Practo interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
Software Developer
Practo
4 rounds | 11 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 4 Months
Topics: Data Structures, Algorithms, DBMS, OS, Aptitude, OOPS
Tip
Tip 1 : Must do Previously asked Interview as well as Online Test Questions.
Tip 2 : Go through all the previous interview experiences from Codestudio and Leetcode.
Tip 3 : Do at-least 2 good projects and you must know every bit of them.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: Above 7 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Have at-least 2 good projects explained in short with all important points covered.
Tip 2 : Every skill must be mentioned.
Tip 3 : Focus on skills, projects and experiences more.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Medium
Online Coding Test
Duration90 minutes
Interview date9 May 2015
Coding problem3
This round had 3 coding questions of Medium to Hard level of difficulty.
1. Balanced parentheses
Moderate
10m average time
90% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Given an integer ‘N’ representing the number of pairs of parentheses, Find all the possible combinations of balanced parentheses with the given number of pairs of parentheses.
Note :
Conditions for valid parentheses:
1. All open brackets must be closed by the closing brackets.
2. Open brackets must be closed in the correct order.
For Example :
()()()() is a valid parentheses.
)()()( is not a valid parentheses.
Problem approach
Approach :
1) First make a recursive function, say ‘solve’ taking the number of opening brackets ‘opening’, number of closing
brackets ‘closing’ output string ‘output’, and an array of strings ‘ans’ as arguments.
2) Make the base condition as if ‘opening’ = 0 and ‘closing’ = 0 then push the output string in the ‘ans’ and return.
3) If ‘opening’ is not equal to zero then call the ‘solve’ function recursively by decrementing ‘opening’ by 1 and
inserting ‘(‘ into the ‘output’.
4) If ‘closing’ > ‘opening’ then call the ‘solve’ function recursively by decrementing ‘closing’ by 1 and inserting ‘)’ into
the ‘output’.
TC : O(2 ^ N), where N is the given integer.
SC : O(N)
2. Trapping Rain Water
Moderate
15m average time
80% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You have been given a long type array/list 'arr’ of size 'n’.
It represents an elevation map wherein 'arr[i]’ denotes the elevation of the 'ith' bar.
Print the total amount of rainwater that can be trapped in these elevations.
Note :
The width of each bar is the same and is equal to 1.
Example:
Input: ‘n’ = 6, ‘arr’ = [3, 0, 0, 2, 0, 4].
Output: 10
Explanation: Refer to the image for better comprehension:

Note :
You don't need to print anything. It has already been taken care of. Just implement the given function.
Problem approach
Approach 1 (Brute Force) :
1) Iterate over every elevation or element and find the maximum elevation on to the left and right of it. Say, the
maximum elevation on to the left of the current elevation or element that we are looking at is ‘maxLeftHeight’ and the
maximum elevation on to the right of it is ‘maxRightHeight’.
2) Take the minimum of ‘maxLeftHeight’ and ‘maxRightHeight’ and subtract it from the current elevation or element.
This will be the units of water that can be stored at this elevation.
3) Compute units of water that every elevation can store and sum them up to return the total units of water that can
be stored.
TC : O(N^2), where ‘N’ is the total number of elevations in the map.
SC : O(1)
Approach 2 (Efficient Approach) :
1) Create two lists or arrays, say, ‘leftMax’ and ‘rightMax’.
2) At every index in the ‘leftMax’ array store the information of the ‘leftMaxHeight’ for every elevation in the map.
3) Similarly, at every index in the ‘rightMax’ array store the information of the ‘rightMaxHeight' for every elevation in
the map.
4) Iterate over the elevation map and find the units of water that can be stored at this location by getting the left max
height and right max height from the initial arrays that we created.
TC : O(N), where ‘N’ is the total number of elevations in the map.
SC : O(N)
3. Rotting Oranges
Moderate
20m average time
78% success
0/80
Asked in companies


You have been given a grid containing some oranges. Each cell of this grid has one of the three integers values:
Every second, any fresh orange that is adjacent(4-directionally) to a rotten orange becomes rotten.
Your task is to find out the minimum time after which no cell has a fresh orange. If it's impossible to rot all the fresh oranges then print -1.
