Snapdeal Ltd. interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - 1
Snapdeal Ltd.
3 rounds | 6 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 6 months
Topics: Data Structures, Algorithms, System Design, Aptitude, OOPS
Tip
Tip 1 : Must do Previously asked Interview as well as Online Test Questions.
Tip 2 : Go through all the previous interview experiences from Codestudio and Leetcode.
Tip 3 : Do at-least 2 good projects and you must know every bit of them.
Application process
Where: Other
Eligibility: Above 7 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Have at-least 2 good projects explained in short with all important points covered.
Tip 2 : Every skill must be mentioned.
Tip 3 : Focus on skills, projects and experiences more.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Medium
Face to Face
Duration60 minutes
Interview date21 May 2015
Coding problem3
It’ll range from the very very basics of programming to the toughest of DPs. In between questions were being popped up on your projects. If you’ve some worth-discussing development projects in your resume(like I’ve my BTP and an Android game), substantial amount of time goes in discussing that.
1. Nth Fibonacci
Easy
0/40
Asked in companies



The n-th term of Fibonacci series F(n), where F(n) is a function, is calculated using the following formula -
F(n) = F(n - 1) + F(n - 2),
Where, F(1) = 1, F(2) = 1
Provided 'n' you have to find out the n-th Fibonacci Number. Handle edges cases like when 'n' = 1 or 'n' = 2 by using conditionals like if else and return what's expected.
"Indexing is start from 1"
Example :
Input: 6
Output: 8
Explanation: The number is ‘6’ so we have to find the “6th” Fibonacci number.
So by using the given formula of the Fibonacci series, we get the series:
[ 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21]
So the “6th” element is “8” hence we get the output.
Problem approach
The recursive approach involves direct implementation of mathematical recurrence formula.
F(n) = F(n-1)+F(n-2)
Pseudocode :
fibonacci(n):
if(n<=1)
return n;
return fibonacci(n-1) + fibonacci(n-2)
This is an exponential approach.
It can be optimized using dynamic programming. Maintain an array that stores all the calculated fibonacci numbers so far and return the nth fibonacci number at last. This approach will take O(n) time complexity and O(n) auxiliary space.
2. Inorder Traversal of Binary Tree without Recursion
Easy
32m average time
0/40
Asked in companies



You have been given a Binary Tree of 'n' nodes, where the nodes have integer values. Your task is to return the In-Order traversal of the given binary tree.
For example :
For the given binary tree:
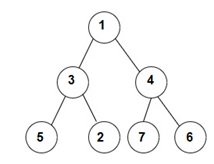
The Inorder traversal will be [5, 3, 2, 1, 7, 4, 6].
Problem approach
Inorder traversal requires that we print the leftmost node first and the right most node at the end.
So basically for each node we need to go as far as down and left as possible and then we need to come back and go right. So the steps would be :
1. Start with the root node.
2. Push the node in the stack and visit it's left child.
3. Repeat step 2 while node is not NULL, if it's NULL then pop the topmost node from the stack and print it.
4. Now move to node's right child and repeat step 1
5. Repeat the above steps while node is not NULL and stack is not empty
3. Largest Rectangular Area In A Histogram
Hard
25m average time
75% success
0/120
Asked in companies



