SDET Tech interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
Test Analyst
SDET Tech
2 rounds | 8 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Journey
I started doing coding in Java by taking course from coding ninjas in 2nd year. Before this I was exploring different programming like Python, C++, Java. So, I choose java. After completing the course, I started practicing on various coding platforms like code studio. After this, in 3rd year I have made mini project. I have also taken inhouse training on ML.
Application story
I applied through Naukri.com. After applying, my resume got shortlisted, and I had a telephonic interview. After this, I have to give 2 technical rounds. I received an email from SDET Tech one day before the first round.
Why selected/rejected for the role?
I was rejected in the last round as I was not able to give an optimized solution to the coding question they asked. Also, they want a candidate who has done some type of training and made projects in automation testing.
Preparation
Duration: 2 month
Topics: Data Structures, Pointers, OOPS, System Design, Algorithms, Dynamic Programming, Selenium, Beautiful soup, SDE lifecycle
Tip
Tip 1 : Practice at least 250 Questions.
Tip 2 : Do at least two projects.
Tip 3 : Do practice on coding platforms.
Tip 4 : Practice past year's questions.
Application process
Where: Naukri
Eligibility: 7 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1: In the projects section, keep a maximum of 3 projects, but ensure that at least one of them is hosted/live that can be shown to the interviewer.
Tip 2: Do not put false things on resume.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date24 Apr 2023
Coding problem5
In this round interviewer asked me 3 coding question and question based upon OOPS, automation testing, lifecycle and manual testing.
1. Bottom View Of Binary Tree
Moderate
10m average time
90% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given a 'Binary Tree'.
Return the bottom view of the binary tree.
Note :
1. A node will be in the bottom-view if it is the bottom-most node at its horizontal distance from the root.
2. The horizontal distance of the root from itself is 0. The horizontal distance of the right child of the root node is 1 and the horizontal distance of the left child of the root node is -1.
3. The horizontal distance of node 'n' from root = horizontal distance of its parent from root + 1, if node 'n' is the right child of its parent.
4. The horizontal distance of node 'n' from root = horizontal distance of its parent from the root - 1, if node 'n' is the left child of its parent.
5. If more than one node is at the same horizontal distance and is the bottom-most node for that horizontal distance, including the one which is more towards the right.
Example:
Input: Consider the given Binary Tree:
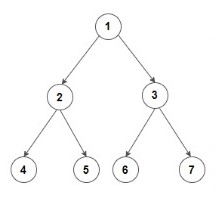
Output: 4 2 6 3 7
Explanation:
Below is the bottom view of the binary tree.
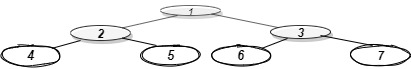
1 is the root node, so its horizontal distance = 0.
Since 2 lies to the left of 0, its horizontal distance = 0-1= -1
3 lies to the right of 0, its horizontal distance = 0+1 = 1
Similarly, horizontal distance of 4 = Horizontal distance of 2 - 1= -1-1=-2
Horizontal distance of 5 = Horizontal distance of 2 + 1= -1+1 = 0
Horizontal distance of 6 = 1-1 =0
Horizontal distance of 7 = 1+1 = 2
The bottom-most node at a horizontal distance of -2 is 4.
The bottom-most node at a horizontal distance of -1 is 2.
The bottom-most node at a horizontal distance of 0 is 5 and 6. However, 6 is more towards the right, so 6 is included.
The bottom-most node at a horizontal distance of 1 is 3.
The bottom-most node at a horizontal distance of 2 is 7.
Hence, the bottom view would be 4 2 6 3 7
Problem approach
Store tree nodes in a queue for the level order traversal. Start with the horizontal distance hd as 0 of the root node, Using a Map which stores key-value pairs sorted by key and keep on adding a left child to the queue along with the horizontal distance as hd-1 and the right child as hd+1.