Note:
1. The grid has 0-based indexing.
2. A rotten orange can affect the adjacent oranges 4 directionally i.e. Up, Down, Left, Right.
Problem approach
Approach : I solved this problem using Multisource-BFS as I had solved questions similar to this while preparing for
my interviews.
Steps :
1) Initialize ‘TIME’ to 0.
2) Declare a Queue data structure and a 2D boolean array ‘VISITED’.
3) Push all cells with rotten orange to the queue.
4) Loop till queue is not empty
4.1) Get the size of the current level/queue.
4.2) Loop till the 'LEVEL_SIZE' is zero:
i) Get the front cell of the queue.
ii) Push all adjacent cells with fresh oranges to the queue.
iii) Mark the cells visited which are pushed into the queue.
4.3) Increment ‘TIME’ by 1.
5) Iterate the grid again. If a fresh orange is still present, return -1.
6) Return maximum of ‘TIME’ - 1 and 0.
TC : O(N * M), where N and M are the numbers of rows and columns of the grid respectively.
SC : O(N*M)
02
Round
Medium
Face to Face
Duration60 Minutes
Interview date9 May 2015
Coding problem3
This was a standard DS/Algo round where I was given 2 questions to solve under 60 minutes. I was able to come up with the optimal approach for both the questions and then at the end of the interview I was also asked the famous Die Hard Water Puzzle.
1. Queue Using Stack
Moderate
30m average time
60% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Implement a queue data structure which follows FIFO(First In First Out) property, using only the instances of the stack data structure.
Note:
1. To implement means you need to complete some predefined functions, which are supported by a normal queue such that it can efficiently handle the given input queries which are defined below.
2. The implemented queue must support the following operations of a normal queue:
a. enQueue(data) : This function should take one argument of type integer and place the integer to the back of the queue.
b. deQueue(): This function should remove an integer from the front of the queue and also return that integer. If the queue is empty, it should return -1.
c. peek(): This function returns the element present in the front of the queue. If the queue is empty, it should return -1.
d. isEmpty(): This function should return true if the queue is empty and false otherwise.
3. You will be given q queries of 4 types:
a. 1 val - For this type of query, you need to insert the integer val to the back of the queue.
b. 2 - For this type of query, you need to remove the element from the front of the queue, and also return it.
c. 3 - For this type of query, you need to return the element present at the front of the queue(No need to remove it from the queue).
d. 4 - For this type of query, you need to return true if the queue is empty and false otherwise.
4. For every query of type:
a. 1, you do not need to return anything.
b. 2, return the integer being deQueued from the queue.
c. 3, return the integer present in the front of the queue.
d. 4, return “true” if the queue is empty, “false” otherwise.
Example
Operations:
1 5
1 10
2
3
4
Enqueue operation 1 5: We insert 5 at the back of the queue.
Queue: [5]
Enqueue operation 1 10: We insert 10 at the back of the queue.
Queue: [5, 10]
Dequeue operation 2: We remove the element from the front of the queue, which is 5, and print it.
Output: 5
Queue: [10]
Peek operation 3: We return the element present at the front of the queue, which is 10, without removing it.
Output: 10
Queue: [10]
IsEmpty operation 4: We check if the queue is empty.
Output: False
Queue: [10]
Problem approach
A queue can be implemented using two stacks. Let queue to be implemented be q and stacks used to implement q be stack1 and stack2. q can be implemented in two ways:
Approach 1 (By making enQueue operation costly) : This method makes sure that oldest entered element is always at the top of stack 1, so that deQueue operation just pops from stack1. To put the element at top of stack1, stack2 is used.
enQueue(q, x):
1) While stack1 is not empty, push everything from stack1 to stack2.
2) Push x to stack1 (assuming size of stacks is unlimited).
3) Push everything back to stack1.
deQueue(q):
1) If stack1 is empty then error
2) Pop an item from stack1 and return it
TC :
Push operation: O(N).
In the worst case we have empty whole of stack 1 into stack 2.
Pop operation: O(1).
Same as pop operation in stack.
SC : O(N)
Approach 2 (By making deQueue operation costly) : n this method, in en-queue operation, the new element is entered at the top of stack1. In de-queue operation, if stack2 is empty then all the elements are moved to stack2 and finally top of stack2 is returned.
enQueue(q, x) :
1) Push x to stack1 (assuming size of stacks is unlimited).
deQueue(q) :
1) If both stacks are empty then error.
