Rakuten India interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - 1
Rakuten India
3 rounds | 6 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Journey
Prepared for around a month. Make sure to go through basics of DSA , Computer Fundamentals. Be thorough with whatever you mention on your resume/CV. Be confident when answering.
Application story
I had put up my profile on sites like Naukri.com. Got a call from 3rd party recruiter regarding the opportunity.
Why selected/rejected for the role?
I was rejected because I could not give precise and optimized solutions to the questions asked .
Preparation
Duration: 2.5 months
Topics: Data Structures, Pointers, OOPS, System Design, Algorithms, Dynamic Programming,System Design, Link List and Graphs
Tip
Tip1: Explore real-world scenarios where data structures are commonly used, such as databases, file systems, and network protocols.
Tip2: Understand how different data structures can be applied to solve specific problems.
Application process
Where: Naukri
Eligibility: Above 6 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1: Quantify your achievements whenever possible. Use numbers, percentages, or other metrics to demonstrate the impact of your work. This adds credibility to your accomplishments and showcases your ability to drive results.
Tip 2: Avoid using generic or overused action verbs. Instead, choose strong and specific verbs that accurately describe your actions and contributions. This will help your resume stand out and create a more memorable impression.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date27 Apr 2023
Coding problem2
The interview was scheduled for 9 am. The duration of the interview is 60 minutes.
1. Overlapping Intervals
Easy
10m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



Given 'N' number of intervals, where each interval contains two integers denoting the boundaries of the interval. The task is to merge all the overlapping intervals and return the list of merged intervals sorted in ascending order.
Two intervals will be considered to be overlapping if the starting integer of one interval is less than or equal to the finishing integer of another interval, and greater than or equal to the starting integer of that interval.
Example:
for the given 5 intervals - [1,4], [3,5], [6,8], [10,12], [8,9].
Since intervals [1,4] and [3,5] overlap with each other, we will merge them into a single interval as [1,5].
Similarly [6,8] and [8,9] overlaps, we merge them into [6,9].
Interval [10,12] does not overlap with any interval.
Final List after merging overlapping intervals: [1,5], [6,9], [10,12]
Problem approach
Check if any two intervals overlap among a given set of intervals. An interval is given in form of start and end time. Given a set of intervals, check if any two intervals overlap or not.
2. Implementation: Hashmap
Easy
30m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



Design a data structure that stores a mapping of a key to a given value and supports the following operations in constant time.
1. INSERT(key, value): Inserts an integer value to the data structure against a string type key if not already present. If already present, it updates the value of the key with the new one. This function will not return anything.
2. DELETE(key): Removes the key from the data structure if present. It doesn't return anything.
3. SEARCH(key): It searches for the key in the data structure. In case it is present, return true. Otherwise, return false.
4. GET(key): It returns the integer value stored against the given key. If the key is not present, return -1.
5. GET_SIZE(): It returns an integer value denoting the size of the data structure.
6. IS_EMPTY(): It returns a boolean value, denoting whether the data structure is empty or not.
Note :
1. Key is always a string value.
2. Value can never be -1.
Operations Performed :
First(Denoted by integer value 1): Insertion to the Data Structure. It is done in a pair of (key, value).
Second(Denoted by integer value 2): Deletion of a key from the Data Structure.
Third(Denoted by integer value 3): Search a given key in the Data Structure.
Fourth(Denoted by integer value 4): Retrieve the value for a given key from the Data Structure.
Fifth(Denoted by integer value 5): Retrieve the size of the Data Structure.
Sixth(Denoted by integer value 6): Retrieve whether the Data Structure is empty or not.
Problem approach
Implement the data structure which takes constant time for insertion, deletion and find operations.
02
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date27 Apr 2023
Coding problem2
1. Find Duplicate in Array
Easy
15m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given an array/list 'ARR' consisting of N integers, which contains elements only in the range 0 to N - 1. Some of the elements may be repeated in 'ARR'. Your task is to find all such duplicate elements.
Note:
1. All the elements are in the range 0 to N - 1.
2. The elements may not be in sorted order.
3. You can return the duplicate elements in any order.
4. If there are no duplicates present then return an empty array.
Problem approach
You have been given an integer array/list (ARR) of size N, which contains numbers from 0 to (N - 2). Each number is present at least once. For example, if N = 5, the array/list contains values ranging from 0 to 3, and among these, there is a single integer value that is present twice. You need to find and return the duplicate number in the array.
2. Preorder traversal of a BST
Moderate
15m average time
85% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You have been given an array/list 'PREORDER' representing the preorder traversal of a BST with 'N' nodes. All the elements in the given array have distinct values.
Your task is to construct a binary search tree that matches the given preorder traversal.
A binary search tree (BST) is a binary tree data structure that has the following properties:
• The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with data less than the node’s data.
• The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with data greater than the node’s data.
• Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
Note:
It is guaranteed that a BST can be always constructed from the given preorder traversal. Hence, the answer will always exist.
Example:
From PREORDER = [20, 10, 5, 15, 13, 35, 30, 42] , the following BST can be constructed:
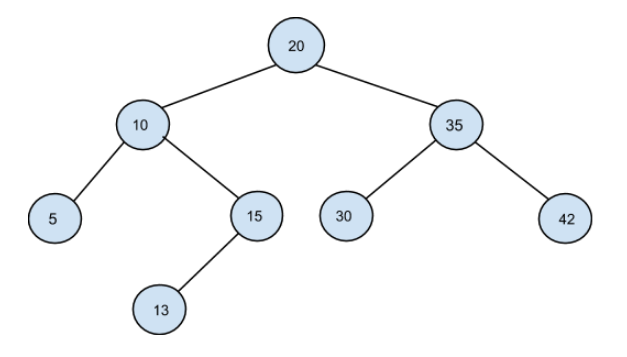
Problem approach
You have been given an array/list 'PREORDER' representing the preorder traversal of a BST with 'N' nodes. All the elements in the given array have distinct values. Your task is to construct a binary search tree that matches the given preorder traversal. A binary search tree (BST) is a binary tree data structure that has the following properties:
• The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with data less than the node’s data.
• The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with data greater than the node’s data.
• Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
03
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration45 minutes
Interview date27 Apr 2023
Coding problem2
1. Check if number is Binary
Easy
10m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



Given a string of integers ‘bin’. Return 'true' if the string represents a valid binary number, else return 'false'. A binary number is a number that has only 0 or 1 in it.
Problem approach
Step 1: First, I converted the number into a string and checked if each character is 0 or 1.
Step 2: The interviewer asked me if there was any other approach to solving this problem.
Step 3: I chose the approach of picking up the digit of the integer from the last and then checking whether it is 0 or 1.
Step 4: If we encounter a digit other than 0 or 1, we break the loop. The interviewer was happy with this approach.
2. Rearrange The Array
Moderate
15m average time
90% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given an array/list 'NUM' of integers. You are supposed to rearrange the elements of the given 'NUM' so that after rearranging the given array/list there are no two adjacent elements present in the rearranged 'NUM' which will be the same.
For example:
Input: NUM[] = {1,1,1,2,2,2}
Output: {1,2,1,2,1,2}
Note: {2,1,2,1,2,1} is also valid because there are no two adjacent which are the same.
Problem approach
Tip 1 : I looked through the array and used a map to count frequency of each digit.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by Rakuten India
2323 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Rakuten India
1659 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Rakuten India
1322 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Rakuten India
941 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by BNY Mellon
6316 views
3 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by BNY Mellon
0 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by CIS - Cyber Infrastructure
2180 views
0 comments
0 upvotes






