Shell india interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
Software Developer
Shell india
3 rounds | 6 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Journey
My journey started when I was in my second year of college, and I saw my friends practicing coding questions, learning new programming languages, and developing individual projects. After seeing them, I decided that I should also start learning more and practicing coding questions. When I started practicing coding questions, I realized that I needed to think more to solve complex problems, and because of that, I developed a habit of solving them.
Application story
I started preparing for companies in the 2nd year of my college, and when I heard that this company was coming to our college, I wanted to get selected.
Why selected/rejected for the role?
I was rejected because I was not able to provide answers with lower time complexity for some coding questions.
Preparation
Duration: 6 months
Topics: Data Structures, Pointers, OOPS, System Design, Algorithms, Dynamic Programming
Tip
Tip 1: OOPS - You should be well-versed in basic OOPS principles.
Tip 2: You should be confident and have profound knowledge about the projects you have worked on.
Tip 3: Basic DB concepts like joins and normalization.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: Above 7 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1: Formatting and Structure:
- Keep the resume clean, organized, and easy to read.
- Use a professional font (e.g., Arial, Calibri) and maintain consistent formatting.
- Include clear section headings (e.g., Summary, Experience, Education, Skills).
- Use bullet points to list information under each section for clarity.
Contact Information:
- Include your full name, phone number, email address, and location (city, state).
- Avoid using overly casual email addresses; opt for a professional one.
Summary/Objective:
- Write a concise summary or objective highlighting your skills, experience, and career goals.
- Tailor this section to match the job you're applying for.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date4 Feb 2023
Coding problem2
There are 2 Coding questions and some basic fundamental questions.
1. 0 1 Knapsack
Moderate
0/80
Asked in companies



A thief is robbing a store and can carry a maximum weight of ‘W’ into his knapsack. There are 'N' items available in the store and the weight and value of each item is known to the thief. Considering the constraints of the maximum weight that a knapsack can carry, you have to find the maximum profit that a thief can generate by stealing items.
Note: The thief is not allowed to break the items.
For example, N = 4, W = 10 and the weights and values of items are weights = [6, 1, 5, 3] and values = [3, 6, 1, 4]. Then the best way to fill the knapsack is to choose items with weight 6, 1 and 3. The total value of knapsack = 3 + 6 + 4 = 13.
Problem approach
The question was a slight variation or modification of the 0-1 Knapsack problem. The main crux of the question was to identify that it was based on the 0-1 Knapsack problem. After identifying the pattern, I solved it using recursion, then memoized my solution, and it passed all the test cases.
2. Anagram Substring Search
Moderate
35m average time
70% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Given two strings ‘STR’ and ‘PTR’. Find all the starting indices of ‘PTR’ anagram substring in ‘STR’. Two strings are anagram if and only if one string can be converted into another string by rearranging the character.
For example, ‘ABCD’ and ‘ACBD’ are two anagram strings because ‘ACBD’ can be converted into ‘ABCD’ by rearranging the ‘B’ and ‘C’. ’ABA’ and ‘ABB’ are not anagram because we can’t convert ‘ABA’ to ‘ABB’ by rearranging the characters of particular strings.
‘ABACD’ and ‘CABAD’ are anagram because ‘ABACD’ can be converted into ‘CABAD’ by rearranging the first ‘A’ with ‘C’ and second ‘A’ with ‘B’.
Note:
Strings ‘STR’ and ‘PTR’ consist only of English uppercases.
Length of string ‘STR’ will always be greater than or equal to the length of string ‘PTR’.
The index is ‘0’ based.
In case, there is no anagram substring then return an empty sequence.
Explanation:
For example, the given ‘STR’ is ‘BACDGABCD’ and ‘PTR’ is ‘ABCD’. Indices are given
0-3 in ‘STR’ index 0,1,2,3 are ‘BACD’ and it is an anagram with ‘ABCD’
1-4 in ‘STR’ index 1,2,3,4 are ‘ACDG’ and it is not anagram with ‘ABCD’
2-5 in ‘STR’ index 2,3,4,5 are ‘CDGA’ and it is not anagram with ‘ABCD’
3-6 in ‘STR’ index 3,4,5,6 are ‘DGAB’ and it is not anagram with ‘ABCD’
4-7 in ‘STR’ index 4,5,6,7 are ‘GABC’ and it is not anagram with ‘ABCD’
5-8 in ‘STR’ index 5,6,7,8 are ‘ABCD’ and it is an anagram with ‘ABCD’
Hence there are 2 starting indices of substrings in the string ‘STR’ that are anagram with given ‘PTR’ which are index 0 and 5.
Problem approach
It was a direct problem on a string matching algorithm. After checking the constraints, it was pretty obvious that I had to use the Rabin-Karp algorithm for the same.
02
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration60 Minutes
Interview date4 Feb 2023
Coding problem2
1. Binary Tree Zigzag Traversal
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You have been given a Binary Tree of 'N' nodes, where the nodes have integer values. Your task is to print the zigzag traversal of the given tree.
Note:
In zigzag order, level 1 is printed from left to right fashion, level 2 is printed from right to left. and level 3 is printed from left to right again, and so on…..
For example:
For the given binary tree
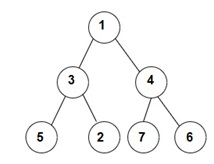
The zigzag traversal is [1, 4, 3, 5, 2, 7, 6]
Problem approach
This is one famous of the question related to Binary Tree.
I solved it with BFS approach using queue Data Structures.
2. Product Of Array Except Self
Easy
26m average time
0/40
Asked in companies



