Reliance Jio interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
Graduate Engineer Trainee
Reliance Jio
4 rounds | 8 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Journey
I got a mail from my college CRC team and I registered for the job and start looking at their process of hiring and also understand the level of interview questions after a few weeks I received the mail for the first round which was a simple interview round where simple basic data structure relate question is asked after few more rounds happened and I prepared my self by practicing related question on the internet and I qualified all the rounds and get the highest package offer as they were offering 3 packages 1st Jio spark 2nd Jio Ignite and 3rd Illuminate. I got offer as illuminate
Application story
I got a mail from my college CRC team and I registered for the job and start looking at their process of hiring and also understand the level of interview questions after a few weeks I received the mail for the first round after all round they will ask for registering their portal for the onboarding process
Why selected/rejected for the role?
Yes I get selected for the Illuminate role which was the highest they were offering and I got confirmation via mail they also needed a medical checkup report before onboarding so completed the process and join the company
Preparation
Duration: 1 Month
Topics: Data Structures, OOPS, a little System Design, Algorithms, also DBMS
Tip
Tip 1 : Do not rush for hard topics be prepared with basic
Tip 2 : They mainly look for your basic knowledge so make strong roots in that.
Tip 3 : Be prepared with famous algorithms and their code also complexity.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: CGPA : 7 , B.tech in any branch
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Clean and short
Tip 2 : Have some projects on your resume.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration30 minutes
Interview date8 May 2022
Coding problem1
1. Technical Questions
It was a simple round just an introduction and asked some data structure-related questions, and DBMS also
it was morning time and I get a slot from 11 am to 11.30
1. What is a list
2 . What is a pointer
3. Does java use a pointer
4. What are SQL and NoSQL
5. What you know about reliance jio
6. What is the OOPS concept
7. DBMS concept ( primary key, 2 vs 3 tier architecture, ACID properties )
8. The logic for basic loops Is there any way to print 1 to 100 without using any loops Also the interviewer started to defend their side and refuse your answer to check whether your confidence will break or not
9. What are joins? Types of joins?
02
Round
Medium
Online Coding Interview
Duration90 Minutes
Interview date12 May 2022
Coding problem2
It was in two parts first is MCQ which contains 22 question mix of Logical Reasoning, Verbal Ability & Programming, and the second part was 2 coding questions. I have cleared this round and get call for interview .
1. Convert binary tree to mirror tree
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



Given a binary tree, convert this binary tree into its mirror tree.
A binary tree is a tree in which each parent node has at most two children.
Mirror of a Tree: Mirror of a Binary Tree T is another Binary Tree M(T) with left and right children of all non-leaf nodes interchanged.
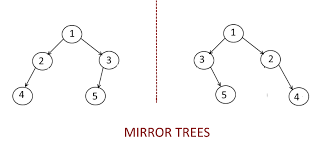
Note:
1. Make in-place changes, that is, modify the nodes given a binary tree to get the required mirror tree.
Problem approach
The idea is to traverse recursively and swap the right and left subtrees after traversing the subtrees.
Follow the steps below to solve the problem:
Call Mirror for left-subtree i.e., Mirror(left-subtree)
Call Mirror for right-subtree i.e., Mirror(right-subtree)
Swap left and right subtrees.
temp = left-subtree
left-subtree = right-subtree
right-subtree = temp
2. Min Cost Path
Moderate
25m average time
65% success
0/80
Asked in companies


