Policybazaar insurance broker interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - 1
Policybazaar insurance broker
3 rounds | 6 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Journey
First, I got selected for a Tier 1 college, and from there, my journey in coding started. I have done most of my coding in my final years, but I regret that I should have started earlier.
Application story
I applied for a software developer position when the company visited my campus for placements. After submitting my resume through the campus portal, I completed pre-interview assessments. These assessments focused on showcasing my technical skills.
Why selected/rejected for the role?
I was rejected for this offer because I could not perform well during all the rounds of the interview process.
Preparation
Duration: 8 months
Topics: Data Structures, Pointers, OOPS, System Design, Algorithms, Dynamic Programming
Tip
Tip 1: Practised topic-wise questions from basics
Tip 2: Watched so many system design mock interviews
Tip 3: I did mock interviews with friends for DSA and system design rounds.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: Above 7 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1: Include some projects on your resume.
Tip 2: Do not include false information on your resume.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date9 Sep 2022
Coding problem2
1. Convert binary tree to mirror tree
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



Given a binary tree, convert this binary tree into its mirror tree.
A binary tree is a tree in which each parent node has at most two children.
Mirror of a Tree: Mirror of a Binary Tree T is another Binary Tree M(T) with left and right children of all non-leaf nodes interchanged.
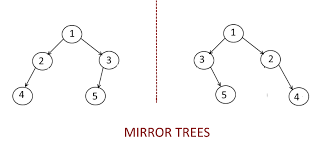
Note:
1. Make in-place changes, that is, modify the nodes given a binary tree to get the required mirror tree.
Problem approach
The idea is to traverse recursively and swap the right and left subtrees after traversing the subtrees.
Follow the steps below to solve the problem:
Call Mirror for left-subtree i.e., Mirror(left-subtree)
Call Mirror for right-subtree i.e., Mirror(right-subtree)
Swap left and right subtrees.
temp = left-subtree
left-subtree = right-subtree
right-subtree = temp
2. Palindrome Partitioning
Moderate
25m average time
75% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given a string 'S'. Your task is to partition 'S' such that every substring of the partition is a palindrome. You need to return all possible palindrome partitioning of 'S'.
Note: A substring is a contiguous segment of a string.
For Example:
For a given string “BaaB”
3 possible palindrome partitioning of the given string are:
{“B”, “a”, “a”, “B”}
{“B”, “aa”, “B”}
{“BaaB”}
Every substring of all the above partitions of “BaaB” is a palindrome.
Problem approach
The problem can be solved by
1) finding the suffix starting from j and ending at index i, (1 <= j <= i <= n – 1), which are palindromes.
2) we can make a cut here that requires 1 + min cut from the rest substring [0, j – 1].
3) For all such palindromic suffixes starting at j and ending at i, keep minimising in minCutDp[i].
4) Similarly, we need to compute results for all such i. (1 <= i <= n – 1) and
5) finally, minCutDp[n – 1] will be the minimum number of cuts needed for palindrome partitioning of the given string.
02
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date10 Sep 2022
Coding problem2
1. Bottom View Of Binary Tree
Moderate
10m average time
90% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given a 'Binary Tree'.
Return the bottom view of the binary tree.
Note :
1. A node will be in the bottom-view if it is the bottom-most node at its horizontal distance from the root.
2. The horizontal distance of the root from itself is 0. The horizontal distance of the right child of the root node is 1 and the horizontal distance of the left child of the root node is -1.
3. The horizontal distance of node 'n' from root = horizontal distance of its parent from root + 1, if node 'n' is the right child of its parent.
4. The horizontal distance of node 'n' from root = horizontal distance of its parent from the root - 1, if node 'n' is the left child of its parent.
5. If more than one node is at the same horizontal distance and is the bottom-most node for that horizontal distance, including the one which is more towards the right.
Example:
Input: Consider the given Binary Tree:
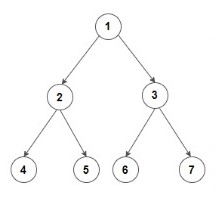
Output: 4 2 6 3 7
Explanation:
Below is the bottom view of the binary tree.
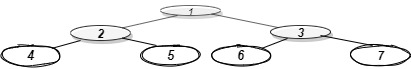
1 is the root node, so its horizontal distance = 0.
