Quest Global Pvt. Services Ltd interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
Software Engineer
Quest Global Pvt. Services Ltd
3 rounds | 16 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 4 months
Topics: Data Structures, Algorithms, OOPS, Java, DBMS, Software Design Patterns
Tip
Tip 1 : Must do Previously asked Interview as well as Online Test Questions.
Tip 2 : Go through all the previous interview experiences from Codestudio and Leetcode.
Tip 3 : Do at-least 2 good projects and you must know every bit of them.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: Above 7 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Have at-least 2 good projects explained in short with all important points covered.
Tip 2 : Every skill must be mentioned.
Tip 3 : Focus on skills, projects and experiences more.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date17 Dec 2021
Coding problem7
This round had 2 coding problems followed by some questions from DBMS.
1. Detect And Remove Cycle in a Linked List
Moderate
10m average time
90% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Given a singly linked list, you have to detect the loop and remove the loop from the linked list, if present. You have to make changes in the given linked list itself and return the updated linked list.
Expected Complexity: Try doing it in O(n) time complexity and O(1) space complexity. Here, n is the number of nodes in the linked list.
Problem approach
Approach :
Finding the cycle :
1) Initialize slow and fast at the beginning.
2) Start moving slow to every next node and move fast 2 jumps, while making sure that fast and its next is not null.
3) If slow and fast refer to the same node anytime during the process, there is a cycle, otherwise, repeat the process.
4) If fast reaches the end or NULL, then the execution stops and we can conclude that no cycle exists.
Removing the cycle :
1) Find the length of the cycle, let’s say ‘L’.
2) We will take two pointers ‘ptr1’ and ‘ptr2’, initially ‘ptr1’ points to head and ‘ptr2’ points to Lth node from the head.
3) We will move the pointers until they meet at the same node.
4) To remove the cycle we have to find the previous node of the ‘ptr2’ and change its ‘next’ values to NULL.
TC : O(N), where N=number of nodes in the Linked List
SC : O(1)
2. Is Matrix Symmetric
Easy
10m average time
80% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given a square matrix, return true if the matrix is symmetric otherwise return false.
A symmetric matrix is that matrix whose transpose is equal to the matrix itself.
Example of symmetric matrix :
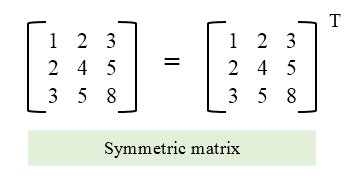
Problem approach
Approach :
1) Traverse the matrix element by element and compare ‘MATRIX' ( i, j) with 'MATRIX" ( j, i).
2) And if anywhere there inequality exists between them simply return false from that point else continue.
3) In the end, if not returned previously from anywhere else just return true, as ‘MATRIX’ is symmetric.
TC : O(N^2), where N=size of the square matrix
SC : O(1)
3. DBMS Question
What is meant by normalization and denormalization?
Problem approach
NORMALIZATION :
1) Normalization is a process of reducing redundancy by organizing the data into multiple tables.
2) Normalization leads to better usage of disk spaces and makes it easier to maintain the integrity of the database.
DENORMALIZATION :
1) Denormalization is the reverse process of normalization as it combines the tables which have been normalized into a single table so that data retrieval becomes faster.
2) JOIN operation allows us to create a denormalized form of the data by reversing the normalization.
4. DBMS Question
What is Cursor? How to use a Cursor?
Problem approach
A database cursor is a control structure that allows for the traversal of records in a database. Cursors, in addition, facilitate processing after traversals, such as retrieval, addition, and deletion of database records. They can be viewed as a pointer to one row in a set of rows.
Working with SQL Cursor :
1) DECLARE a cursor after any variable declaration. The cursor declaration must always be associated with a SELECT Statement.
2) Open the cursor to initialize the result set. The OPEN statement must be called before fetching rows from the result set.
3) FETCH statement to retrieve and move to the next row in the result set.
4) Call the CLOSE statement to deactivate the cursor.
5) Finally use the DEALLOCATE statement to delete the cursor definition and release the associated resources.
5. DBMS Question
What are the three levels of data abstraction?
Problem approach
Following are three levels of data abstraction :
Physical level : It is the lowest level of abstraction. It describes how data are stored.
Logical level : It is the next higher level of abstraction. It describes what data are stored in the database and what the relationship among those data is.
View level : It is the highest level of data abstraction. It describes only part of the entire database.
For example- User interacts with the system using the GUI and fill the required details, but the user doesn't have any idea how the data is being used. So, the abstraction level is entirely high in VIEW LEVEL.
