Snapdeal Ltd. interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
Software Developer
Snapdeal Ltd.
4 rounds | 10 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 5 months
Topics: Data Structures, Algorithms, System Design, Aptitude, OOPS
Tip
Tip 1 : Must do Previously asked Interview as well as Online Test Questions.
Tip 2 : Go through all the previous interview experiences from Codestudio and Leetcode.
Tip 3 : Do at-least 2 good projects and you must know every bit of them.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: Above 7 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Have at-least 2 good projects explained in short with all important points covered.
Tip 2 : Every skill must be mentioned.
Tip 3 : Focus on skills, projects and experiences more.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Easy
Face to Face
Duration75 minutes
Interview date11 May 2015
Coding problem4
Technical round with questions based on DSA, DBMS and discussion on Internship project.
1. Gas Tank
Moderate
20m average time
90% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You have a car with a gas tank of infinite capacity. There are ‘N’ gas stations along a circular route. Gas stations are numbered from 0 to N - 1. You begin the journey with an empty tank at one of the gas stations. You want to travel around the circular route once in the clockwise direction. I.e if you start to travel from station ‘i’, then you will go to i + 1, i + 2, …, n - 1, 0, 1, 2, i - 1 and then return back to ‘i’.
You are given two integer arrays ‘gas’ and ‘cost’. ‘gas[i]’ gives the amount of gas available at station ‘i’ and cost[i] gives the amount of gas required to travel from station ‘i’ to next station i.e station ‘i’+1 (or 0 if the station is N - 1).
Return the starting gas station's index if it is possible to complete cycle of given circular route once in the clockwise direction. If there are multiple possible starting gas station’s indexes, then return the minimum of those gas station indexes. If there is no such gas station then return -1.
2. DBMS Question
Difference between SQL and NoSQL
Problem approach
Type –
SQL databases are primarily called as Relational Databases (RDBMS); whereas NoSQL database are primarily called as non-relational or distributed database.
Language –
SQL databases defines and manipulates data based structured query language (SQL). Seeing from a side this language is extremely powerful. SQL is one of the most versatile and widely-used options available which makes it a safe choice especially for great complex queries. But from other side it can be restrictive. SQL requires you to use predefined schemas to determine the structure of your data before you work with it.
A NoSQL database has dynamic schema for unstructured data. Data is stored in many ways which means it can be document-oriented, column-oriented, graph-based or organized as a KeyValue store. This flexibility means that documents can be created without having defined structure first. Also each document can have its own unique structure.
The Scalability –
In almost all situations SQL databases are vertically scalable. This means that you can increase the load on a single server by increasing things like RAM, CPU or SSD. But on the other hand NoSQL databases are horizontally scalable. This means that you handle more traffic by sharding, or adding more servers in your NoSQL database. It is similar to adding more floors to the same building versus adding more buildings to the neighborhood. Thus NoSQL can ultimately become larger and more powerful, making these databases the preferred choice for large or ever-changing data sets.
The Structure –
SQL databases are table-based on the other hand NoSQL databases are either key-value pairs, document-based, graph databases or wide-column stores. This makes relational SQL databases a better option for applications that require multi-row transactions such as an accounting system or for legacy systems that were built for a relational structure.
Property followed –
SQL databases follow ACID properties (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation and Durability) whereas the NoSQL database follows the Brewers CAP theorem (Consistency, Availability and Partition tolerance).
Support –
Great support is available for all SQL database from their vendors. Also a lot of independent consultations are there who can help you with SQL database for a very large scale deployments but for some NoSQL database you still have to rely on community support and only limited outside experts are available for setting up and deploying your large scale NoSQL deployments.
Some examples of SQL databases include PostgreSQL, MySQL, Oracle and Microsoft SQL Server. NoSQL database examples include Redis, RavenDB Cassandra, MongoDB, BigTable, HBase, Neo4j and CouchDB.
3. DBMS Question
Where is No-SQL database used?
