Samsung interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
Research Intern
Samsung
3 rounds | 6 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Journey
I started my coding journey on YouTube, where I first learned about data structures and algorithms. Then, I continued my preparation for data structures on LinkedIn.
Application story
The company visited our campus to hire research interns.
Why selected/rejected for the role?
I think I was rejected because I was not able to answer all the questions correctly within the given time during the interview.
Preparation
Duration: 6 months
Topics: Data Structures, Pointers, OOPS, System Design, Algorithms, Dynamic Programming
Tip
Tip 1: Practice at least 250 questions.
Tip 2: Complete at least 2 projects.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: Above 7 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1: Include some projects on your resume.
Tip 2: Do not include false information on your resume.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date21 Apr 2023
Coding problem2
1. Advanced GCD
Easy
0/40
Asked in company

You are given two integers A and B, where A is a small integer and B can have at most 250 digits. Your task is to find GCD(A, B), where GCD is Greatest Common Divisor.
Follow Up :
Can you solve the problem in logarithmic time and constant space complexity?
2. Quadratic Probing in Hashing
Easy
25m average time
65% success
0/40
Asked in companies



‘Hashing’ is a technique in which a large non-negative integer is mapped with a smaller non-negative integer using a function called ‘hash function’ and this smaller integer is used as an index of an array called ‘hash table’.
We define ‘Collision’ as a situation when a large integer is mapped to the index in a hash table that is already mapped with some other integer.
‘Quadratic Probing’ is a collision handling technique in which we take the original hash value and successively add ‘i*i’ in ‘ith’ iteration until an unmapped index is found in the hash table. This technique works as follows:
Let ‘x’ be a larger integer, ‘n’ be the size of the hash table, and ‘h(x) = x mod n’ be a hash function. Then in Quadratic Probing -:
1. If we find that the index h(x), is already mapped to some other integer in the hashtable, then we try for index (h(x) + 1 * 1) mod n.
2. If the index (h(x) + 1*1) mod n, is also already mapped to some other integer in the hashtable, then we try for index (h(x) + 2 * 2) mod n.
3. If the index (h(x) + 2*2) mod n, is also already mapped to some other integer in the hashtable, then we try for index ‘(h(x) + 3 * 3) mod n.
4. We repeat this process until an unmapped index is found in the hashtable or index values start repeating.
In Quadratic probing, sometimes, it is possible that we cannot map an integer with any index in the hashtable.
Given an array ‘keys’ consisting of ‘n’ non-negative integers. Let's consider the hash function h(x) = x mod n. Assume that you are traversing the array ‘keys’ from left to right and you need to insert all these keys in the hash table. For each element of the array ‘keys’, your task is to determine the index by which this element is mapped in the hash table if ‘Quadratic Probing’ technique is used to handle the collision. Return an array ‘hashTable’ of size ‘n’ where the element at index ‘i’ is the element from the given array ‘keys’ that is mapped to that index or -1 if no element is mapped to that index.
For Example -: Consider, array ‘keys’ = {50, 49, 76, 85, 92, 73, 18}, ‘n’ = 7 and the hash function h(x) = x mod 7. Then -:
1. h(50) = 50 mod 7 = 1, thus it will be mapped to index ‘1’ in the hashtable.
2. h(49) = 49 mod 7 = 0, thus it will be mapped to index ‘0’ in hashtable.
3. h(76) = 76 mod 7 = 6, thus it will be mapped to index ‘6’ in the hashtable.
4. h(85) = 85 mod 7 = 1, thus it should be mapped to index ‘1’ in the hashtable, but index ‘1’is already mapped with 50, so we try for index (h(85) + 1*1) mod 7 = ‘2’, as index ‘2’ is not mapped previously, thus it will be mapped to index ‘2’ in hashtable’.
5. h(92) = 92 mod 7 = 1, thus it should be mapped to index ‘1’ in the hashtable, but index ‘1’ is already mapped with 50, so we try for index (h(92) + 1*1) mod 7 = 2, but index ‘2’ is also occupied so we try for index (h(92) + 2*2) mod 7 = ‘5’, as index ‘5’ is not mapped previously, thus it will be mapped to index ‘5’ in hashtable
6. h(73) = 73 mod 7 = 3, thus it will be mapped to index ‘3’ in the hashtable.
7. h(18) = 18 mod 7 = 4, thus it will be mapped to index ‘4’ in the hashtable.
Thus the resultant array ‘hashTable’ should be {49, 50, 85, 73, 18, 92, 76}.