2) If stack2 is empty
While stack1 is not empty, push everything from stack1 to stack2.
3) Pop the element from stack2 and return it.
TC :
Push operation: O(1).
Same as pop operation in stack.
Pop operation: O(N).
In the worst case we have empty whole of stack 1 into stack 2
SC : O(N)
2. Merge Intervals
Moderate
20m average time
80% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given N number of intervals, where each interval contains two integers denoting the start time and the end time for the interval.
The task is to merge all the overlapping intervals and return the list of merged intervals sorted by increasing order of their start time.
Two intervals [A,B] and [C,D] are said to be overlapping with each other if there is at least one integer that is covered by both of them.
For example:
For the given 5 intervals - [1, 4], [3, 5], [6, 8], [10, 12], [8, 9].
Since intervals [1, 4] and [3, 5] overlap with each other, we will merge them into a single interval as [1, 5].
Similarly, [6, 8] and [8, 9] overlap, merge them into [6,9].
Interval [10, 12] does not overlap with any interval.
Final List after merging overlapping intervals: [1, 5], [6, 9], [10, 12].
Problem approach
Approach :
1) We will first sort the intervals by non-decreasing order of their start time.
2) Then we will add the first interval to our resultant list.
3) Now, for each of the next intervals, we will check whether the current interval is overlapping with the last interval in
our resultant list.
4) If it is overlapping then we will update the finish time of the last interval in the list by the maximum of the finish time
of both overlapping intervals.
5) Otherwise, we will add the current interval to the list.
TC : O(N * log(N)), where N = number of intervals
SC : O(1)
3. Puzzle
Measure 4L using 3L and 5L jars (Die Hard Water Puzzle)
Problem approach
Approach :
1) Fill the 5 liter jug from the tap.
2) Empty the 5 liter jug into the 3 liter jug - leaving 2 liters in the 5 liter jug.
3) Pour away the contents of the 3 liter jug.
4) Fill the 3 liter jug with the 2 liters from the 5 liter jug - leaving 2 liters in the 3 liter jug.
5) Fill the 5 liter jug from the tap.
6) Fill the remaining 1 liter space in the 3 liter jug from the 5 liter jug.
7) Leaving 4 liters in the 5 liter jug.
03
Round
Medium
Face to Face
Duration60 Minutes
Interview date9 May 2015
Coding problem4
This round had 2 coding questions - first one related to Binary Tree and the second one was a simple question from Bit Manipulation. This was followed by some questions from OOPS.
1. Diameter Of Binary Tree
Easy
10m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given a Binary Tree.
Return the length of the diameter of the tree.
Note :
The diameter of a binary tree is the length of the longest path between any two end nodes in a tree.
The number of edges between two nodes represents the length of the path between them.
Example :
Input: Consider the given binary tree:
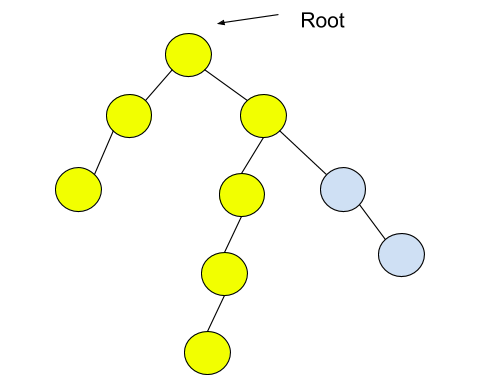
Output: 6
Explanation:
Nodes in the diameter are highlighted. The length of the diameter, i.e., the path length, is 6.
Problem approach
Approach 1 :
Steps :
1) If the ‘root’ node is NULL, return 0. The diameter of an empty tree is 0.
2) Recur for the left subtree and store the diameter of the left subtree in a variable ‘leftDiameter’, i.e.
‘leftDiameter’ = getDiameter(left child of the root node)
3) Similarly, recur for the right subtree and store the diameter of the right subtree in a variable
‘rightDiameter’ i.e. ‘rightDiameter’ = getDiameter(right child of the root node)
4) Now, get the height of the left subtree and right subtree and store it in a variable.