Problem approach
The major purpose of using a NoSQL database is for distributed data stores with humongous data storage needs. NoSQL is used for Big data and real-time web apps. For example, companies like Twitter, Facebook and Google collect terabytes of user data every single day.
4. System Design Question
How would you design DBMS for Snapdeal's website's shoe section?
Now if you want to further break it into Sports and Casual Shoe would you break the DB into two or add another entity ?
Problem approach
I initially answered with a multi-level indexed structure for DBMS storage.
Could not answer on the second part of the question. He asked if I knew DBMS and I told him I do not know DBMS.
He skipped the question and ended the interview. I told him I had advanced DBMS lab in my course currently and would learn it before graduating.
02
Round
Medium
Face to Face
Duration60 minutes
Interview date11 May 2015
Coding problem3
Technical Interview round entirely based on DSA.
1. Triplets with Given Sum
Moderate
15m average time
85% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given an array/list ARR consisting of N integers. Your task is to find all the distinct triplets present in the array which adds up to a given number K.
An array is said to have a triplet {ARR[i], ARR[j], ARR[k]} with sum = 'K' if there exists three indices i, j and k such that i!=j, j!=k and i!=j and ARR[i] + ARR[j] + ARR[k] = 'K'.
Note:
1. You can return the list of values in any order. For example, if a valid triplet is {1, 2, -3}, then {2, -3, 1}, {-3, 2, 1} etc is also valid triplet. Also, the ordering of different triplets can be random i.e if there are more than one valid triplets, you can return them in any order.
2. The elements in the array need not be distinct.
3. If no such triplet is present in the array, then return an empty list, and the output printed for such a test case will be "-1".
Problem approach
• Sorting can be used to solve this problem. Next, two -pointer technique can be applied on the sorted array.
Traverse the array and fix the first element of the triplet. Now use the Two Pointer technique to find if there is a pair whose sum is equal to x – array[i].
• Algorithm :
1. Sort the given array.
2. Loop over the array and fix the first element of the possible triplet, arr[i].
3. Then fix two pointers, one at i + 1 and the other at n – 1. And look at the sum,
