Red Hat interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
Software Engineer Intern
Red Hat
3 rounds | 8 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 1 Month
Topics: Linux commands, Windows commands, DSA, Python, Operating System
Tip
Tip 1 : basic knowl;edge of operating system is a must
Tip 2 : Basic Knowledge of Linux is a plus
Tip 3 : good Knowledge of Data structures and problem solving
Application process
Where: Linkedin
Eligibility: No criteria
Resume tip
Tip 1 : development projects
Tip 2 : course and learning certificates to showcase your skills on any of programming language
Interview rounds
01
Round
Medium
Online Coding Test
Duration90 minutes
Interview date23 Sep 2021
Coding problem2
Coding round Includes two coding questions of medium level each in language of your choice , I was able to solve all questions correctly
1. Minimum operation needed to convert to the given string
Moderate
26m average time
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given two strings 'str1' and 'str2'. Find the minimum operations required to convert str1 into str2.
An Operation is defined as:
A character from an index of a string(str1) is put at the end of it, is defined as a single operation.
Note :
You cannot perform any operation on the string, str2.
Problem approach
1) Find if A can be transformed to B or not by first creating a count array for all characters of A, then checking with B if B has same count for every character.
2) Initialize result as 0.
3) Start traversing from end of both strings.
……a) If current characters of A and B match, i.e., A[i] == B[j]
………then do i = i-1 and j = j-1
b) If current characters don’t match, then search B[j] in remaining
………A. While searching, keep incrementing result as these characters
………must be moved ahead for A to B transformation.
2. LCA - Lowest Common Ancestor
Hard
40m average time
70% success
0/120
Asked in companies



The lowest common ancestor (LCA) is a concept in graph theory and computer science.
Let ‘T’ be a rooted tree with ‘N’ nodes. The lowest common ancestor is defined between two nodes, ‘u’ and ‘v’, as the lowest node in ‘T’ that has both ‘u’ and ‘v’ as descendants (where we allow a node to be a descendant of itself). - Wikipedia
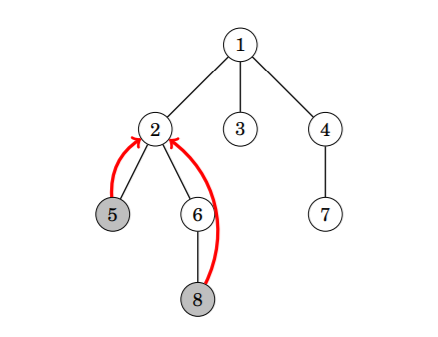
For the given tree, The LCA of nodes 5 and 8 will be node 2, as node 2 is the first node that lies in the path from node 5 to root node 1 and from node 8 to root node 1.
Path from node 5 to root node looks like 5 → 2 → 1.
Path from node 8 to root node looks like 8 → 6 → 2 → 1.
Since 2 is the first node that lies in both paths. Hence LCA will be 2.
Given any two nodes ‘u’ and ‘v’, find the LCA for the two nodes in the given Tree ‘T’.
Note: For each test case, the tree is rooted at node 1.
Problem approach
1>Find a path from the root to n1 and store it in a array.
2>Find a path from the root to n2 and store it in another vector or array.
3>Traverse both paths till the values in arrays are the same. Return the common element just before the mismatch.
02
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date1 Oct 2021
Coding problem3
This was completely technical round
Started with Introduction
Then interviewer asked me to solve puzzle problems
He gave me two puzzles , i was able to solve both
Then he tested my programming skills and my knowledge on Python
1. Puzzle
There are 10 machines in a factory. Each produces coins weighing 10 grams each. One day the factory owner cones to know that one of the machine is not functioning properly and produces coins of weight 9 grams. You have to find out the faulted machine. You ONLY have a weighing machine and you can use it only ONCE.
Problem approach
Tip 1: Think Logically
Tip 2: Discuss it with the interviewer whatever comes in your mind
Tip 3: Treat it like a discussion and not an interview
2. Puzzle
You have 9 balls, equally big, equally heavy - except for one, which is a little heavier.
