Siemens EDA interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - Intern
Siemens EDA
4 rounds | 13 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Journey
It started in the first year when a senior told me about the importance of DSA. The preparation was a sum of all the hard work that I put in from the first year of college to the final year.
Application story
Around 5000 candidates applied for the opportunity, out of which 535 were shortlisted for the Online Assessment based on CGPA and resume. After clearing the OA, 3 technical interviews were conducted.
Why selected/rejected for the role?
I was selected because I was able to solve all the DSA problems within the time limit and answered all the other questions confidently. I did not fake anything—if I didn’t know something, I honestly admitted it.
Preparation
Duration: 12 months
Topics: Data Structures, Algorithms, Software Engineering, DBMS, Operating System, OOPS, Computer Networks
Tip
Tip 1: Revise core CSE subjects using the top 100 interview questions available on reliable websites.
Tip 2: Know your resume thoroughly, inside and out.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: Above 9 CGPA, (Stipend: 40k per month)
Resume tip
Tip 1: Keep a minimum of 2 projects and a maximum of 3 projects on your resume.
Tip 2: Don’t include anything in your resume that you don’t actually know.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Easy
Online Coding Interview
Duration90 minutes
Interview date14 Sep 2024
Coding problem1
The assessment lasted for 1.5 hours and included 20 MCQs and a coding question. Out of the MCQs, 10 were from the aptitude section and 10 were technical.
1. Counting GCD Pairs in a Range
Easy
0/40
Asked in company
You are given three positive integers: L, R, and G.
Your task is to count the number of ordered pairs (x, y) that satisfy two conditions:
1) Both x and y must be within the inclusive range [L, R].
2) The Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) of x and y must be exactly G.
Problem approach
Transform the range: Convert [L, R] to [ceil(L/G), floor(R/G)] by dividing by G
Count coprime pairs: Find all pairs (a, b) in the new range where GCD(a, b) = 1
Use nested loops: Iterate through all possible pairs in the transformed range
Check GCD condition: For each pair, verify if GCD equals 1.
Return count: Sum up all valid pairs found.
02
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date18 Sep 2024
Coding problem4
It was in the morning on MS Teams. Interviewer was friendly.
3. LRU Cache Implementation
Moderate
25m average time
65% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Design and implement a data structure for Least Recently Used (LRU) cache to support the following operations:
1. get(key) - Return the value of the key if the key exists in the cache, otherwise return -1.
2. put(key, value), Insert the value in the cache if the key is not already present or update the value of the given key if the key is already present. When the cache reaches its capacity, it should invalidate the least recently used item before inserting the new item.
You will be given ‘Q’ queries. Each query will belong to one of these two types:
Type 0: for get(key) operation.
Type 1: for put(key, value) operation.
Note :
1. The cache is initialized with a capacity (the maximum number of unique keys it can hold at a time).
2. Access to an item or key is defined as a get or a put operation on the key. The least recently used key is the one with the oldest access time.
Problem approach
Use HashMap + Doubly Linked List: HashMap for O(1) access, DLL for O(1) insertion/deletion
Create Node structure: Define nodes with key, value, prev, and next pointers
Initialize dummy nodes: Create head and tail dummy nodes to simplify edge cases
Implement addNode(): Add new node right after head
Implement removeNode(): Remove an existing node from the list
Implement moveToHead(): Move existing node to head (mark as recently used)
Implement popTail(): Remove last node before tail (least recently used)
Implement get(): Return value if key exists and move to head, else return -1
Implement put(): Add/update key-value, move to head, evict if capacity exceeded
Maintain capacity: Always check and remove LRU item when size exceeds capacity
4. Data Structures
A number is given which is greater than 10^18 so you can't store this number in any data type. Find the last digit of its square.
Problem approach
Use String.
03
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date18 Sep 2024
Coding problem5
It was in the afternoon on the same day as the first interview. It was on MS Teams as well.
1. Project-Based Questions
- Started with project discussion.
- Why ReactJS?
- Why MongoDB?
- Why JWT?
- Difference between event loop of NodeJS and browser?
- Explain Payment integration on website, etc.
3. Bottom View Of Binary Tree
Moderate
10m average time
90% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given a 'Binary Tree'.
Return the bottom view of the binary tree.
Note :
1. A node will be in the bottom-view if it is the bottom-most node at its horizontal distance from the root.
2. The horizontal distance of the root from itself is 0. The horizontal distance of the right child of the root node is 1 and the horizontal distance of the left child of the root node is -1.
3. The horizontal distance of node 'n' from root = horizontal distance of its parent from root + 1, if node 'n' is the right child of its parent.
4. The horizontal distance of node 'n' from root = horizontal distance of its parent from the root - 1, if node 'n' is the left child of its parent.
5. If more than one node is at the same horizontal distance and is the bottom-most node for that horizontal distance, including the one which is more towards the right.
Example:
Input: Consider the given Binary Tree:
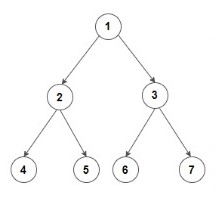
Output: 4 2 6 3 7
Explanation:
Below is the bottom view of the binary tree.
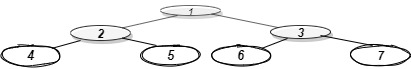
1 is the root node, so its horizontal distance = 0.