Note:
1. Consider ‘0’ based indexing.
2. Don’t print anything, just return the integer array ‘hashTable’.
02
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date21 Apr 2023
Coding problem2
1. Minimum operation needed to convert to the given string
Moderate
26m average time
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given two strings 'str1' and 'str2'. Find the minimum operations required to convert str1 into str2.
An Operation is defined as:
A character from an index of a string(str1) is put at the end of it, is defined as a single operation.
Note :
You cannot perform any operation on the string, str2.
2. Merge Intervals
Moderate
20m average time
80% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given N number of intervals, where each interval contains two integers denoting the start time and the end time for the interval.
The task is to merge all the overlapping intervals and return the list of merged intervals sorted by increasing order of their start time.
Two intervals [A,B] and [C,D] are said to be overlapping with each other if there is at least one integer that is covered by both of them.
For example:
For the given 5 intervals - [1, 4], [3, 5], [6, 8], [10, 12], [8, 9].
Since intervals [1, 4] and [3, 5] overlap with each other, we will merge them into a single interval as [1, 5].
Similarly, [6, 8] and [8, 9] overlap, merge them into [6,9].
Interval [10, 12] does not overlap with any interval.
Final List after merging overlapping intervals: [1, 5], [6, 9], [10, 12].
Problem approach
I first sorted the intervals in ascending order of 'R', then traversed the intervals from left to right, keeping track of the last interval's endpoint and checking if it intersects with a new interval or not, updating the answer accordingly.
03
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date21 Apr 2023
Coding problem2
1. Diagonal Traversal
Moderate
20m average time
80% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You have been given a binary tree of integers. You have to return all the diagonal paths of the binary tree. A diagonal path is one in which all the nodes pass through -1 slope line.
A binary tree is a tree in which each parent node has at most two children.
Note:
Order of return of diagonal path’s array/vector: The rightmost diagonal path must come first, and so on.
Every parent node comes first then the child node. In other words, return the diagonal element from top to bottom.
Example
Consider the given binary tree.
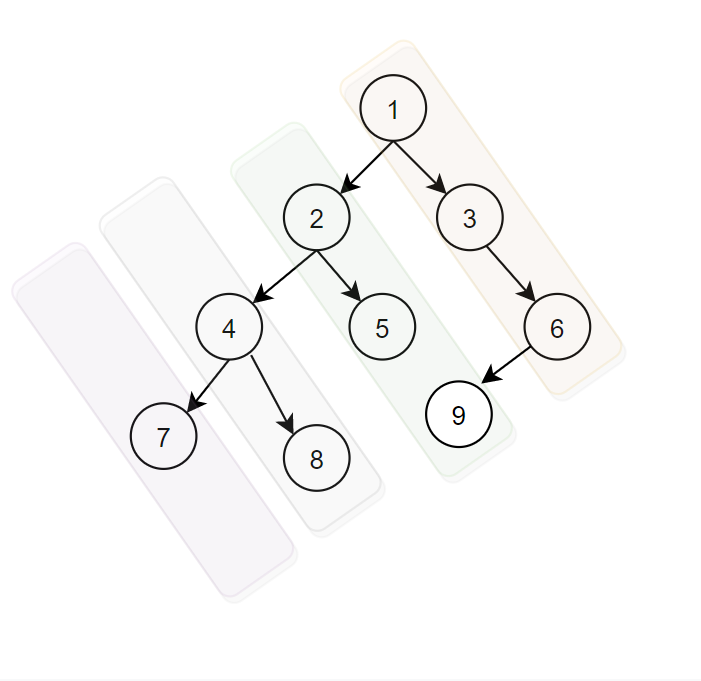
There are 4 diagonal paths:
1 3 6
2 5 9
4 8
7
You need to return ‘1 3 6 2 5 9 4 8 7’.
Let's consider this example
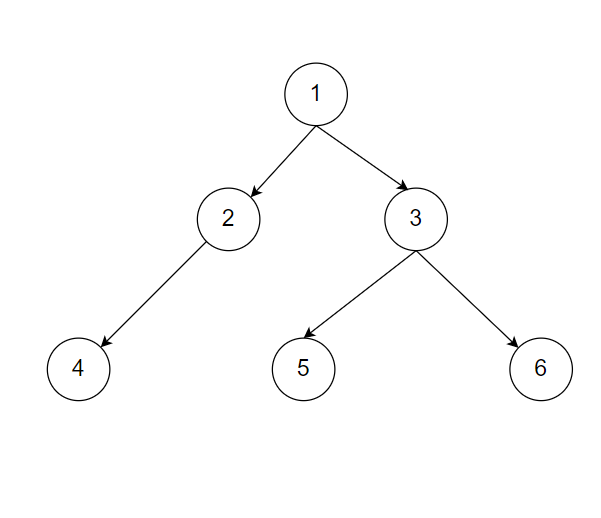
Diagonal paths are:
1 3 6
2 5
4
You need to return ‘1 3 6 2 5 4’.
2. Total Number of BSTs using array elements as root node
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You have been given an array ‘levelOrder’ consisting of ‘N’ elements. The array represents the level order traversal of a Binary Search Tree(BST). You need to construct the BST from this level order traversal.
A Binary Search Tree (BST) is a binary tree data structure that has the following properties -
• The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with data less than the node’s data.
• The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with data greater than the node’s data.
• Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
For Example:
For the given level order traversal: 5 3 6 2 4 7
The BST will be:
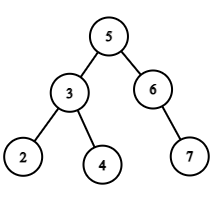
The Inorder Traversal of this BST is 2 3 4 5 6 7.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
Research Intern
1 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Samsung
788 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Software Engineer
2 rounds | 2 problems
Interviewed by Samsung
1590 views
1 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Samsung
1604 views
1 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Samsung
411 views
0 comments
0 upvotes