Every time a new horizontal distance or an existing horizontal distance is encountered, put the node data for that horizontal distance as the key. The first time it will be added to the map; subsequent times it will replace the existing value. This will ensure that the bottom-most element for that horizontal distance is present in the map, and if you view the tree from below, you will see that element. Finally, traverse the keys of the map and print their respective values.
2. Find All Triplets With Zero Sum
Moderate
30m average time
50% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given an array Arr consisting of n integers, you need to find all the distinct triplets present in the array which adds up to zero.
An array is said to have a triplet {arr[i], arr[j], arr[k]} with 0 sum if there exists three indices i, j and k such that i!=j, j!=k and i!=k and arr[i] + arr[j] + arr[k] = 0.
Note :
1. You can return the list of values in any order. For example, if a valid triplet is {1, 2, -3}, then (2, -3, 1), (-3, 2, 1) etc is also valid triplet. Also, the ordering of different triplets can be random i.e if there are more than one valid triplets, you can return them in any order.
2. The elements in the array need not be distinct.
3. If no such triplet is present in the array, then return an empty list, and the output printed for such a test case will be "-1".
Problem approach
Run three loops and check one by one whether the sum of the three elements is zero or not. If the sum of the three elements is zero, then print the elements; otherwise, print ‘not found’.
3. Rotate Linked List
Moderate
25m average time
65% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given a linked list having ‘n’ nodes and an integer ‘k’.
You have to rotate the linked list to the right by ‘k’ positions .
Example :
Input: linked list = [1 2 3 4] , k = 2
Output: 3 4 1 2
Explanation:
We have to rotate the given linked list to the right 2 times. After rotating it to the right once it becomes 4->1->2->3. After rotating it to the right again, it becomes 3->4->1->2.
Problem approach
To rotate the linked list, we need to change the next pointer of the kth node to NULL, the next pointer of the last node should point to the previous head node, and finally, change the head to the (k+1)th node. So we need to get hold of three nodes: the kth node, the (k+1)th node, and the last node. Traverse the list from the beginning and stop at the kth node. Store k’s next in a temp pointer and point k’s next to NULL. Then start traversing from temp, keep traversing till the end, point the end node’s next to the start node, and make temp the new head.
02
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration45 minutes
Interview date26 Apr 2023
Coding problem3
1. Valid Parentheses
Easy
10m average time
80% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You're given a string 'S' consisting of "{", "}", "(", ")", "[" and "]" .
Return true if the given string 'S' is balanced, else return false.
For example:
'S' = "{}()".
There is always an opening brace before a closing brace i.e. '{' before '}', '(' before ').
So the 'S' is Balanced.
Problem approach
The idea is to put all the opening brackets in the stack. Whenever you hit a closing bracket, check if the top of the stack is the opening bracket of the same nature. If this holds, then pop the stack and continue the iteration. In the end, if the stack is empty, it means all brackets are balanced or well-formed. Otherwise, they are not balanced.
2. Spiral Matrix
Easy
15m average time
80% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given a 2-D array 'MATRIX' of dimensions N x M, of integers. You need to return the spiral path of the matrix.
