Siemens interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - 1
Siemens
4 rounds | 11 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 4 Months
Topics: Data Structures, Algorithms, System Design, Aptitude, OOPS
Tip
Tip 1 : Must do Previously asked Interview as well as Online Test Questions.
Tip 2 : Go through all the previous interview experiences from Codestudio and Leetcode.
Tip 3 : Do at-least 2 good projects and you must know every bit of them.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: Above 7 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Have at-least 2 good projects explained in short with all important points covered.
Tip 2 : Every skill must be mentioned.
Tip 3 : Focus on skills, projects and experiences more.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Medium
Online Coding Interview
Duration120 Minutes
Interview date20 Aug 2020
Coding problem2
This was an online MCQ + coding round where we had 1 hour to solve the MCQ's and another 1 hour to solve 2 coding
questions. The MCQ's were related to both General and Technical Aptitude.
1. Path Sum
Easy
15m average time
80% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given the root node of a binary tree consisting of ‘N’ nodes and an integer value ‘TARGET’. Your task is to find the number of leaf nodes in the given binary tree such that the sum of all nodes from the root to leaf is equal to ‘TARGET’.
A leaf node is defined as a node having no child nodes.
You are given a root node ‘ROOT’.Your task is to return the number of leaf nodes satisfying the given condition.
Example:
Elements are in the level order form. The input consists of values of nodes separated by a single space in a single line. In case a node is null, we take -1 in its place.
For example, the input for the tree depicted in the below image would be :
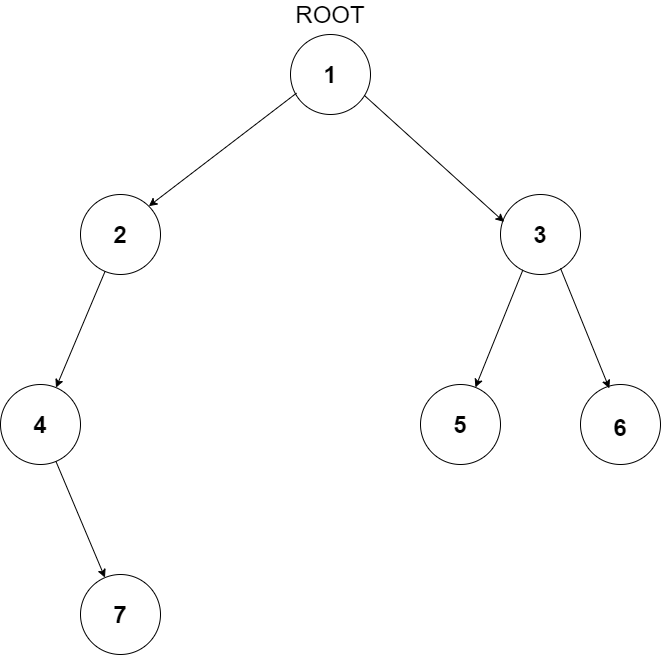
1
2 3
4 -1 5 6
-1 7 -1 -1 -1 -1
-1 -1
Explanation :
Level 1 :
The root node of the tree is 1
Level 2 :
Left child of 1 = 2
Right child of 1 = 3
Level 3 :
Left child of 2 = 4
Right child of 2 = null (-1)
Left child of 3 = 5
Right child of 3 = 6
Level 4 :
Left child of 4 = null (-1)
Right child of 4 = 7
Left child of 5 = null (-1)
Right child of 5 = null (-1)
Left child of 6 = null (-1)
Right child of 6 = null (-1)
Level 5 :
Left child of 7 = null (-1)
Right child of 7 = null (-1)
The first not-null node (of the previous level) is treated as the parent of the first two nodes of the current level.
The second not-null node (of the previous level) is treated as the parent node for the next two nodes of the current level and so on.
The input ends when all nodes at the last level are null (-1).
Note :
The above format was just to provide clarity on how the input is formed for a given tree.
The sequence will be put together in a single line separated by a single space. Hence, for the above-depicted tree, the input will be given as:
1 2 3 4 -1 5 6 -1 7 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1
Problem approach
Approach : I approached this problem using DFS .
1) Create a boolean recursive function with parameters as root and target .
2) If we reached at the leaf node (root and !root->left and !root->right) and target-root->value==0 , return true as we
found out a path that sums up to target.
3) If root is not null , call 1) dfs with root->left and target-root->val and 2) dfs with root->right and target-root->value .
Return the OR of both these values.
TC : O(N) where N=number of nodes in the binary tree.
SC : O(N)
2. Check If Given Numbers Are Coprime
Easy
28m average time
0/40
Asked in companies


You have been given two numbers 'a' and 'b'. Write a function that checks if the given numbers are co-prime.
Problem approach
Approach :
1) Run a loop from i = 2 to i = min(m, n).
2) Find the remainder for (m / i) and (n / i).
3) If both the remainders are zero, then m and n are not co-prime.
