Pristyn Care interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - 2
Pristyn Care
3 rounds | 5 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 2 months
Topics: Data structures, algorithms, Object Oriented programming, Java 8, Spring boot
Tip
Focus on at-least Leetcode easy questions
Standard theory fundamental questions will be there
Application process
Where: Linkedin
Eligibility: B.tech, BCA/MCA
Resume tip
Be precise and avoid irrelevant points.
Put everything you have achieved.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Medium
Online Coding Test
Duration60 minutes
Interview date28 Aug 2022
Coding problem2
1. Target Sum
Moderate
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given an array ‘ARR’ of ‘N’ integers and a target number, ‘TARGET’. Your task is to build an expression out of an array by adding one of the symbols '+' and '-' before each integer in an array, and then by concatenating all the integers, you want to achieve a target. You have to return the number of ways the target can be achieved.
For Example :
You are given the array ‘ARR’ = [1, 1, 1, 1, 1], ‘TARGET’ = 3. The number of ways this target can be achieved is:
1. -1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 = 3
2. +1 - 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 = 3
3. +1 + 1 - 1 + 1 + 1 = 3
4. +1 + 1 + 1 - 1 + 1 = 3
5. +1 + 1 + 1 + 1 - 1 = 3
These are the 5 ways to make. Hence the answer is 5.
Problem approach
int low = 0, high = nums.length-1;
while(low<=high){
int mid = low+(high-low)/2;
System.out.print(mid+" ");
if(nums[mid]==target) return mid;
if(nums[mid] else high = mid-1;
}
2. Reverse Linked List
Moderate
15m average time
85% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Given a singly linked list of integers. Your task is to return the head of the reversed linked list.
For example:
The given linked list is 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4-> NULL. Then the reverse linked list is 4 -> 3 -> 2 -> 1 -> NULL and the head of the reversed linked list will be 4.
Follow Up :
Can you solve this problem in O(N) time and O(1) space complexity?
Problem approach
ListNode prev = null;
ListNode curr = head;
ListNode currNext = head;
while(curr!=null){
currNext = curr.next;
curr.next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = currNext;
}
return prev;
02
Round
Easy
Online Coding Test
Duration60 minutes
Interview date30 Sep 2022
Coding problem2
1. Merge Two Sorted Linked Lists
Moderate
15m average time
80% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given two sorted linked lists. You have to merge them to produce a combined sorted linked list. You need to return the head of the final linked list.
Note:
The given linked lists may or may not be null.
For example:
If the first list is: 1 -> 4 -> 5 -> NULL and the second list is: 2 -> 3 -> 5 -> NULL
The final list would be: 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 -> 5 -> NULL
Problem approach
ListNode res = new ListNode(0);
ListNode newList = res;
while(list1!=null && list2!=null){
if(list1.val newList.next = new ListNode(list1.val);
newList = newList.next;
list1 = list1.next;
}
else{
newList.next = new ListNode(list2.val);
newList = newList.next;
list2 = list2.next;
}
}
if(list1==null) newList.next = list2;
else newList.next = list1;
return res.next;
2. Majority element
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You have been given an array/list 'ARR' consisting of 'N' integers. Your task is to find the majority element in the array. If there is no majority element present, print -1.
Note:
A majority element is an element that occurs more than floor('N' / 2) times in the array.
Problem approach
int maj = nums[0];
int count = 0;
for(int i=0; i if(maj == nums[i]) count++;
else count--;
if(count == 0) {
maj = nums[i];
count = 1;
}
}
return maj;
03
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration20 minutes
Interview date3 Oct 2022
Coding problem1
1. Insert Into A Binary Search Tree
Easy
20m average time
80% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You have been given a root node of the binary search tree and a positive integer value. You need to perform an insertion operation i.e. inserting a new node with the given value in the given binary search tree such that the resultant tree is also a binary search tree.
If there can be more than one possible tree, then you can return any.
Note :
A binary search tree is a binary tree data structure, with the following properties :
a. The left subtree of any node contains nodes with a value less than the node’s value.
b. The right subtree of any node contains nodes with a value equal to or greater than the node’s value.
c. Right, and left subtrees are also binary search trees.
It is guaranteed that,
d. All nodes in the given tree are distinct positive integers.
e. The given BST does not contain any node with a given integer value.
Example, below the tree, is a binary search tree.
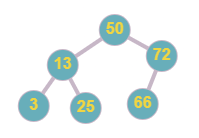
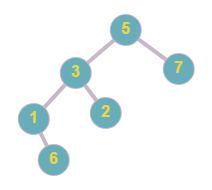
Below the tree is not a BST as node ‘2’ is less than node ‘3’ but ‘2’ is the right child of ‘3’, and node ‘6’ is greater than node ‘5’ but it is in the left subtree of node ‘5’.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
Software Engineer
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Pristyn Care
1073 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 2
3 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Pristyn Care
901 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 1 problems
Interviewed by Pristyn Care
385 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 2 problems
Interviewed by Pristyn Care
358 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - 2
3 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by HashedIn
9654 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 2
3 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Arcesium
1811 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 2
3 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by HashedIn
1921 views
0 comments
0 upvotes