How would you identify the heavier ball if you could use a pair of balance scales only twice?
Problem approach
Tip 1: Divide the 9 balls into 3 groups of 3
Tip 2: Compare the weight of two of those groups.
3. Stack using queue
Moderate
25m average time
65% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Implement a Stack Data Structure specifically to store integer data using two Queues.
There should be two data members, both being Queues to store the data internally. You may use the inbuilt Queue.
Implement the following public functions :
1. Constructor:
It initializes the data members(queues) as required.
2. push(data) :
This function should take one argument of type integer. It pushes the element into the stack and returns nothing.
3. pop() :
It pops the element from the top of the stack and, in turn, returns the element being popped or deleted. In case the stack is empty, it returns -1.
4. top :
It returns the element being kept at the top of the stack. In case the stack is empty, it returns -1.
5. size() :
It returns the size of the stack at any given instance of time.
6. isEmpty() :
It returns a boolean value indicating whether the stack is empty or not.
Operations Performed on the Stack:
Query-1(Denoted by an integer 1): Pushes an integer data to the stack. (push function)
Query-2(Denoted by an integer 2): Pops the data kept at the top of the stack and returns it to the caller. (pop function)
Query-3(Denoted by an integer 3): Fetches and returns the data being kept at the top of the stack but doesn't remove it, unlike the pop function. (top function)
Query-4(Denoted by an integer 4): Returns the current size of the stack. (size function)
Query-5(Denoted by an integer 5): Returns a boolean value denoting whether the stack is empty or not. (isEmpty function)
Example
Operations:
1 5
1 10
2
3
4
Enqueue operation 1 5: We insert 5 at the back of the queue.
Queue: [5]
Enqueue operation 1 10: We insert 10 at the back of the queue.
Queue: [5, 10]
Dequeue operation 2: We remove the element from the front of the queue, which is 5, and print it.
Output: 5
Queue: [10]
Peek operation 3: We return the element present at the front of the queue, which is 10, without removing it.
Output: 10
Queue: [10]
IsEmpty operation 4: We check if the queue is empty.
Output: False
Queue: [10]
Problem approach
In a push operation, the new element is always enqueued to q1. In pop() operation, if q2 is empty then all the elements except the last, are moved to q2. Finally, the last element is dequeued from q1 and returned.
1> push(s, x) operation:
Enqueue x to q1 (assuming size of q1 is unlimited).
2> pop(s) operation:
One by one dequeue everything except the last element from q1 and enqueue to q2.
Dequeue the last item of q1, the dequeued item is result, store it.
Swap the names of q1 and q2
Return the item stored in step 2
03
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date12 Oct 2021
Coding problem3
This round was similar to 2nd round
Started with introduction
Then the interviewer asked me few linux based questions
Then some questions related to operating system and networking
1. Operating System Based Questions
What is Process Synchronization, Deadlock, Virtual Memory?
2. Operating System Question
What is memory leak?
3. Middle Of Linked List
Easy
20m average time
80% success
0/40
Asked in companies



Given a singly linked list of 'N' nodes. The objective is to determine the middle node of a singly linked list. However, if the list has an even number of nodes, we return the second middle node.
Note:
1. If the list is empty, the function immediately returns None because there is no middle node to find.
2. If the list has only one node, then the only node in the list is trivially the middle node, and the function returns that node.
Problem approach
Traverse the whole linked list and count the no. of nodes. Now traverse the list again till count/2 and return the node at count/2.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
Intern
3 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Red Hat
1022 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Software Engineer
3 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Red Hat
1702 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Red Hat
845 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Red Hat
723 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
Software Engineer Intern
4 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
1362 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Software Engineer Intern
3 rounds | 9 problems
Interviewed by NCR Corporation
1249 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Software Engineer Intern
2 rounds | 2 problems
Interviewed by CIS - Cyber Infrastructure
605 views
1 comments
0 upvotes






