr' = [7, 8, 1, 3, 5].
Now, your task is to find the index at which ‘k’ is present in 'arr'.
Note :
1. If ‘k’ is not present in 'arr', then print -1.
2. There are no duplicate elements present in 'arr'.
3. 'arr' can be rotated only in the right direction.
Example:
Input: 'arr' = [12, 15, 18, 2, 4] , 'k' = 2
Output: 3
Explanation:
If 'arr' = [12, 15, 18, 2, 4] and 'k' = 2, then the position at which 'k' is present in the array is 3 (0-indexed).
Problem approach
When array is rotated then two possiblities are :
1) low to mid part is sorted
a) if the target lies btw this part ` (target>= nums[low] and target<=nums[mid])`
then `high=mid-1;`
b) else target will be present after the mid `low=mid+1;`
2) mid to high part is sorted
a) if the target lies btw this part` (target>=nums[mid] and target<=nums[high])`
then `low=mid+1;`
b) else target will be present before the mid `high=mid-1`
04
Round
Medium
HR Round
Duration45 Minutes
Interview date9 Jun 2022
Coding problem0
This round was Hiring manager round with one of the Head Of Engineering in the company. Majorly it was knowing about me and my interest on which they can decide which team i should be aligned to if i get selected. It majorly covered my resume grilling, my projects, some technical discussions on how better projects could have been done so that it can maintain scale etc. Atlast he asked if i have any question for him, i simply said everything looks good as of now. We greeted each other and interview was ended.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
5 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by PhonePe
2787 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by PhonePe
3040 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by PhonePe
0 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by PhonePe
2183 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
5 rounds | 12 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
114869 views
24 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
58031 views
5 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
35057 views
7 comments
0 upvotes







