Snapdeal Ltd. interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
Software Developer
Snapdeal Ltd.
3 rounds | 9 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 6 months
Topics: Data Structures, Algorithms, System Design, Aptitude, OOPS
Tip
Tip 1 : Must do Previously asked Interview as well as Online Test Questions.
Tip 2 : Go through all the previous interview experiences from Codestudio and Leetcode.
Tip 3 : Do at-least 2 good projects and you must know every bit of them.
Application process
Where: Other
Eligibility: Above 7 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Have at-least 2 good projects explained in short with all important points covered.
Tip 2 : Every skill must be mentioned.
Tip 3 : Focus on skills, projects and experiences more.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Easy
Face to Face
Duration60 minutes
Interview date14 May 2015
Coding problem3
Technical Interview round with questions based on DSA.
1. LCA of Binary Tree
Moderate
10m average time
90% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You have been given a Binary Tree of distinct integers and two nodes ‘X’ and ‘Y’. You are supposed to return the LCA (Lowest Common Ancestor) of ‘X’ and ‘Y’.
The LCA of ‘X’ and ‘Y’ in the binary tree is the shared ancestor of ‘X’ and ‘Y’ that is located farthest from the root.
Note :
You may assume that given ‘X’ and ‘Y’ definitely exist in the given binary tree.
For example :
For the given binary tree
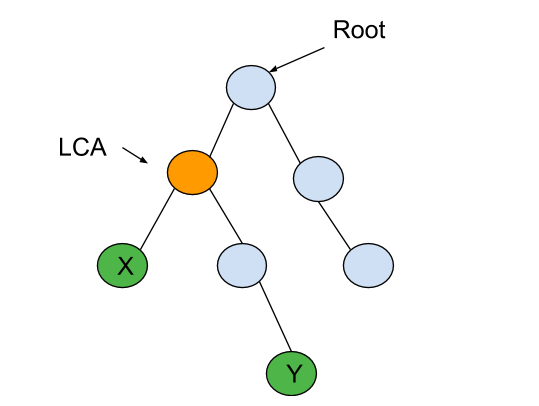
LCA of ‘X’ and ‘Y’ is highlighted in yellow colour.
Problem approach
The recursive approach is to traverse the tree in a depth-first manner. The moment you encounter either of the nodes node1 or node2, return the node. The least common ancestor would then be the node for which both the subtree recursions return a non-NULL node. It can also be the node which itself is one of node1 or node2 and for which one of the subtree recursions returns that particular node.
Pseudo code :
LowestCommonAncestor(root, node1, node2)
{
if(not root)
return NULL
if (root == node1 or root == node2)
return root
left = LowestCommonAncestor(root.left, node1, node2)
right = LowestCommonAncestor(root.right, node1, node2)
if(not left)
return right
else if(not right)
return left
else
return root
}2. Reverse a linked list
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given a Singly Linked List of integers. You need to reverse the Linked List by changing the links between nodes.
Note :
You do not need to print anything, just return the head of the reversed linked list.
Problem approach
This can be solved both: recursively and iteratively.
The recursive approach is more intuitive. First reverse all the nodes after head. Then we need to set head to be the final node in the reversed list. We simply set its next node in the original list (head -> next) to point to it and sets its next to NULL. The recursive approach has a O(N) time complexity and auxiliary space complexity.
For solving the question is constant auxiliary space, iterative approach can be used. We maintain 3 pointers, current, next and previous, abbreviated as cur, n and prev respectively. All the events occur in a chain.
1. Assign prev=NULL, cur=head .
2. Next, repeat the below steps until no node is left to reverse:
1. Initialize n to be the node after cur. i.e. (n=cur->next)
2. Then make cur->next point to prev (next node pointer).
3. Then make prev now point to the cur node.
4. At last move cur also one node ahead to n.
The prev pointer will be the last non null node and hence the answer.
3. Detect loop in a linked list
Moderate
15m average time
80% success
0/80
Asked in companies



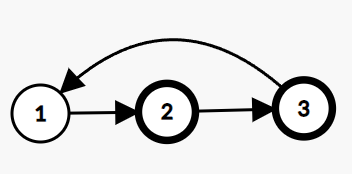
You are given a Singly Linked List of integers. Return true if it has a cycle, else return false.
A cycle occurs when a node's next points back to a previous node in the list.
Example:
In the given linked list, there is a cycle, hence we return true.
Problem approach
Floyd's algorithm can be used to solve this question.
Define two pointers slow and fast. Both point to the head node, fast is twice as fast as slow. There will be no cycle if it reaches the end. Otherwise, it will eventually catch up to the slow pointer somewhere in the cycle.
Let X be the distance from the first node to the node where the cycle begins, and let X+Y be the distance the slow pointer travels. To catch up, the fast pointer must travel 2X + 2Y. L is the cycle size. The total distance that the fast pointer has travelled over the slow pointer at the meeting point is what we call the full cycle.
X+Y+L = 2X+2Y
L=X+Y
Based on our calculation, slow pointer had already traveled one full cycle when it met fast pointer, and since it had originally travelled A before the cycle began, it had to travel A to reach the cycle's beginning!
After the two pointers meet, fast pointer can be made to point to head. And both slow and fast pointers are moved till they meet at a node. The node at which both the pointers meet is the beginning of the loop.
Pseudocode :
detectCycle(Node *head)
{
Node *slow=head,*fast=head;
while(slow!=NULL && fast!=NULL && fast->next!=NULL)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
if(slow==fast)
{
fast = head;
while(slow!=fast)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast=fast->next;
}
return slow;
}
}
return NULL;
} 02
Round
Medium
Face to Face
Duration45 minutes
Interview date14 May 2015
Coding problem3
Technical round with questions on DSA and DBMS.
1. DBMS Question
What is Inner Join?
Problem approach
It is a type of join operation in SQL. Inner join is an operation that returns combined tuples between two or more tables where at least one attribute is in common. If there is no attribute in common between tables then it will return nothing.
Syntax:
select *
from table1 INNER JOIN table2
on table1.column_name = table2.column_name;
2. DBMS Question
What is Outer join?
Problem approach
It is a type of Join operation in SQL. Outer join is an operation that returns combined tuples from a specified table even if the join condition fails. There are three types of outer join in SQL i.e.
Left Outer Join
Right Outer Join
Full Outer Join
Syntax of Left Outer Join:
select *
from table1 LEFT OUTER JOIN table2
on table1.column_name = table2.column_name;
3. Number of rectangles in N*M grid
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given an arbitrary grid with M rows and N columns. You have to print the total number of rectangles which can be formed using the rows and columns of this grid. In simple words, print the number of unique rectangles in the grid.
For example:
Consider the grid shown below. The dark black boundary encloses a grid of dimension 3x4.