You have been given a matrix of ‘N’ rows and ‘M’ columns filled up with integers. Find the minimum sum that can be obtained from a path which starts from the top left corner and ends with the bottom right corner.
From any cell in a row, we can move to the right, down or the down-right diagonal cell. So from a particular cell (row, col), we can move to the following three cells:
Down: (row+1,col)
Right: (row, col+1)
Down right diagonal: (row+1, col+1)
Problem approach
This problem has the optimal substructure property. The path to reach (m, n) must be through one of the 3 cells: (m-1, n-1) or (m-1, n) or (m, n-1). So minimum cost to reach (m, n) can be written as “minimum of the 3 cells plus cost[m][n]”.
minCost(m, n) = min (minCost(m-1, n-1), minCost(m-1, n), minCost(m, n-1)) + cost[m][n]
Follow the below steps to solve the problem:
If N is less than zero or M is less than zero then return Integer Maximum(Base Case)
If M is equal to zero and N is equal to zero then return cost[M][N](Base Case)
Return cost[M][N] + minimum of (minCost(M-1, N-1), minCost(M-1, N), minCost(M, N-1))
03
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration30 Minutes
Interview date16 May 2022
Coding problem2
The panel had Two members. one of them was from technical and another from the HR department.
1. Power of Two
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You have been given an integer 'N'.
Your task is to return true if it is a power of two. Otherwise, return false.
An integer 'N' is a power of two, if it can be expressed as 2 ^ 'K' where 'K' is an integer.
For example:
'N' = 4,
4 can be represented as 2^2. So, 4 is the power of two, and hence true is our answer.
Problem approach
We can a^n (let’s say 3^5) as 3^4 * 3^0 * 3^1 = 3^5, so we can represent 5 as its binary i.e. 101
.calculate last bit(rightmost) bit of n
.if the last bit is 1 then multiply ans and a
.make an equal to the square of an as on every succeeding bit it got squared like a^0, a^1, a^2, a^4, a^8
2. Technical Questions
1. Introduce yourself
2. What is your role in the company
3. Which language do you prefer python java
4 what is memory management in java
5 what is memory management in python
6 How garbage collector works in java
7 what is a cache
9 What are AI and cloud computing do you have any experience
10 print power of a given number without using multiple symbols in java
11 write SQL query to show 2nd topper of the class
12 what is a group by
13 Differences between truncate delete remove
14 Show polymorphism in java by writing code
15 real-life examples of Inheritance
HR Question
16 What you know about jio
17 Are you willing to reallocate
18 why do you want to leave this company
04
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration45 minutes
Interview date20 Jan 2023
Coding problem3
this round was for ignite and Illuminate after this round they declared the final result and I got selected as the illuminate round.
In this round, there were two interviewers 1st from HR and a second from a technical field
1. N Queens
Hard
55m average time
35% success
0/120
Asked in companies



You are given an integer 'N'. For a given 'N' x 'N' chessboard, find a way to place 'N' queens such that no queen can attack any other queen on the chessboard.
A queen can be killed when it lies in the same row, or same column, or the same diagonal of any of the other queens. You have to print all such configurations.
Problem approach
Method 2:
0) Make a board, and make a space to collect all solution states.
1) Start in the topmost row.
2) Make a recursive function that takes the state of the board and the current row number
as its parameter.
3) Fill a queen in a safe place and use this state of the board to advance to the next recursive
call, add 1 to the current row. Revert the state of the board after making the call.
a) Safe function checks the current column, left top diagonal, and right top diagonal.
b) If no queen is present then fill else return false and stop exploring that state
and track back to the next possible solution state
4) Keep calling the function till the current row is out of bound.
5) If the current row reaches the number of rows in the board then the board is filled.
6) Store the state and return.
2. Travelling Salesman Problem
Hard
50m average time
50% success
0/120
Asked in companies



Given a list of cities numbered from 0 to N-1 and a matrix 'DISTANCE' consisting of 'N' rows and 'N' columns denoting the distances between each pair of cities, what is the shortest possible route that visits each city exactly once and returns to the starting city?
Problem approach
Consider city 1 as the starting and ending point. Since the route is cyclic, we can consider any point as a starting point.
Generate all (n-1)! permutations of cities.
Calculate the cost of every permutation and keep track of the minimum cost permutation.
Return the permutation with minimum cost.
3. Technical Questions
The interview started with basic questions
1. Introduction
2 Tell me about your internship
3 What stream API in java
4. Interface in java.
5. Is multiple inheritances possible, why is possible in c++ no in java
6. What is hibernate (Internship related question)
7. What is PostgreSQL
8 . Best sorting algorithm
9 Tell about merge sort
10 why merge sort better than quick sort
11 ask about n queen problem and traveling salesman problem then ask to write code
HR
the same person as 1st interview so does not ask me anything

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
Software Engineer
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Reliance Jio
1768 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 8 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
8770 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
1 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
3407 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Backend Developer
2 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Reliance Jio
921 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
Graduate Engineer Trainee
2 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by HCL Technologies
13592 views
3 comments
0 upvotes
Graduate Engineer Trainee
3 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by HCL Technologies
2823 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Graduate Engineer Trainee
2 rounds | 2 problems
Interviewed by HCL Technologies
3489 views
0 comments
0 upvotes