Then, the next level is for PROGRAMMERS as in this level the fields and records are visible and the programmers have the knowledge of this layer. So, the level of abstraction here is a little low in VIEW LEVEL.
And lastly, physical level in which storage blocks are described.
6. DBMS Question
Explain Left Outer Join and Right Outer Join.
Problem approach
LEFT JOIN :
The LEFT JOIN or the LEFT OUTER JOIN returns all the records from the left table and also those records which satisfy a condition from the right table. Also, for the records having no matching values in the right table, the output or the result-set will contain the NULL values.
Syntax:
SELECT Table1.Column1,Table1.Column2,Table2.Column1,....
FROM Table1
LEFT JOIN Table2
ON Table1.MatchingColumnName = Table2.MatchingColumnName;
RIGHT JOIN :
The RIGHT JOIN or the RIGHT OUTER JOIN returns all the records from the right table and also those records which satisfy a condition from the left table. Also, for the records having no matching values in the left table, the output or the result-set will contain the NULL values.
Syntax:
SELECT Table1.Column1,Table1.Column2,Table2.Column1,....
FROM Table1
RIGHT JOIN Table2
ON Table1.MatchingColumnName = Table2.MatchingColumnName;
7. DBMS Question
Difference between Primary key and Unique key
Problem approach
Primary Key : Used to serve as a unique identifier for each row in a table.
Unique Key : Uniquely determines a row which isn’t primary key.
Key Differences Between Primary key and Unique key :
1) Primary key will not accept NULL values whereas Unique key can accept NULL values.
2) A table can have only one primary key whereas there can be multiple unique key on a table.
3) A Clustered index automatically created when a primary key is defined whereas Unique key generates the non-clustered index.
02
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date17 Dec 2021
Coding problem8
This round also had 2 coding problems in which I had to only explain my approach and write the pseudo code for it. This was followed by some more questions from Java and Operating System.
1. Intersection Point in 2 Linked List
Easy
20m average time
70% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given two linked lists L1 and L2 which are sorted in ascending order. You have to make a linked list with the elements which are present in both the linked lists and are present in ascending order.
Example:-
L1 = 1->2->3->4->7
L2 = 2->4->6->7
ANSWER:- The answer should be 2->4->7 because 2,4, and 7 are present in both the linked lists.
Problem approach
Approach (Using 2-pointers) :
1) Initialize two pointers ptr1 and ptr2 at the head1 and head2.
2) Traverse through the lists,one node at a time.
3) When ptr1 reaches the end of a list, then redirect it to the head2.
4) Similarly when ptr2 reaches the end of a list, redirect it the head1.
5) Once both of them go through reassigning, they will be equidistant from the collision point
6) If at any node ptr1 meets ptr2, then it is the intersection node.
7) After second iteration if there is no intersection node it returns NULL.
TC : O(m+n) where m=Length of LL-1 and n=Length of LL-2
SC : O(1)
2. Terms of an AP
Easy
10m average time
80% success
0/40
Asked in companies



Ayush is given a number ‘X’. He has been told that he has to find the first ‘X’ terms of the series 3 * ‘N’ + 2, which are not multiples of 4. Help Ayush to find it as he has not been able to answer.
Example: Given an ‘X’ = 4. The output array/list which must be passed to Ayush will be [ 5, 11, 14, 17 ].
Problem approach
Approach :
1) Declare a temporary array/list variable ‘ANS’ in which we store our answer.
2) Declare a temporary variable ‘GOT’ that will store the total number of elements we obtained until now, which are acceptable.
3) Declare a temporary variable ‘CURRENT’ that will store the current number of series 3 * ‘N’ + 2 and initialize with the first number of series 5.
4) Run a loop while ‘GOT’ is not equal to ‘X’ :
4.1) If ‘CURRENT’ is not divisible by 4, we will append the value at the end of ‘ANS’ and increment the value of ‘GOT’ by 1.
4.2) Increment the value of ‘CURRENT’ by three as the next value of the series.
5) Finally, return ‘ANS’.
TC : O(N), where N=number of elements in the series.
SC : O(N)
3. Java Question
Why Java is platform independent and JVM platform dependent?
Problem approach
JVM is platform dependent because it takes java byte code and generates byte code for the current operating system. So Java software is platform dependent but Java language is platform independent because different operating system have different JVMs.
4. Java Question
Why are Java Strings immutable in nature?
Problem approach
String objects in Java are immutable by definition. This signifies that the String object's state cannot be changed once it has been created. As a result, if you try to update the value of that object rather than the values of that object, Java creates a new string object.
Because String objects are often cached in the String pool, Java String objects are immutable. Because String literals are frequently shared among numerous clients, one client's action may have an impact on the others. It improves the application's security, caching, synchronization, and performance by doing so.
