Snapdeal Ltd. interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
Software Engineer
Snapdeal Ltd.
4 rounds | 7 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 6 months
Topics: Data Structures, Algorithms, System Design, Aptitude, OOPS
Tip
Tip 1 : Must do Previously asked Interview as well as Online Test Questions.
Tip 2 : Go through all the previous interview experiences from Codestudio and Leetcode.
Tip 3 : Do at-least 2 good projects and you must know every bit of them.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: Above 7 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Have at-least 2 good projects explained in short with all important points covered.
Tip 2 : Every skill must be mentioned.
Tip 3 : Focus on skills, projects and experiences more.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Easy
Online Coding Test
Duration60 minutes
Interview date19 May 2015
Coding problem2
Only 1 or 2 Questions were asked to each of us and all of them were from DATA STRUCTURES. For both the question they were looking for full optimization and proper code starting from scratch.
1. Validate BST
Moderate
25m average time
0/80
Asked in companies



You have been given a binary tree of integers with N number of nodes. Your task is to check if that input tree is a BST (Binary Search Tree) or not.
A binary search tree (BST) is a binary tree data structure which has the following properties.
• The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with data less than the node’s data.
• The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with data greater than the node’s data.
• Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
Example :
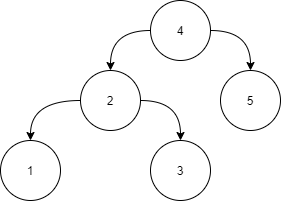
Answer :
Level 1:
All the nodes in the left subtree of 4 (2, 1, 3) are smaller
than 4, all the nodes in the right subtree of the 4 (5) are
larger than 4.
Level 2 :
For node 2:
All the nodes in the left subtree of 2 (1) are smaller than
2, all the nodes in the right subtree of the 2 (3) are larger than 2.
For node 5:
The left and right subtrees for node 5 are empty.
Level 3:
For node 1:
The left and right subtrees for node 1 are empty.
For node 3:
The left and right subtrees for node 3 are empty.
Because all the nodes follow the property of a binary search tree, the above tree is a binary search tree.
Problem approach
A simple O(N) approach for this question would be to do an inorder traversal of the tree and store all the values in a temporary array. Next, check if the array is sorted in ascending order or not. If it is sorted, the given tree is a BST.
The above approach uses an auxiliary array. In order to avoid using auxiliary array, maintain track of the previously visited node in a variable prev. So, do an inorder traversal of the tree and store the value of the previously visited node in prev. If the value of the current node is less than prev, then the given tree is not a BST.
2. Matrix Game
Easy
15m average time
80% success
0/40
Asked in companies



Ninja is a teacher at a school. He introduced a game of matrix. He gives a square matrix, i.e., NxN matrix, to all the school students and asks them to check if the matrix is idempotent or not.
A matrix is an idempotent matrix if a matrix multiplied by itself returns the same matrix. The matrix M is said to be an idempotent matrix if and only if M * M = M. In the idempotent matrix, M is a square matrix.
Among them, a student Ninja is new to programming; he doesn’t have much experience; he asks you to solve the problem. Can you help Ninja figure out whether the matrix is idempotent?
02
Round
Medium
Face to Face
Duration60 minutes
Interview date19 May 2015
Coding problem2
Technical Interview round with questions based on DSA.
1. Maximum Subarray Sum
Moderate
35m average time
81% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given an array 'arr' of length 'n', consisting of integers.
A subarray is a contiguous segment of an array. In other words, a subarray can be formed by removing 0 or more integers from the beginning and 0 or more integers from the end of an array.
Find the sum of the subarray (including empty subarray) having maximum sum among all subarrays.
The sum of an empty subarray is 0.
Example :
Input: 'arr' = [1, 2, 7, -4, 3, 2, -10, 9, 1]
Output: 11
Explanation: The subarray yielding the maximum sum is [1, 2, 7, -4, 3, 2].
Problem approach
The direct approach to solve this problem is to run two for loops and for every subarray check if it is the maximum sum possible.
Time complexity: O(N^2), Where N is the size of the array.
Space complexity: O(1)
The efficient approach is to use Kadane's algorithm. It calculates the maximum sum subarray ending at a particular index by using the maximum sum subarray ending at the previous position.
Steps :
Declare two variables : currSum which stores maximum sum ending here and maxSum which stores maximum sum so far.
Initialize currSum = 0 and maxSum = INT_MIN.
Now, traverse the array and add the value of the current element to currSum and check :
1. If currSum > maxSum, update maxSum equals to currSum.
2. If currSum < 0, make currSum equal to zero.
Finally, print the value of maxSum.
2. Longest Increasing Subsequence
Moderate
0/80
Asked in companies