4.1) ‘leftHeight’ = getHeight(left child of the root node)
4.2) ‘rightHeight’ = getHeight(right child of the root node)
5) The diameter of the given tree will be the maximum of the following terms:
i) ‘leftDiameter’
ii) ‘rightDiameter’
iii) 1 + ‘leftHeight’ + ‘rightHeight’
6) Return the maximum of above terms i.e.max(leftDiameter, rightDiameter, 1 + leftHeight + rightHeight).
TC : O(N^2), where ‘N’ is the number of nodes in the given binary tree.
SC : O(N)
Approach 2 :
Steps :
1) If the root node is NULL, assign “height” = 0 and return 0 because the height and diameter of an empty
tree will be 0.
2) Initialize two variables, “leftHeight” and “rightHeight” to 0, which denotes the height of the left subtree
and right subtree, respectively.
3) Recur for the left subtree and store the diameter of the left subtree in a variable i.e. leftDiameter =
getDiameter(root->left, leftHeight)
4) Similarly, recur for the right subtree and store the diameter of the right subtree in a variable i.e.
rightDiamater = getDiamter(root->right, rightHeight)
5) Update the height of the tree i.e. height = max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1
6) The diameter of the given tree will be the maximum of the following terms:
i) “leftDiameter”
ii) “rightDiameter”
iii) “leftHeight” + “rightHeight”
7) Return the maximum of above terms i.e. max(leftDiameter, rightDiameter, leftHeight + rightHeight).
TC : O(N), where 'N' is the number of nodes in the binary tree.
SC : O(N)
2. Power of 2
Moderate
20m average time
70% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given an integer ‘N’. We can reorder the digits in any order (including the original order) such that the leading digit is not zero.
Return true if and only if we can do this so that the resulting number is a power of two. Else, return false.
For Example :
Given :-
‘N’ = 218
Then the answer will be true because it can be rearranged to 128, which is 2 raised to the power of 7.
Problem approach
Approach : If a number N is power of 2 then bitwise & of N and N-1 will be zero. We can say N is a power of 2 or not
based on the value of N&(N-1). The expression N&(N-1) will not work when N is 0.
So,handle that case separately.
TC : O(1)
SC : O(1)
3. OOPS Question
What are some advantages of using OOPs?
Problem approach
1) OOPs is very helpful in solving very complex level of problems.
2) Highly complex programs can be created, handled, and maintained easily using object-oriented programming.
3) OOPs, promote code reuse, thereby reducing redundancy.
4) OOPs also helps to hide the unnecessary details with the help of Data Abstraction.
5) OOPs, are based on a bottom-up approach, unlike the Structural programming paradigm, which uses a top-down
approach.
6) Polymorphism offers a lot of flexibility in OOPs.
4. OOPS Question
What are access specifiers and what is their significance?
Problem approach
Access specifiers, as the name suggests, are a special type of keywords, which are used to control or specify the
accessibility of entities like classes, methods, etc. Some of the access specifiers or access modifiers include “private”,
“public”, etc. These access specifiers also play a very vital role in achieving Encapsulation - one of the major features
of OOPs.
04
Round
Easy
HR Round
Duration30 Minutes
Interview date9 May 2015
Coding problem1
This was my last round and I hoped it to go good just like the other rounds. The interviewer was very straight to point
and professional. The interview lasted for 30 minutes.
1. Basic HR Question
Why should we hire you ?
Problem approach
Tip 1 : The cross questioning can go intense some time, think before you speak.
Tip 2 : Be open minded and answer whatever you are thinking, in these rounds I feel it is important to have opinion.
Tip 3 : Context of questions can be switched, pay attention to the details. It is okay to ask questions in these round,
like what are the projects currently the company is investing, which team you are mentoring. How all is the work
environment etc.
Tip 4 : Since everybody in the interview panel is from tech background, here too you can expect some technical
questions. No coding in most of the cases but some discussions over the design can surely happen.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
Software Developer
4 rounds | 17 problems
Interviewed by Practo
1762 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Practo
2338 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by Practo
1008 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Practo
907 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
Software Developer
5 rounds | 14 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
3986 views
1 comments
0 upvotes
Software Developer
6 rounds | 12 problems
Interviewed by SAP Labs
2872 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Software Developer
3 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
1201 views
0 comments
0 upvotes