You have been given an integer array/list (ARR) of size N. You have to return an array/list PRODUCT such that PRODUCT[i] is equal to the product of all the elements of ARR except ARR[i]
Note :
Each product can cross the integer limits, so we should take modulo of the operation.
Take MOD = 10^9 + 7 to always stay in the limits.
Follow up :
Can you try solving the problem in O(1) space?
Problem approach
I started with the brute force approach since initially, there were no conditions on using the division operator. However, I was given some test cases where my solution was giving wrong answers. Then, I made some changes, and eventually, I was given the condition that I couldn't use the division operator. After some time, I proposed a solution using two arrays: one prefix array and one suffix array to store the product of array elements from the start to index \(i\) and from the end to index \(i\), respectively. Later on, I was asked to optimize the space, and I did this using one array instead of two.
03
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date5 Feb 2023
Coding problem2
1. Min Stack
Easy
0/40
Asked in companies


Design a stack that supports push, pop, top, and retrieving the minimum element in constant time.
1. Push(num): Push the given number in the stack.
2. Pop: Remove and return the top element from the stack if present, else return -1.
3. Top: return the top element of the stack if present, else return -1.
4. getMin: Returns minimum element of the stack if present, else return -1.
For Example:
For the following input:
1
5
1 1
1 2
4
2
3
For the first two operations, we will just insert 1 and then 2 into the stack which was empty earlier. So now the stack is => [2,1]
In the third operation, we need to return the minimum element of the stack, i.e., 1. So now the stack is => [2,1]
For the fourth operation, we need to pop the topmost element of the stack, i.e., 2. Now the stack is => [1]
In the fifth operation, we return the top element of the stack, i.e. 1 as it has one element. Now the stack is => [1]
So, the final output will be:
1 2 1
Problem approach
I used reference with the variation of next greater element problem.
2. Cycle Detection in a Singly Linked List
Moderate
15m average time
80% success
0/80
Asked in companies



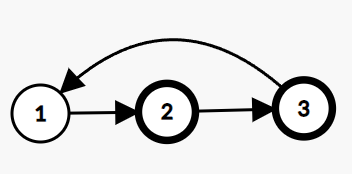
You are given a Singly Linked List of integers. Return true if it has a cycle, else return false.
A cycle occurs when a node's next points back to a previous node in the list.
Example:
In the given linked list, there is a cycle, hence we return true.
Problem approach
I applied the most optimal approach of FAST AND SLOW.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by OYO
4782 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Associate Software Engineer
2 rounds | 2 problems
Interviewed by Shell india
0 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE
3 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by Shell india
1270 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 9 problems
Interviewed by Salesforce
3567 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
Software Developer
5 rounds | 14 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
3986 views
1 comments
0 upvotes
Software Developer
6 rounds | 12 problems
Interviewed by SAP Labs
2872 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Software Developer
3 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
1202 views
0 comments
0 upvotes