Since 2 lies to the left of 0, its horizontal distance = 0-1= -1
3 lies to the right of 0, its horizontal distance = 0+1 = 1
Similarly, horizontal distance of 4 = Horizontal distance of 2 - 1= -1-1=-2
Horizontal distance of 5 = Horizontal distance of 2 + 1= -1+1 = 0
Horizontal distance of 6 = 1-1 =0
Horizontal distance of 7 = 1+1 = 2
The bottom-most node at a horizontal distance of -2 is 4.
The bottom-most node at a horizontal distance of -1 is 2.
The bottom-most node at a horizontal distance of 0 is 5 and 6. However, 6 is more towards the right, so 6 is included.
The bottom-most node at a horizontal distance of 1 is 3.
The bottom-most node at a horizontal distance of 2 is 7.
Hence, the bottom view would be 4 2 6 3 7
Problem approach
Use level order traversal: Traverse tree level by level using queue
Track horizontal distance: Assign horizontal distance to each node (root = 0, left = -1, right = +1)
Use map for bottom nodes: Store horizontal distance as key and node value as value
Update map during traversal: For each horizontal distance, keep updating with latest node value
Process queue with distance: Store pairs of (node, horizontal_distance) in queue
Extract final result: Traverse map from leftmost to rightmost horizontal distance
Return sorted bottom view: Convert map values to array in left-to-right order
4. Diameter Of Binary Tree
Easy
10m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given a Binary Tree.
Return the length of the diameter of the tree.
Note :
The diameter of a binary tree is the length of the longest path between any two end nodes in a tree.
The number of edges between two nodes represents the length of the path between them.
Example :
Input: Consider the given binary tree:
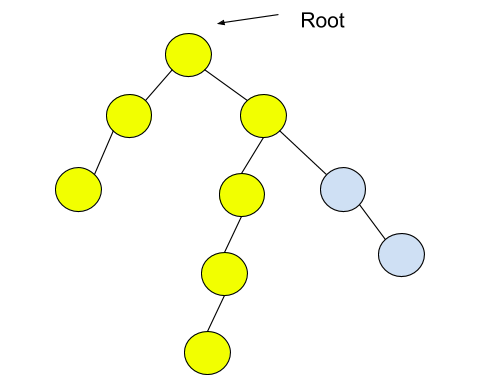
Output: 6
Explanation:
Nodes in the diameter are highlighted. The length of the diameter, i.e., the path length, is 6.
Problem approach
Use recursive approach: Calculate diameter using DFS traversal
Track maximum diameter: Maintain global variable to store maximum diameter found
Calculate height for each node: Return height of subtree rooted at current node
Compute diameter at each node: Diameter = left_height + right_height
Update global maximum: Compare current diameter with global maximum
Return height to parent: Return max(left_height, right_height) + 1
Handle base case: Return 0 for null nodes
04
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date18 Sep 2024
Coding problem3
Took place on the same date as the first two interview rounds. This one was the last round. It happened in the evening.
1. Core Fundamentals
- What are cookies? (Learn)
- Diamond problem in Java. (Learn)
- Use of interfaces. (Learn)
- Explain use of Static keyword. (Learn)
- Difference between auto and register.
- Heap and stack memory. (Learn)
- Malloc vs calloc vs new. (Learn)
- Use cases of merge and quick sort. (Learn)
- Create a n-ary tree node and write create, delete functions. (Learn)
- Write a code for run time polymorphism. (Learn)
2. Longest Common Subsequence
Moderate
39m average time
0/80
Asked in companies



Given two strings, 'S' and 'T' with lengths 'M' and 'N', find the length of the 'Longest Common Subsequence'.
For a string 'str'(per se) of length K, the subsequences are the strings containing characters in the same relative order as they are present in 'str,' but not necessarily contiguous. Subsequences contain all the strings of length varying from 0 to K.
Example :
Subsequences of string "abc" are: ""(empty string), a, b, c, ab, bc, ac, abc.
Problem approach
use a 2D memoization table of size (m+1)×(n+1)(m+1) \times (n+1)(m+1)×(n+1), initialized to −1-1−1 to track computed values. Before making recursive calls, we check this table to avoid redundant computations of overlapping subproblems. This prevents repeated calculations, improving efficiency through memoization or tabulation
3. Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters
Moderate
30m average time
65% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Given a string input of length n, find the length of the longest substring without repeating characters i.e return a substring that does not have any repeating characters.
Substring is the continuous sub-part of the string formed by removing zero or more characters from both ends.
Problem approach
The approach stores the last indexes of already visited characters. The idea is to maintain a window of distinct characters. Start from the first character, and keep extending the window on the right side till we see distinct characters. When we see a repeating character, we check for the last index of the repeated character:
If last index of repeated character >= starting index of the current window, then we update the starting index of the current window to last index of repeated character + 1 to remove the repeated character.
If last index of repeated character < starting index of the current window, then it means that the repeated character is already outside the current window so the window size remains unchanged.
After iterating over all the characters, the largest window size will be our answer.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by OYO
4782 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
2 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
1012 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Meesho
6543 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 9 problems
Interviewed by Salesforce
3567 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - Intern
3 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
15556 views
4 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
4 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
15417 views
1 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
10180 views
2 comments
0 upvotes





