ShareChat interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - Intern
ShareChat
3 rounds | 3 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 6 Months
Topics: Data Structures and Algorithms, Operating system, Computer networks, System design, OOPS concept
Tip
Tip 1 : OOPS concepts are a must
Tip 2 : Graph and binary search are important concept because generally two medium DSA question will be asked
Tip 3 : Basic understanding of computer fundamentals is required
Application process
Where: Referral
Eligibility: Need Development project on Resume
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Preferred work experience in backend or frontend
Tip 2 : Referral is required
Interview rounds
01
Round
Medium
Online Coding Interview
Duration60 minutes
Interview date3 Jan 2023
Coding problem1
There were three coding questions, All were of medium level, mainly including implementation, binary search, and DSU.
1. Unique Binary Search Trees
Moderate
20m average time
80% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given an integer ‘N’, your task is to return the number of structurally unique BST's (binary search trees) which have exactly 'N' nodes of unique values from 1 to 'N'.
For example:
Given ‘N’ = 2, The total number of BST’s is 2.
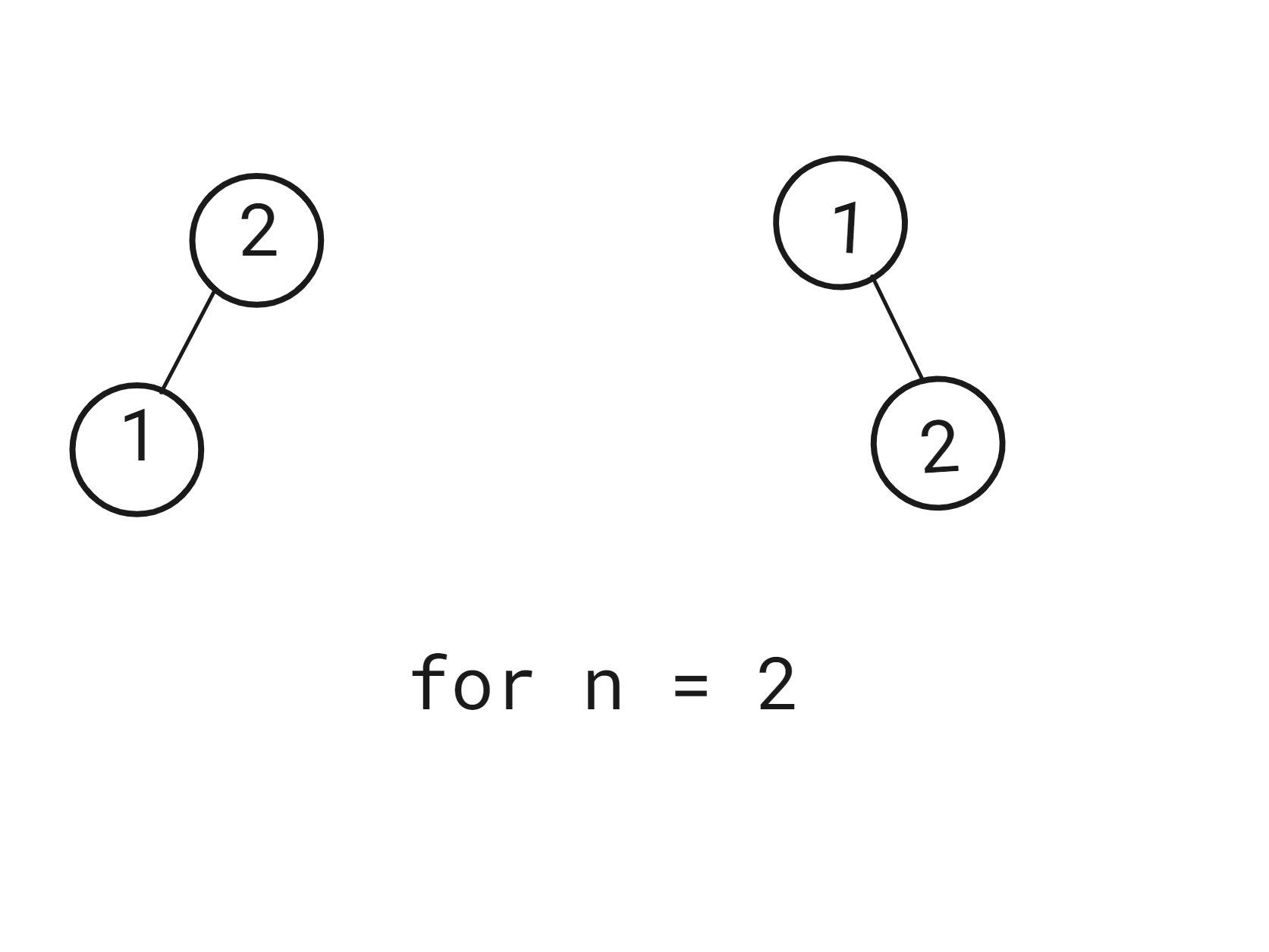
Note:
1. A binary search tree is a rooted binary tree whose internal nodes each store a key greater than all the keys in the node's left subtree and less than those in its right subtree.
2. A structurally unique binary search tree is a tree that has at least 1 node at a different position or with a different value compared to another binary search tree.
02
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date6 Jun 2022
Coding problem1
There was a coding question, one was of binary search, and the other was a dfs implementation on graph
1. Single Number II
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given an arbitrary array ‘arr’ consisting of N non-negative integers, where every element appears thrice except one. You need to find the element that appears only once.
Problem approach
First I explained O(n) solution and then optimized it to Log(n).
03
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date16 Jun 2022
Coding problem1
Single DSA question, Parking lot system design, and computer fundamental questions from the operating systems, Computer networks, and OOPs concepts.
1. Remove Half Nodes
Easy
15m average time
80% success
0/40
Asked in companies