1. If the sum < required sum, increment the first pointer.
2. Else, If the sum > required sum, Decrease the end pointer to reduce the sum.
3. Else, if the sum of elements at two-pointers == required sum, then print the triplet and break.
Time Complexity : O(nlogn)
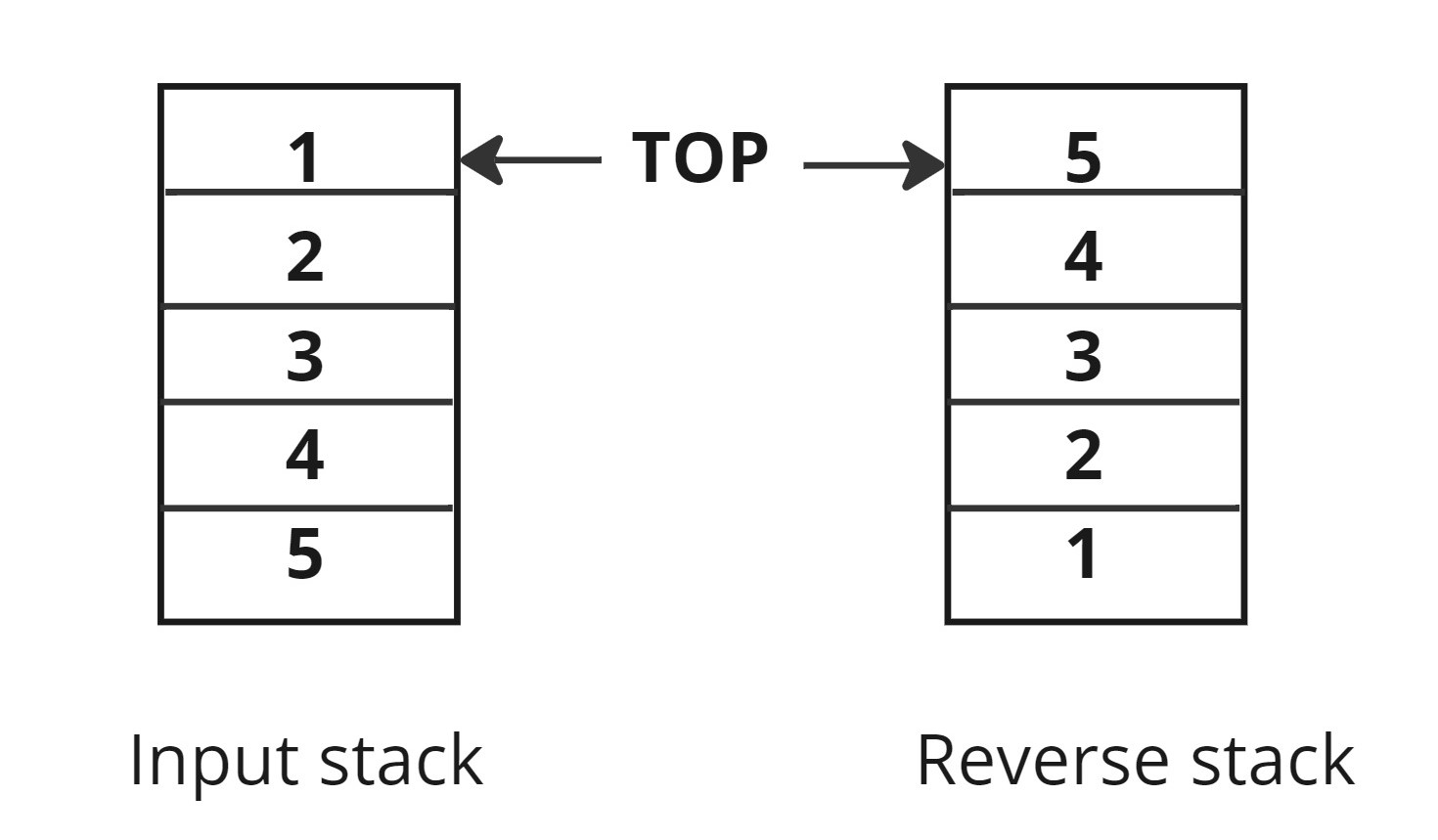
2. Reverse Stack Using Recursion
Easy
21m average time
80% success
0/40
Asked in companies



Reverse a given stack of 'N' integers using recursion. You are required to make changes in the input parameter itself.
Note: You are not allowed to use any extra space other than the internal stack space used due to recursion.
Example:
Input: [1,2,3,4,5]
Output: [5,4,3,2,1]
3. Group Anagrams Together
Moderate
0/80
Asked in companies



You have been given an array/list of strings 'STR_LIST'. You are supposed to return the strings as groups of anagrams such that strings belonging to a particular group are anagrams of one another.
Note :
An Anagram is a word or phrase formed by rearranging the letters of a different word or phrase. We can generalize this in string processing by saying that an anagram of a string is another string with the same quantity of each character in it, in any order.
Example:
{ “abc”, “ged”, “dge”, “bac” }
In the above example the array should be divided into 2 groups. The first group consists of { “abc”, “bac” } and the second group consists of { “ged”, “dge” }.
Problem approach
Approach: A hash map based solution can be built here. In the hash map, the key will be the sorted set of characters and value will be the output string. Two anagrams will be similar when their characters are sorted. Now :
Store the vector elements in HashMap with key as the sorted string.
If the key is same, then add the string to the value of HashMap(string vector).
Traverse the HashMap and print the anagram strings.
Time Complexity: O(n * m(log m)), where m is the length of a word.
Space Complexity: O(n).
03
Round
Medium
Face to Face
Duration45 minutes
Interview date11 May 2015
Coding problem2
Technical Interview with questions based on DSA.
1. Possible Words From A Phone Number
Hard
55m average time
45% success
0/120
Asked in companies



After years of research, Ninja is finally able to invent the time machine, and now he is back to the good old days when T9 keypads were being used in mobile phones.