Since 2 lies to the left of 0, its horizontal distance = 0-1= -1
3 lies to the right of 0, its horizontal distance = 0+1 = 1
Similarly, horizontal distance of 4 = Horizontal distance of 2 - 1= -1-1=-2
Horizontal distance of 5 = Horizontal distance of 2 + 1= -1+1 = 0
Horizontal distance of 6 = 1-1 =0
Horizontal distance of 7 = 1+1 = 2
The bottom-most node at a horizontal distance of -2 is 4.
The bottom-most node at a horizontal distance of -1 is 2.
The bottom-most node at a horizontal distance of 0 is 5 and 6. However, 6 is more towards the right, so 6 is included.
The bottom-most node at a horizontal distance of 1 is 3.
The bottom-most node at a horizontal distance of 2 is 7.
Hence, the bottom view would be 4 2 6 3 7
Problem approach
Store tree nodes in a queue for the level order traversal. Start with the horizontal distance hd as 0 of the root node, Using a Map that stores key-value pairs sorted by key and keep adding a left child to the queue along with the horizontal distance as hd-1 and the right child as hd+1.
Every time a new horizontal distance or an existing horizontal distance is encountered, the node data for the horizontal distance is used as the key. For the first time, it will add it to the map, next time it will replace the value. This will ensure that the bottom-most element for that horizontal distance is present on the map, and if you see the tree from beneath, you will see that element. At last traverse the keys of the map and print their respective values.
2. Anagram Pairs
Moderate
30m average time
60% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given two strings 'str1' and 'str1'.
You have to tell whether these strings form an anagram pair or not.
The strings form an anagram pair if the letters of one string can be rearranged to form another string.
Pre-requisites:
Anagrams are defined as words or names that can be formed by rearranging the letters of another word. Such as "spar" can be formed by rearranging letters of "rasp". Hence, "spar" and "rasp" are anagrams.
Other examples include:
'triangle' and 'integral'
'listen' and 'silent'
Note:
Since it is a binary problem, there is no partial marking. Marks will only be awarded if you get all the test cases correct.
Problem approach
I used hashing to solve this problem by checking the frequency of characters in both strings.
03
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date11 Sep 2022
Coding problem2
1. Flatten Binary Tree to Linked List
Moderate
25m average time
70% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given a binary tree consisting of 'n' nodes.
Convert the given binary tree into a linked list where the linked list nodes follow the same order as the pre-order traversal of the given binary tree.
Use the right pointer of the binary tree as the “next” pointer for the linked list and set the left pointer to NULL.
Use these nodes only. Do not create extra nodes.
Example :
Input: Let the binary be as shown in the figure:
Output: Linked List: 15 -> 40 -> 62 -> 10 -> 20 -> NULL
Explanation: As shown in the figure, the right child of every node points to the next node, while the left node points to null.
Also, the nodes are in the same order as the pre-order traversal of the binary tree.
Problem approach
You are given a binary tree consisting of integer values. Your task is to convert the given binary tree into a linked list where the nodes of the linked list follow the same order as the pre-order traversal of the given binary tree.
2. Implementation: Hashmap
Easy
30m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



Design a data structure that stores a mapping of a key to a given value and supports the following operations in constant time.
1. INSERT(key, value): Inserts an integer value to the data structure against a string type key if not already present. If already present, it updates the value of the key with the new one. This function will not return anything.
2. DELETE(key): Removes the key from the data structure if present. It doesn't return anything.
3. SEARCH(key): It searches for the key in the data structure. In case it is present, return true. Otherwise, return false.
4. GET(key): It returns the integer value stored against the given key. If the key is not present, return -1.
5. GET_SIZE(): It returns an integer value denoting the size of the data structure.
6. IS_EMPTY(): It returns a boolean value, denoting whether the data structure is empty or not.
Note :
1. Key is always a string value.
2. Value can never be -1.
Operations Performed :
First(Denoted by integer value 1): Insertion to the Data Structure. It is done in a pair of (key, value).
Second(Denoted by integer value 2): Deletion of a key from the Data Structure.
Third(Denoted by integer value 3): Search a given key in the Data Structure.
Fourth(Denoted by integer value 4): Retrieve the value for a given key from the Data Structure.
Fifth(Denoted by integer value 5): Retrieve the size of the Data Structure.
Sixth(Denoted by integer value 6): Retrieve whether the Data Structure is empty or not.
Problem approach
I implemented a hashmap using hashing with chaining technique in C++ and the interviewer further extended the discussion on hashing with chaining.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by OYO
4782 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
2 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
1011 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Meesho
6543 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 9 problems
Interviewed by Salesforce
3566 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
5 rounds | 12 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
114869 views
24 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
58030 views
5 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
35057 views
7 comments
0 upvotes