You are given a binary tree consisting of ‘N’ nodes. Your task is to replace all the half nodes present in the binary tree with its child node. Half nodes are those nodes that have only one child.
For Example:
In this given binary tree, nodes 7, 5, and 9 are half nodes because they have only one child node. So we have to replace these nodes with their child. The inorder traversal of the updated binary tree is [1, 6, 11, 2, 4]. Hence, the answer is [1, 6, 11, 2, 4].

Example:
Elements are in the level order form. The input consists of values of nodes separated by a single space in a single line. In case a node is null, we take -1 in its place.
For example, the input for the tree depicted in the below image would be :
 1
2 3
4 -1 5 6
-1 7 -1 -1 -1 -1
-1 -1
1
2 3
4 -1 5 6
-1 7 -1 -1 -1 -1
-1 -1
Explanation :
Level 1 :
The root node of the tree is 1
Level 2 :
Left child of 1 = 2
Right child of 1 = 3
Level 3 :
Left child of 2 = 4
Right child of 2 = null (-1)
Left child of 3 = 5
Right child of 3 = 6
Level 4 :
Left child of 4 = null (-1)
Right child of 4 = 7
Left child of 5 = null (-1)
Right child of 5 = null (-1)
Left child of 6 = null (-1)
Right child of 6 = null (-1)
Level 5 :
Left child of 7 = null (-1)
Right child of 7 = null (-1)
The first not-null node (of the previous level) is treated as the parent of the first two nodes of the current level.
The second not-null node (of the previous level) is treated as the parent node for the next two nodes of the current level and so on.
The input ends when all nodes at the last level are null (-1).
Note :
The above format was just to provide clarity on how the input is formed for a given tree.
The sequence will be put together in a single line separated by a single space. Hence, for the above-depicted tree, the input will be given as:
1 2 3 4 -1 5 6 -1 7 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1
Problem approach
DFS

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - Intern
1 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by ShareChat
1682 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
3 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by ShareChat
1187 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
3 rounds | 8 problems
Interviewed by ShareChat
1029 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
2 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by ShareChat
568 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - Intern
3 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
15557 views
4 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
4 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
15418 views
1 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
10180 views
2 comments
0 upvotes