Example Of Spiral Path:
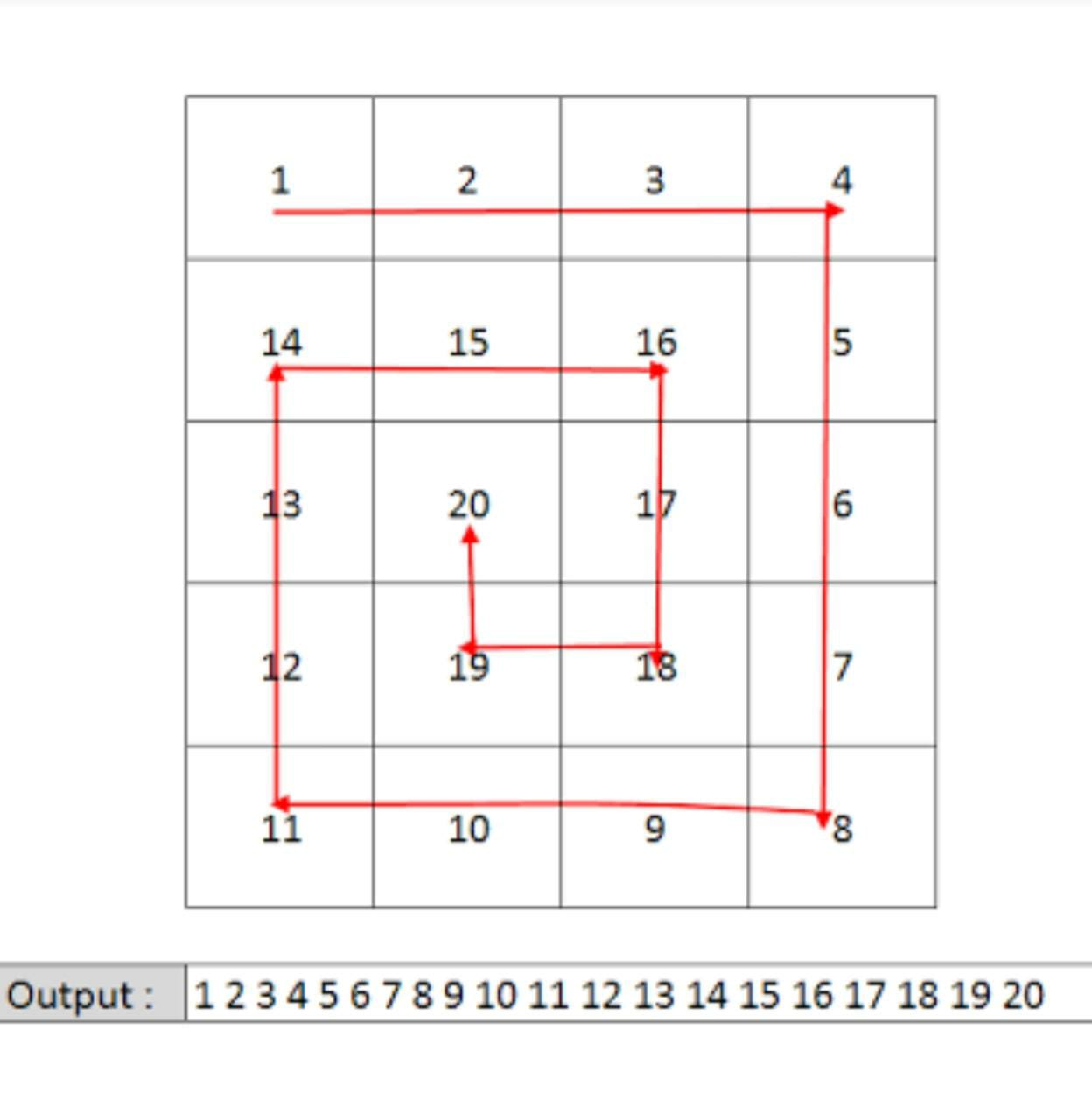
Problem approach
Draw the path that the spiral makes. We know that the path should turn clockwise whenever it would go out of bounds or into a cell that was previously visited.
Follow the given steps to solve the problem:
Let the array have R rows and C columns.
seen[r] denotes that the cell in the r-th row and c-th column was previously visited. Our current position is (r, c), facing direction di, and we want to visit R x C total cells.
As we move through the matrix, our candidate’s next position is (cr, cc).
If the candidate is within the bounds of the matrix and unseen, then it becomes our next position; otherwise, our next position is the one after performing a clockwise turn.
3. Automation Testing
Write a selenium script to search food bloggers on Google automatically?
What is the difference between automation testing and manual testing? (Learn)

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by OYO
4782 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
2 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
1012 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Meesho
6544 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 9 problems
Interviewed by Salesforce
3567 views
0 comments
0 upvotes