'N' students are standing in a row. You are given the height of every student standing in the row. Your task is to find the longest strictly increasing subsequence of heights from the row such that the relative order of the students does not change.
A subsequence is a sequence that can be derived from another sequence by deleting zero or more elements without changing the order of the remaining elements.
03
Round
Easy
Face to Face
Duration45 minutes
Interview date19 May 2015
Coding problem2
This was a puzzle interview.
1. Puzzle
5 Pirates and 100 Gold Coins
Problem approach
The answer is 98 which is not intuitive.
A uses the facts below to get 98.
Consider the situation when A, B, and C die, only D and E are left. E knows that he will not get anything (D is senior and will make a distribution of (100, 0). So E would be fine with anything greater than 0.
Consider the situation when A and B die, C, D, and E are left. D knows that he will not get anything (C will make a distribution of (99, 0, 1)and E will vote in favor of C).
Consider the situation when A dies. B, C, D, and E are left. To survive, B only needs to give 1 coin to D. So distribution is (99, 0, 1, 0)
Similarly, A knows about point 3, so he just needs to give 1 coin to C and 1 coin to E to get them in favor. So distribution is (98, 0, 1, 0, 1).
2. Puzzle
You are given a function foo() that represents a biased coin. When foo() is called, it returns 0 with 60% probability, and 1 with 40% probability. Write a new function that returns 0 and 1 with a 50% probability each.
Problem approach
If we can somehow get two cases with equal probability, then we are done. We call foo() two times. Both calls will return 0 with a 60% probability. So the two pairs (0, 1) and (1, 0) will be generated with equal probability from two calls of foo(). Let us see how.
(0, 1): The probability to get 0 followed by 1 from two calls of foo() = 0.6 * 0.4 = 0.24
(1, 0): The probability to get 1 followed by 0 from two calls of foo() = 0.4 * 0.6 = 0.24
So the two cases appear with equal probability. The idea is to return consider only the above two cases, return 0 in one case, return 1 in other case. For other cases [(0, 0) and (1, 1)], recur until you end up in any of the above two cases.
04
Round
Easy
HR Round
Duration30 minutes
Interview date19 May 2015
Coding problem1
This was a standard HR round.
1. Basic HR Questions
Q1.Tell me about yourself
Q2. What is your real goal in life?
Q3. Your manager is being bossy. How will you tackle this situation?
Q4. Toughest challenge you faced in your college.
Problem approach
Tip 1 : The cross questioning can go intense some time, think before you speak.
Tip 2 : Be open minded and answer whatever you are thinking, in these rounds I feel it is important to have opinion.
Tip 3 : Context of questions can be switched, pay attention to the details. It is okay to ask questions in these round, like what are the projects currently the company is investing, which team you are mentoring. How all is the work environment etc.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
Software Engineer
4 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Snapdeal Ltd.
805 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Business Analyst
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Snapdeal Ltd.
1212 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by Snapdeal Ltd.
938 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Snapdeal Ltd.
1003 views
1 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
Software Engineer
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Optum
7923 views
1 comments
0 upvotes
Software Engineer
5 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
10070 views
1 comments
0 upvotes
Software Engineer
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
4395 views
1 comments
0 upvotes