5. Java Question
How would you differentiate between a String, StringBuffer, and a StringBuilder?
Problem approach
1) Storage area : In string, the String pool serves as the storage area. For StringBuilder and StringBuffer, heap memory is the storage area.
2) Mutability : A String is immutable, whereas both the StringBuilder and StringBuffer are mutable.
3) Efficiency : It is quite slow to work with a String. However, StringBuilder is the fastest in performing operations. The speed of a StringBuffer is more than a String and less than a StringBuilder. (For example, appending a character is fastest in StringBuilder and very slow in String because a new memory is required for the new String with appended
character.)
4) Thread-safe : In the case of a threaded environment, StringBuilder and StringBuffer are used whereas a String is not used. However, StringBuilder is suitable for an environment with a single thread, and a StringBuffer is suitable for multiple threads.
6. Operating System Question
Explain multitasking and multiprogramming.
Problem approach
Multitasking :
1) In Multitasking, a single resource is used to process multiple tasks.
2) The process resides in the same CPU.
3) It is time-sharing as the task assigned switches regularly.
4) Multitasking follows the concept of context switching.
Multiprogramming :
1) In multiprogramming, multiple programs execute at the same time on a single device.
2) The process resides in the main memory.
3) It uses batch OS. The CPU is utilized completely while execution.
4) The processing is slower, as a single job resides in the main memory while execution.
7. Operating System Question
Difference between Process and Program
Problem approach
Process : A Process is an execution of a specific program. It is an active entity that actions the purpose of the application. Multiple processes may be related to the same program. For example, if we double-click on Google Chrome browser, we start a process that runs Google Chrome and when we open another instance of Chrome, we essentially create a second process.
Program : A Program is an executable file which contains a certain set of instructions written to complete the specific job or operation on your computer. For example, Google browser chrome.exe is an executable file which stores a set of instructions written in it which allows us to open the browser and explore web pages.
Major Differences b/w Process and Program :
1) Process is an executing part of a program whereas a program is a group of ordered operations to achieve a programming goal.
2) The process has a shorter and minimal lifespan whereas the program has a longer lifespan.
3) Process contains many resources like a memory address, disk, and printer while Program needs memory space on the disk to store all instructions.
4) When we distinguish between process and program, Process is a dynamic or active entity whereas Program is a passive or static entity.
5) To differentiate between program and process, Process has considerable overhead whereas Program has no significant overhead cost.
8. Operating System Question
Explain demand paging
Problem approach
Demand paging is a method that loads pages into memory on demand. This method is mostly used in virtual memory. In this, a page is only brought into memory when a location on that particular page is referenced during execution.
The following steps are generally followed :
1) Attempt to access the page.
2) If the page is valid (in memory) then continue processing instructions as normal.
3) If a page is invalid then a page-fault trap occurs.
4) Check if the memory reference is a valid reference to a location on secondary memory. If not, the process is terminated (illegal memory access). Otherwise, we have to page in the required page.
5) Schedule disk operation to read the desired page into the main memory.
6) Restart the instruction that was interrupted by the operating system trap.
03
Round
Easy
HR Round
Duration30 minutes
Interview date17 Dec 2021
Coding problem1
This is a cultural fitment testing round. HR was very frank and asked standard questions. Then we discussed about my role.
1. Basic HR Question
Why should we hire you?
Problem approach
Tip 1 : The cross questioning can go intense some time, think before you speak.
Tip 2 : Be open minded and answer whatever you are thinking, in these rounds I feel it is important to have opinion.
Tip 3 : Context of questions can be switched, pay attention to the details. It is okay to ask questions in these round, like what are the projects currently the company is investing, which team you are mentoring. How all is the work environment etc.
Tip 4 : Since everybody in the interview panel is from tech background, here too you can expect some technical questions. No coding in most of the cases but some discussions over the design can surely happen.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
Software Engineer
3 rounds | 18 problems
Interviewed by Quest Global Pvt. Services Ltd
1151 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
System Engineer
3 rounds | 18 problems
Interviewed by Quest Global Pvt. Services Ltd
621 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Trainee Engineer
4 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Quest Global Pvt. Services Ltd
1708 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 9 problems
Interviewed by Salesforce
3567 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
Software Engineer
4 rounds | 1 problems
Interviewed by Newgen Software
3238 views
2 comments
0 upvotes
Software Engineer
3 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by HashedIn
2620 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Software Engineer
2 rounds | 2 problems
Interviewed by Ernst & Young (EY)
0 views
0 comments
0 upvotes