Being a curious person, Ninja wants to find out all possible strings that can be formed by pressing the keys of the phone.
Formally, you are given a string S, that consists of digits from 2-9 (both inclusive), your task is to find out all the possible strings that can be formed from the input string by mapping the digits to the letters as in a T9 keypad. Then, print the strings in a lexicographically sorted order.

For Example:
If S = “34”, then all the possible letters that can be formed from string S are {“dg”, “dh”, “di”, “eg”, “eh”, “ei”, “fg”, “fh”, “fi”}.
Problem approach
Approach: This can be solved using recursion. It can be observed that each digit can represent 3 to 4 different alphabets (apart from 0 and 1). Map the number with its string of probable alphabets, i.e 2 with “abc”, 3 with “def” etc. Now the recursive function will try all the alphabets, mapped to the current digit in alphabetic order, and again call the recursive function for the next digit and will pass on the current output string.
Algorithm:
Map the number with its string of probable alphabets, i.e 2 with “abc”, 3 with “def” etc.
Create a recursive function which takes the following parameters, output string, number array, current index, and length of number array
If the current index is equal to the length of the number array then print the output string.
Extract the string at digit[current_index] from the Map, where the digit is the input number array.
Run a loop to traverse the string from start to end
For every index again call the recursive function with the output string concatenated with the ith character of the string and the current_index + 1.
Time Complexity: O(4^n), where n is a number of digits in the input number. .
Space Complexity:O(1).
2. Minimum Operations To Make Array Equal
Easy
10m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given an array ‘ARR’ of length ‘N’ which is filled with the values such that ARR[i] = (2*i + 1). You have to perform operations on the ‘ARR’ to make all elements of the array equal. In one operation, you can choose two elements from the array ‘ARR’ say ‘i’ and ‘j’, and can increment the value of ‘ARR[i]’ by one and decrement the value of ‘ARR[j]’ by one.
You have to find the minimum number of operations to make all the elements of the array ‘ARR’ equal. It is guaranteed that all elements of the array can be made equal using some operations.
Problem approach
A simple approach is to make all elements equal is that at each step find the largest elements and then increase all rest n-1 elements by 1. Keep doing this operation till all elements become equal.
Time Complexity : O(n^2)
An efficient approach of O(n) time complexity can also be built. Increasing all n-1 element except the largest one is similar to decreasing the largest element only. So, the smallest elements need not to decrease any more and rest of elements will got decremented upto smallest one. In this way the total number of operation required for making all elements equal will be arraySum – n * (smallestElement).
Algorithm:
1. Find the array sum.
2. Find the smallest element from array.
3. Calculate min operation required : minOperation = sum - (n * small)
4. Return result.
04
Round
Easy
HR Round
Duration30 minutes
Interview date11 May 2015
Coding problem1
This was a typical managerial round with behavioral problems.
1. Basic HR Questions
Q1. Introduction
Q2. Your strengths and weaknesses
Q3. Why Snapdeal?
Problem approach
Tip 1 : The cross questioning can go intense some time, think before you speak.
Tip 2 : Be open minded and answer whatever you are thinking, in these rounds I feel it is important to have opinion.
Tip 3 : Context of questions can be switched, pay attention to the details. It is okay to ask questions in these round, like what are the projects currently the company is investing, which team you are mentoring. How all is the work environment etc.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
Software Developer
3 rounds | 9 problems
Interviewed by Snapdeal Ltd.
1029 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Software Developer
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Snapdeal Ltd.
881 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Software Developer
4 rounds | 10 problems
Interviewed by Snapdeal Ltd.
667 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Snapdeal Ltd.
1003 views
1 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
Software Developer
5 rounds | 14 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
3986 views
1 comments
0 upvotes
Software Developer
6 rounds | 12 problems
Interviewed by SAP Labs
2872 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Software Developer
3 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
1202 views
0 comments
0 upvotes





