Rakuten India interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - 1
Rakuten India
2 rounds | 6 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 6 months
Topics: Java, SQL, Spring Boot, Data Structures, Algorithms, OOPS
Tip
Tip 1 : Must do Previously asked Interview as well as Online Test Questions.
Tip 2 : Go through all the previous interview experiences from Codestudio and Leetcode.
Tip 3 : Do at-least 2 good projects and you must know every bit of them.
Application process
Where: Other
Eligibility: Above 7 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Have at-least 2 good projects explained in short with all important points covered.
Tip 2 : Every skill must be mentioned.
Tip 3 : Focus on skills, projects and experiences more.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date20 Dec 2021
Coding problem2
Technical Interview round with questions on DSA.
1. Merge two sorted arrays
Moderate
15m average time
85% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Ninja has been given two sorted integer arrays/lists ‘ARR1’ and ‘ARR2’ of size ‘M’ and ‘N’. Ninja has to merge these sorted arrays/lists into ‘ARR1’ as one sorted array. You may have to assume that ‘ARR1’ has a size equal to ‘M’ + ‘N’ such that ‘ARR1’ has enough space to add all the elements of ‘ARR2’ in ‘ARR1’.
For example:
‘ARR1’ = [3 6 9 0 0]
‘ARR2’ = [4 10]
After merging the ‘ARR1’ and ‘ARR2’ in ‘ARR1’.
‘ARR1’ = [3 4 6 9 10]
Problem approach
A simple approach would be to create a new arrays with size as sum of the sizes of both the arrays. Copy the elements of both the arrays in the new array and sort the array.
A space optimised approach also exists. While traversing the two sorted arrays parallelly, if we encounter the jth second array element is smaller than ith first array element, then jth element is to be included and replace some kth element in the first array.
Algorithm :
1) Initialize i,j,k as 0,0,n-1 where n is size of arr1
2) Iterate through every element of arr1 and arr2 using two pointers i and j respectively
if arr1[i] is less than arr2[j]
increment i
else
swap the arr2[j] and arr1[k]
increment j and decrement k
3) Sort both arr1 and arr2
2. Reverse a stack
Easy
21m average time
80% success
0/40
Asked in companies



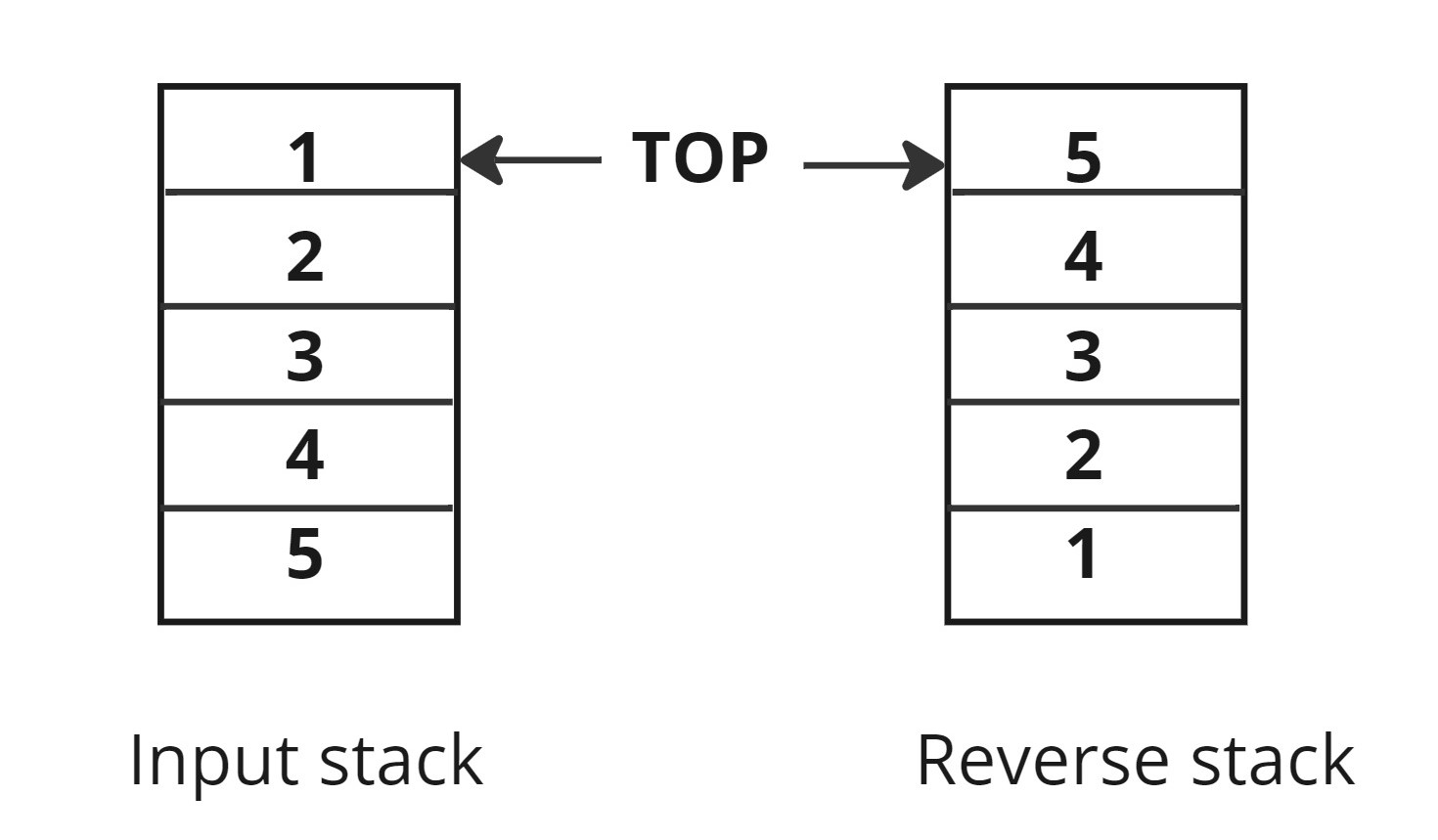
Reverse a given stack of 'N' integers using recursion. You are required to make changes in the input parameter itself.
Note: You are not allowed to use any extra space other than the internal stack space used due to recursion.
Example:
Input: [1,2,3,4,5]
Output: [5,4,3,2,1]
Problem approach
Recursion can be used to reverse a stack. In this approach, we pop the top element from the given stack and recursively call another instance of the same function. When this child function returns to the parent function, append the popped element to the bottom of the stack. For this, two recursive functions can be used: reverseStack() and insertAtBottom().
reverseStack() :
It checks if the stack is empty or not. The top element is popped out and stored in the element variable if the stack is not empty. We then call reverseStack() function again on the updated stack. When this child function returns, we call the helper function insertAtBottom().
insertAtBottom() :