You have been given an array/list 'HEIGHTS' of length ‘N. 'HEIGHTS' represents the histogram and each element of 'HEIGHTS' represents the height of the histogram bar. Consider that the width of each histogram is 1.
You are supposed to return the area of the largest rectangle possible in the given histogram.
For example :
In the below histogram where array/list elements are {2, 1, 5, 6, 2, 3}.
The area of largest rectangle possible in the given histogram is 10.
Problem approach
Traverse all bars from left to right, maintain a stack of bars. Every bar is pushed to stack once. A bar is popped from stack when a bar of smaller height is seen. When a bar is popped, calculate the area with the popped bar as smallest bar. The current index is the ‘right index’ and index of previous item in stack is the ‘left index’.
Following is the complete algorithm.
1) Create an empty stack.
2) Start from first bar, and do following for every bar ‘hist[i]’ where ‘i’ varies from 0 to n-1.
……a) If stack is empty or hist[i] is higher than the bar at top of stack, then push ‘i’ to stack.
……b) If this bar is smaller than the top of stack, then keep removing the top of stack while top of the stack is greater. Let the removed bar be hist[tp]. Calculate area of rectangle with hist[tp] as smallest bar. For hist[tp], the ‘left index’ is previous (previous to tp) item in stack and ‘right index’ is ‘i’ (current index).
3) If the stack is not empty, then one by one remove all bars from stack and do step 2.b for every removed bar.
02
Round
Hard
Face to Face
Duration60 minutes
Interview date21 May 2015
Coding problem2
Director (search) had come along with the recruitment team this time. So, he was only taking the rounds for all the candidates in this round. Summary, two questions were asked.
After these two, he asked me if I’d any questions for him. I asked about the work culture and what kind of people he was looking for. It’ll give you an idea whether you’re selected or not. Be eager to hear the answer he gives and feel attracted to the prospects he puts forward about the company! AGAIN IMPORTANT, DON’T GIVE UP ANY QUESTION. UNTIL HE DECIDES TO MOVE ON TO THE NEXT. If you’re not able to come up with a solution. Don’t panic. Show your fighting spirit.
1. Search in a row wise and column wise sorted matrix
Moderate
15m average time
80% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given an 'N * N' matrix of integers where each row and each column is sorted in increasing order. You are given a target integer 'X'.
Find the position of 'X' in the matrix. If it exists then return the pair {i, j} where 'i' represents the row and 'j' represents the column of the array, otherwise return {-1,-1}
For example:
If the given matrix is:
[ [1, 2, 5],
[3, 4, 9],
[6, 7, 10]]
We have to find the position of 4. We will return {1,1} since A[1][1] = 4.
Problem approach
The brute force solution is to traverse the array and to search elements one by one. Run a nested loop, outer loop for row and inner loop for the column
Check every element with x and if the element is found then print “element found”. If the element is not found, then print “element not found”.
Efficient Approach : The idea here is to remove a row or column in each comparison until an element is found. Start searching from the top-right corner of the matrix. There are three possible cases :
1. The given number > the current number: This will ensure that all the elements in the current row are smaller than the given number as the pointer is already at the right-most elements and the row is sorted. Thus, the entire row gets eliminated and continues the search for the next row.
2. The given number < the current number: This will ensure that all the elements in the current column are greater than the given number. Thus, the entire column gets eliminated and continues the search for the previous column, i.e. the column on the immediate left.
3. The given number == the current number: This will end the search.
• Algorithm:
1. Let the given element be x, create two variable i = 0, j = n-1 as index of row and column
2. Run a loop until i = n
3. Check if the current element is greater than x then decrease the count of j. Exclude the current column.
4. Check if the current element is less than x then increase the count of i. Exclude the current row.
5. If the element is equal, then print the position and end.
2. Closest Pair of Points
Easy
20m average time
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given an array containing 'N' points in the plane. The task is to find out the distance of the closest points.
Note :
Where distance between two points (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) is calculated as [(x1 - x2) ^ 2] + [(y1 - y2) ^ 2].
Problem approach
Algorithm:
1) Sort all points according to x coordinates.
2) Divide all points in two halves.
3) Recursively find the smallest distances in both subarrays.
4) Take the minimum of two smallest distances. Let the minimum be d.
5) Create an array that stores all points which are at most d distance away from the middle line dividing the two sets.
6) Find the smallest distance in the created array.
7) Return the minimum of d and the smallest distance calculated in above step 6.
Time Complexity : O(n (Logn)^2)
03
Round
Easy
HR Round
Duration30 minutes
Interview date21 May 2015
Coding problem1
Most Important here is do not fake your personality here. They’re HR guys, they’re trained to catch the fake ones. So, be genuine.
1. Basic HR Questions
1. Your strengths and weaknesses.
2. If your colleague is slow in catching up and deadline is fast approaching, what will you do?
3. Your manager from the beginning has set high expectations on you and you’ve proved your worth to him. But one time, he assigned you something which no matter how much you try you just can’t understand and you’ve gone blank! What will you do in this case then?
Problem approach
Tip 1 : The cross questioning can go intense some time, think before you speak.
Tip 2 : Be open minded and answer whatever you are thinking, in these rounds I feel it is important to have opinion.
Tip 3 : Context of questions can be switched, pay attention to the details. It is okay to ask questions in these round, like what are the projects currently the company is investing, which team you are mentoring. How all is the work environment etc.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
Software Engineer
4 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Snapdeal Ltd.
805 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
5 rounds | 17 problems
Interviewed by Snapdeal Ltd.
748 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by Snapdeal Ltd.
870 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Snapdeal Ltd.
1002 views
1 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
5 rounds | 12 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
114868 views
24 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
58030 views
5 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
35056 views
7 comments
0 upvotes