4) If you run through the entire loop without finding an 'i' that divides both m and n, then they are co-prime.
TC : O(min(m, n)), where m and n are the two input integers.
SC : O(1)
02
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration50 Minutes
Interview date20 Aug 2020
Coding problem2
This was a standard DSA round where I was given 2 coding questions - the first one was related to DP and the second one was of Linked List. I first explained my approach and then coded the solutions in a production ready manner by applying proper coding principles.
1. Maximum length pair chain
Moderate
15m average time
85% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given ‘N’ pairs of integers in which the first number is always smaller than the second number i.e in pair (a,b) -> a < b always. Now we define a pair chain as the continuous arrangement of pairs in which a pair (c,d) can follow another pair (a,b) only when b < c.
Find the length of the longest pair chain that can be formed using the given pairs.
Example:
Given Pairs = [3,4], [1,2], [2,3].
The length of the maximum chain will be 2. The longest chain is [1,2] -> [3,4].
Note:
1. You can select a pair only once.
2. You needn’t use up all the given pairs.
3. You can select pairs in any order.
Problem approach
Approach (Using DP) : This problem is a variation of LIS (longest increasing subsequence).
1) We will sort the array according to the first element to define an order of picking pairs in the chain.
2) Now the elements are sorted according to the first elements we need to find the longest increasing subsequence according to their second elements.
3) We will use a ‘DP’ table of size ‘N’ to calculate the results for each index. Definition: ‘DP’[i] will store the max length pair chain ending at index ‘i’.
4) Base case: Each pair can make a valid chain of length 1 so we initialize each entry in the ‘DP’ table with value 1.
5) Transitions: If the current pair is the ending element of the chain then the maximum length of pair chain ending at this pair will be 1 + maximum ‘DP[j]’ where 0<= ‘j’ < ‘i’ and the first element of the current pair is greater than the second element of the pair having index ‘j’.
6) The final answer will be the maximum length among all the lengths we found so far in our ‘DP’ table.
TC : O(N ^ 2), where N = number of pairs
SC : O(N)
2. Palindrome Linked List
Easy
20m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given a singly Linked List of integers. Your task is to return true if the given singly linked list is a palindrome otherwise returns false.
For example:
The given linked list is 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 2-> 1-> NULL.
It is a palindrome linked list because the given linked list has the same order of elements when traversed forwards and backward.
Follow Up:
Can you solve the problem in O(N) time complexity and O(1) space complexity iteratively?
Problem approach
Approach (Using Recursion) :
1) Recursively traverse the entire linked list to get the last node as a rightmost node.
2) When we return from the last recursion stack. We will be at the last node of the Linked List. Then the last node value is compared with the first node value of Linked List.
3) In order to access the first node of Linked List, we create a global left pointer that points to the head of Linked List initially that will be available for every call of recursion and the right pointer which passes in the function parameter of recursion.
4) Now, if the left and right pointer node value is matched then return true from the current recursion call. Then the recursion falls back to (n-2)th node, and then we need a reference to the 2nd node from head. So we advance the left pointer in the previous call to refer to the next node in the Linked List.
5) If all the recursive calls are returning true, it means the given Linked List is a palindrome else it is not a palindrome.
TC : O(N), where N = number of nodes in the linked list
SC : O(N)
03
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration60 Minutes
Interview date20 Aug 2020
Coding problem5
This round started with 2 preety decent coding questions - one from DP and the other one was from Binary Search. This was followed by some questions from OOPS and then the interview ended with the interviewer asking me the famous 3-Ants and the Triangle Puzzle.
1. Subset Sum Equal To K
Moderate
30m average time
65% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given an array/list ‘ARR’ of ‘N’ positive integers and an integer ‘K’. Your task is to check if there exists a subset in ‘ARR’ with a sum equal to ‘K’.
Note: Return true if there exists a subset with sum equal to ‘K’. Otherwise, return false.
For Example :
If ‘ARR’ is {1,2,3,4} and ‘K’ = 4, then there exists 2 subsets with sum = 4. These are {1,3} and {4}. Hence, return true.
Problem approach
Approach (Using DP) :
1) Create a boolean 2D array/list ‘DP’ of size (‘N+1’)*(‘K+1’) i.e. ‘DP[N+1][K+1]’.
2) If ‘K’ is equal to 0, then the answer should be ‘true’. Hence, run a loop from 0 to ‘N’ (say iterator = ‘i’):
‘DP[i][0]’ = true.
3) If ‘K’ is not zero but ‘ARR’ is empty then the answer should be ‘false’. Hence, run a loop from 1 to ‘K’ (say iterator =
‘i’):
‘DP[0][i]’ = false.
4) To fill the ‘DP’ table, run a loop from 1 to ‘N’ (say iterator = ‘i’):
4.1) Run a loop from 1 to ‘K’ (say iterator = ‘j’):
‘DP[i][j]’ = ‘DP[i-1][j]’.
