SDG Software India interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - 1
SDG Software India
3 rounds | 5 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Journey
I have completed my Engineering in Computer Science Engineering. I started learning java and data structure from online platforms in the second year. After learning DSA I started working on projects. I was pretty confident on my skills. I used to practice dsa questions daily on GFG, Leetcode. I was pretty much confident with my skills.
Application story
SDG corporation comes on our campus regularly to hire people and thus I also started preparing for the role. After that I when the time came I cleared the first round that was purely coding interview where most of the people were not able to clear it. Second and third round were taken on video call.
Why selected/rejected for the role?
I was selected as I cracked their coding round and was eligible for technical rounds also. I was able to answer all the questions they asked during interview except few tricky questions related to my projects.
Preparation
Duration: 7 months
Topics: Graphs, Trees, Stack, OOPS, DBMS, SQL queries
Tip
Tip 1 : practice regularly in kickstart rounds
Tip 2 : solve previous year problems
Tip 3 : coding ninjas also has google asked problems
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: 7.5 cgpa
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Keep it short and attractive.
Tip 2 : Be confident about everything you write in your resume.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Medium
Online Coding Test
Duration90 minutes
Interview date4 Feb 2019
Coding problem2
Two questions were asked .
1. Favorite Numbers
Moderate
25m average time
75% success
0/80
Asked in company

You are given an array ‘arr’ consisting of integers and an array of favorite numbers ‘favArr’. Your task is to find the number of sub-arrays of 'arr' that includes all the favorite numbers, at least once.
For Example:
You are given, ‘arr’ = [1, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1] and ‘favArr’ = [1, 1, 2], then all the subarrays which contains the same elements as in the ‘favArr’ are [1, 2, 1] , [1, 2, 1, 1], [1, 2, 1, 1, 1], [1, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1], [2, 1, 1], [2, 1, 1, 1], [2, 1, 1, 1, 1]. There are total of 7 sub arrays. Hence the answer is 7.
2. Product of Array except self
Easy
26m average time
0/40
Asked in companies



You have been given an integer array/list (ARR) of size N. You have to return an array/list PRODUCT such that PRODUCT[i] is equal to the product of all the elements of ARR except ARR[i]
Note :
Each product can cross the integer limits, so we should take modulo of the operation.
Take MOD = 10^9 + 7 to always stay in the limits.
Follow up :
Can you try solving the problem in O(1) space?
Problem approach
using Bitwise XOR
02
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date5 Feb 2019
Coding problem2
1. Critical Connection
Hard
60m average time
55% success
0/120
Asked in companies



You are given a network with ‘N’ system nodes [0 to N - 1] and ‘M’ connection. Your task is to find out all critical connections in a given network.
Note: A connection between node ‘u’ and ‘v’ is said to be a critical connection, if after removal of a connection ‘u’ - ‘v’, there is no connection between node ‘u’ and ‘v’ and the network goes down.
For example:
For given N = 4, M = 4,
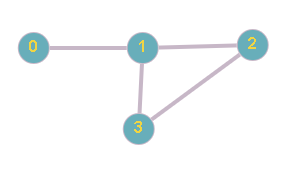
The connection between system node 0 and 1 is a critical connection.
2. DBMS Questions
Different types of keys, normalization, some queries.
03
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration50 minutes
Interview date5 Feb 2019
Coding problem1
One question was asked which was implementation based
1. LRU Cache Implementation
Moderate
25m average time
65% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Design and implement a data structure for Least Recently Used (LRU) cache to support the following operations:
1. get(key) - Return the value of the key if the key exists in the cache, otherwise return -1.
2. put(key, value), Insert the value in the cache if the key is not already present or update the value of the given key if the key is already present. When the cache reaches its capacity, it should invalidate the least recently used item before inserting the new item.
You will be given ‘Q’ queries. Each query will belong to one of these two types:
Type 0: for get(key) operation.
Type 1: for put(key, value) operation.
Note :
1. The cache is initialized with a capacity (the maximum number of unique keys it can hold at a time).
2. Access to an item or key is defined as a get or a put operation on the key. The least recently used key is the one with the oldest access time.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 8 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
8770 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Analytics Consultant
3 rounds | 10 problems
Interviewed by ZS
937 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
1 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
3407 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 2
4 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by Expedia Group
2661 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
5 rounds | 12 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
114869 views
24 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
58031 views
5 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
35057 views
7 comments
0 upvotes






