Red Hat interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - 1
Red Hat
4 rounds | 5 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 3 Months
Topics: Data Structure, Algorithms, OOPs, Java, MERN Stack
Tip
Tip 1 : Practice previously asked DSA Questions
Tip 2 : Do personal projects.
Tip 3 : Be consistent and patient.
Application process
Where: Referral
Eligibility: 8 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Have some projects/internships on resume.
Tip 2 : Do not put false things on resume and also use singe page template only.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Medium
Online Coding Test
Duration90 minutes
Interview date4 Dec 2020
Coding problem1
It was in the evening.
It was held online.
DSA based questions were asked.
And was conducted by HackerRank.
1. Snake and Ladder
Moderate
30m average time
60% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You have been given a Snake and Ladder Board with 'N' rows and 'N' columns with the numbers written from 1 to (N*N) starting from the bottom left of the board, and alternating direction each row.
For example
For a (6 x 6) board, the numbers are written as follows:
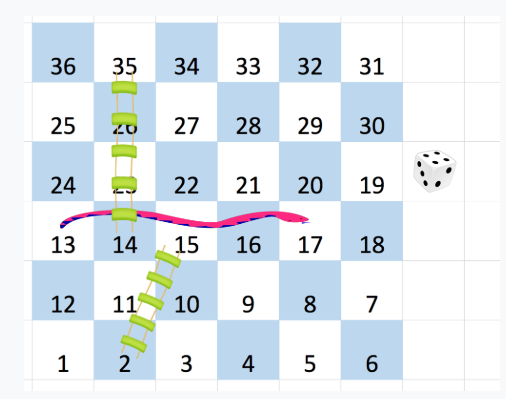
You start from square 1 of the board (which is always in the last row and first column). On each square say 'X', you can throw a dice which can have six outcomes and you have total control over the outcome of dice throw and you want to find out the minimum number of throws required to reach the last cell.
Some of the squares contain Snakes and Ladders, and these are possibilities of a throw at square 'X':
You choose a destination square 'S' with number 'X+1', 'X+2', 'X+3', 'X+4', 'X+5', or 'X+6', provided this number is <= N*N.
If 'S' has a snake or ladder, you move to the destination of that snake or ladder. Otherwise, you move to S.
A board square on row 'i' and column 'j' has a "Snake or Ladder" if board[i][j] != -1. The destination of that snake or ladder is board[i][j].
Note :
You can only take a snake or ladder at most once per move: if the destination to a snake or ladder is the start of another snake or ladder, you do not continue moving - you have to ignore the snake or ladder present on that square.
For example, if the board is:
-1 1 -1
-1 -1 9
-1 4 -1
Let's say on the first move your destination square is 2 [at row 2, column 1], then you finish your first move at 4 [at row 1, column 2] because you do not continue moving to 9 [at row 0, column 0] by taking the ladder from 4.
A square can also have a Snake or Ladder which will end at the same cell.
For example, if the board is:
-1 3 -1
-1 5 -1
-1 -1 9
Here we can see Snake/Ladder on square 5 [at row 1, column 1] will end on the same square 5.
Problem approach
Understand the statement and try to visualize it as a Graph (Directed).
Now, ideally we need to find shortest path in the graph considering each path having equal weightage.
Use BFS for reaching your aim of determining shortest path.
02
Round
Hard
Video Call
Duration90 minutes
Interview date11 Dec 2020
Coding problem1
The second one was held for a 1.5 hour and it was a technical round, based on your resume and JS+React+OS concepts.
There were 4 interviewers and everyone was friendly.
Had a detailed discussion regarding above mentioned concepts.
1. Operating System Questions
Semaphores.
Virtual Memory.
Deadlock and its implementation with real life examples.
Memory and there representation.
React and JavaScript related output questions.
Problem approach
Tip 1 : Read Galvin for OS (best source).
Tip 2 : Do projects for learning JavaScript.
03
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration90 minutes
Interview date18 Dec 2020
Coding problem2
It was 90 minutes long.
One interviewer was taking the interview and other was there as an observer.
They were friendly.
1. Sort An Array of 0s, 1s and 2s
Easy
10m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You have been given an array/list 'arr' consisting of 'n' elements.
Each element in the array is either 0, 1 or 2.
Sort this array/list in increasing order.
Do not make a new array/list. Make changes in the given array/list.
Example :
Input: 'arr' = [2, 2, 2, 2, 0, 0, 1, 0]
Output: Final 'arr' = [0, 0, 0, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2]
Explanation: The array is sorted in increasing order.
Problem approach
Idea behind this is to solve issue in single loop.
Use 3 pointers for interacting with the elements.
Use while loop on those pointers to traverse the array.
Perform asked operations on the array and finally return the array.
2. Balanced parentheses
Moderate
10m average time
90% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Given an integer ‘N’ representing the number of pairs of parentheses, Find all the possible combinations of balanced parentheses with the given number of pairs of parentheses.
Note :
Conditions for valid parentheses:
1. All open brackets must be closed by the closing brackets.
2. Open brackets must be closed in the correct order.
For Example :
()()()() is a valid parentheses.
)()()( is not a valid parentheses.
Problem approach
It is easy problem, you have to traverse the input.
Store the opening braces in a Data Structure (Stack will be best here).
When encountered with closing braces, pop one item from Stack and match.
04
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date25 Dec 2020
Coding problem1
Held online.
Was for an hour of duration.
Interviewer was friendly.
1. Implement your own doubly Linked List with all the required functionality.
Easy
15m average time
95% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given a Doubly linked list, where every node in the linked list contains two pointers ‘next’ and ‘prev’ which point to the next node and previous node in the list respectively. All nodes have some positive integer value associated with them. Your task is to insert an integer value ‘VAL’ in the linked list at a given position ‘K’.
Note:
The position given will always be less than or equal to the length of the linked list.
Assume that the Indexing for the linked list starts from 0.
EXAMPLE:
Input :
‘K’ = 3, ‘VAL’ = 4
list = [1, 2, 3]
Output: [1, 2, 3, 4]

The ‘VAL’ = 4, is inserted at end of the above doubly linked list.
Problem approach
This question is to test person's OOPS concepts.
You need to make classes/objects and implement data members/member functions.
You can use an array to handle this problem.
Store starting and ending index and use them in your member functions.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 2 problems
Interviewed by Red Hat
1436 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by Red Hat
1205 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Red Hat
845 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Red Hat
723 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
5 rounds | 12 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
114869 views
24 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
58031 views
5 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
35057 views
7 comments
0 upvotes