4.2) If ‘j’ is greater than equal to ‘ARR[i-1]’:
‘DP[i][j]’ = ‘DP[i][j]’ OR ‘DP[i-1][j - ARR[i-1]]’.
5) Finally, return ‘DP[N][K]’.
TC : O(N*K), where N = size of the array and K = required sum
SC : O(N*K)
2. Search In Rotated Sorted Array
Easy
12m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You have been given a sorted array/list 'arr' consisting of ‘n’ elements. You are also given an integer ‘k’.
Now the array is rotated at some pivot point unknown to you.
For example, if 'arr' = [ 1, 3, 5, 7, 8], then after rotating 'arr' at index 3, the array will be 'arr' = [7, 8, 1, 3, 5].
Now, your task is to find the index at which ‘k’ is present in 'arr'.
Note :
1. If ‘k’ is not present in 'arr', then print -1.
2. There are no duplicate elements present in 'arr'.
3. 'arr' can be rotated only in the right direction.
Example:
Input: 'arr' = [12, 15, 18, 2, 4] , 'k' = 2
Output: 3
Explanation:
If 'arr' = [12, 15, 18, 2, 4] and 'k' = 2, then the position at which 'k' is present in the array is 3 (0-indexed).
Problem approach
Approach (Using Binary Search) :
1) Find the mid index.
2) If the value(key) being searched for is at the mid index, then return the mid index.
3) Compare values at start index, end index, and mid-index:
3.1) If the left subarray is sorted, check if the value(key) to be searched lies in the range:
a) If it does, then search space reduces between [start, (mid-1)].
b) Otherwise, the search space reduces between [(mid + 1), end]
3.2) If the right subarray is sorted, check if the value(key) to be searched lies in the range:
a) If it does, then search space reduces between [(mid + 1), end].
b) Otherwise, the search space reduces between [start, (mid -1)]
4) Repeat from step-1 until the key is found.
5) Return -1 if never found.
TC : O(log(N)), Where N = size of the array.
SC : O(1)
3. OOPS Question
What is meant by static and dynamic polymorphism?
Problem approach
Static Polymorphism : Static Polymorphism is commonly known as the Compile time polymorphism. Static polymorphism is the feature by which an object is linked with the respective function or operator based on the values during the compile time. Static or Compile time Polymorphism can be achieved through Method overloading or operator overloading.
Dynamic Polymorphism : Dynamic Polymorphism or Runtime polymorphism refers to the type of Polymorphism in OOPs, by which the actual implementation of the function is decided during the runtime or execution. The dynamic or runtime polymorphism can be achieved with the help of method overriding.
4. OOPS Question
What is Abstraction?
Problem approach
If you are a user, and you have a problem statement, you don't want to know how the components of the software work, or how it's made. You only want to know how the software solves your problem. Abstraction is the method of hiding unnecessary details from the necessary ones. It is one of the main features of OOPs.
For example, consider a car. You only need to know how to run a car, and not how the wires are connected inside it. This is obtained using Abstraction.
5. Puzzle
3 Ants and Triangle
Problem approach
Collision doesn’t happen only in following two cases :
1) All ants move in counterclockwise direction.
2) All ants move in clockwise direction.
Since every ant has two choices (pick either of two edges going through the corner on which ant is initially sitting),
there are total 23 possibilities.
Out of 23 possibilities, only 2 don’t cause collision. So, the probability of collision is 6/8 or 3/4 and the probability of
non-collision is 2/8 or 1/4.
04
Round
Easy
HR Round
Duration30 Minutes
Interview date20 Aug 2020
Coding problem2
This was a Technical Cum HR round where I was first asked some basic OOPS related concepts and then we discussed
about my expectations from the company , learnings and growth in the forthcomig years. I would suggest be honest and
try to communicate your thoughts properly in these type of rounds to maximise your chances of getting selected.
1. Basic HR Question
Do you know anything about the company ?
Problem approach
General Tip : Before an interview for any company , have a breif insight about the company , what it does , when was
it founded and so on . All these info can be easily acquired from the Company Website itself .
2. Basic HR Question
Why should we hire you ?
Problem approach
Tip 1 : The cross questioning can go intense some time, think before you speak.
Tip 2 : Be open minded and answer whatever you are thinking, in these rounds I feel it is important to have opinion.
Tip 3 : Context of questions can be switched, pay attention to the details. It is okay to ask questions in these round,
like what are the projects currently the company is investing, which team you are mentoring. How all is the work
environment etc.
Tip 4 : Since everybody in the interview panel is from tech background, here too you can expect some technical
questions. No coding in most of the cases but some discussions over the design can surely happen.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
Which SQL clause is used to specify the conditions in a query?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
1 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Siemens
2766 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 8 problems
Interviewed by Siemens
1870 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Siemens
1823 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Siemens
1429 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
5 rounds | 12 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
113896 views
24 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
57279 views
5 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
34687 views
6 comments
0 upvotes