The green colour represents rectangles of dimension 1x1.
The brown colour represents the rectangles of dimension 1x2.
The blue colour represents the rectangles of dimension 2x2.
The red colour represents the rectangles of dimension 3x3.
The yellow colour represents the rectangles of dimension 3x1.
There can be many different other possibilities as well. You need to print the total number of all such rectangles.
Note:
Two rectangles are said to be unique if atleast one of their 4 sides is non-overlapping.
Problem approach
If the grid is 1×1, there is 1 rectangle.
If the grid is 2×1, there will be 2 + 1 = 3 rectangles
If it grid is 3×1, there will be 3 + 2 + 1 = 6 rectangles.
we can say that for N*1 there will be N + (N-1) + (n-2) … + 1 = (N)(N+1)/2 rectangles
If we add one more column to N×1, firstly we will have as many rectangles in the 2nd column as the first,
and then we have that same number of 2×M rectangles.
So N×2 = 3 (N)(N+1)/2
After deducing this we can say
For N*M we’ll have (M)(M+1)/2 (N)(N+1)/2 = M(M+1)(N)(N+1)/4
So the formula for total rectangles will be M(M+1)(N)(N+1)/4 03
Round
Easy
Face to Face
Duration40 minutes
Interview date14 May 2015
Coding problem3
Technical round with questions on DSA and Puzzles.
1. Puzzle
Mislabeled Jars
Problem approach
1 pick of an eatable is required to correctly label the Jars.
Solution :
You have to pick only one eatable from jar C. Suppose the eatable is a candy, then the jar C contains candies only(because all the jars were mislabeled).
Now, since the jar C has candies only, Jar B can contain sweets or mixture. But, jar B can contain only the mixture because its label reads “sweets” which is wrong.
Therefore, Jar A contains sweets. Thus the correct labels are:
A: Sweets.
B: Candies and Sweets.
C: Candies.
2. Puzzle
How to Measure 45 minutes using two identical wires?
Problem approach
If we light a stick, it takes 60 minutes to burn completely. What if we light the stick from both sides? It will take exactly half the original time, i.e. 30 minutes to burn completely.
0 minutes – Light stick 1 on both sides and stick 2 on one side.
30 minutes – Stick 1 will be burnt out. Light the other end of stick 2.
45 minutes – Stick 2 will be burnt out. Thus 45 minutes is completely measured.
3. Find All Anagrams in a String
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You have been given a string STR and a non-empty string PTR. Your task is to find all the starting indices of PTR’s anagram in STR.
An anagram of a string is another string which contains the same characters and is obtained by rearranging the characters.
For example: ‘SILENT’ and ‘LISTEN’ are anagrams of each other. ‘ABA’ and ‘ABB’ are not anagram because we can’t convert ‘ABA’ to ‘ABB’ by rearranging the characters of particular strings.
Note:
1. Both STR and PTR consist of English uppercase letters.
2. Length of string 'STR' will always be greater than or equal to the length of string ‘PTR’.
3. In case, there is no anagram substring, then return an empty sequence.
4. In case of more than one anagrams, return the indices in increasing order.
Problem approach
Algorithm :
Define a map m, n := size of s, set left := 0, right := 0, counter := size of p
define an array ans
store the frequency of characters in p into the map m
for right := 0 to n – 1
if m has s[right] and m[s[right]] is non zero, then decrease m[s[right]] by 1, decrease counter by 1 and if counter = 0, then insert left into ans
otherwise
while left < right{
if s[left] is not present in m, then increase counter by 1, and increase m[s[left]] by 1
increase left by 1
if m has s[right] and m[s[right]] is non zero, then decrease right by 1, and come out from the loop
if m has no s[left], then set left := right + 1
return ans
}

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
Software Developer
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Snapdeal Ltd.
881 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Software Developer
4 rounds | 10 problems
Interviewed by Snapdeal Ltd.
667 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Software Developer
4 rounds | 10 problems
Interviewed by Snapdeal Ltd.
935 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 2
5 rounds | 12 problems
Interviewed by Snapdeal Ltd.
0 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
Software Developer
5 rounds | 14 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
3986 views
1 comments
0 upvotes
Software Developer
6 rounds | 12 problems
Interviewed by SAP Labs
2872 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Software Developer
3 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
1202 views
0 comments
0 upvotes