It recursively inserts an element at the bottom of a stack. If the stack is empty, it simply pushes the element else; the top element is popped out and stored in the topElement variable. Then insertAtBottom() is called again on the updated stack. When this child function returns, it pushes the topElement back in the stack.
Time Complexity : O(N²)
Two recursive functions are there in which the first function is calling itself recursively and the second function in each call. Also, the second function is recursively called.
Space Complexity : O(N)
The recursive program uses a memory of O(N) to store the function call stack.
02
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date20 Dec 2021
Coding problem4
Technical Interview round with question on OOPS.
1. Java Question
What is JVM?
Problem approach
It is:
A specification where working of Java Virtual Machine is specified. But implementation provider is independent to choose the algorithm. Its implementation has been provided by Oracle and other companies.
An implementation Its implementation is known as JRE (Java Runtime Environment).
Runtime Instance Whenever you write java command on the command prompt to run the java class, an instance of JVM is created.
2. Java Question
How objects created and managed in jvm memory ?
Problem approach
When you use a new keyword, the JVM creates an instance for the object in a heap. While the reference of that object stores in the stack. There exists only one heap for each running JVM process. When heap becomes full, the garbage is collected.
3. Java Question
What is Polymorphism?
Problem approach
Polymorphism in Java is a concept by which we can perform a single action in different ways. Polymorphism is derived from 2 Greek words: poly and morphs. The word "poly" means many and "morphs" means forms. So polymorphism means many forms.
There are two types of polymorphism in Java: compile-time polymorphism and runtime polymorphism. We can perform polymorphism in java by method overloading and method overriding.
If you overload a static method in Java, it is the example of compile time polymorphism. Here, we will focus on runtime polymorphism in java.
4. Java Question
Explain Method Overriding.
Problem approach
If subclass (child class) has the same method as declared in the parent class, it is known as method overriding in Java. In other words, If a subclass provides the specific implementation of the method that has been declared by one of its parent class, it is known as method overriding.
Rules for Java Method Overriding
The method must have the same name as in the parent class
The method must have the same parameter as in the parent class.
There must be an IS-A relationship (inheritance).

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Rakuten India
1659 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Rakuten India
1322 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Rakuten India
940 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by Rakuten India
980 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by BNY Mellon
6315 views
3 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by BNY Mellon
0 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by CIS - Cyber Infrastructure
2179 views
0 comments
0 upvotes






