Soroco interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - 1
Soroco
3 rounds | 6 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 5 Months
Topics: OOPS, System Design, Algorithms, Data Structures, DBMS
Tip
Tip 1 : Prepare System Design
Tip 2 : Practice DSA Questions properly
Tip 3 : Practice OOPS and DBMS Concepts
Application process
Where: Referral
Eligibility: No criteria
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Your Resume should consist mainly of skills, projects, and achievements. Projects would play a crucial part in your interview and you should have at least one most relevant and good project that shows how strong your concepts are in development.
Tip 2 : The most important tip is that never lie on your resume If you have worked upon some technology for the project part only and don't know the proper depth you could write basics only in your resume.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Easy
Online Coding Test
Duration60 Minutes
Interview date25 Feb 2022
Coding problem2
This round had 2 very basic questions needed to be completed in 60 minutes.I think the criteria as set on if the candidate can identify the edge cases and how quickly he completes the round.
1. Maximum In Sliding Windows Of Size K
Moderate
20m average time
80% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Given an array/list of integers of length ‘N’, there is a sliding window of size ‘K’ which moves from the beginning of the array, to the very end. You can only see the ‘K’ numbers in a particular window at a time. For each of the 'N'-'K'+1 different windows thus formed, you are supposed to return the maximum element in each of them, from the given array/list.
Problem approach
We scan the array from 0 to n-1, keep "promising" elements in the deque. The algorithm is amortized O(n) as each element is put and polled once.
At each i, we keep "promising" elements, which are potentially max number in window [i-(k-1),i] or any subsequent window. This means
If an element in the deque and it is out of i-(k-1), we discard them. We just need to poll from the head, as we are using a deque and elements are ordered as the sequence in the array
Now only those elements within [i-(k-1),i] are in the deque. We then discard elements smaller than a[i] from the tail. This is because if a[x]
As a result elements in the deque are ordered in both sequence in array and their value. At each step the head of the deque is the max element in [i-(k-1),i]
2. Maximum Product Subarray
Moderate
25m average time
75% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given an array “arr'' of integers. Your task is to find the contiguous subarray within the array which has the largest product of its elements. You have to report this maximum product.
An array c is a subarray of array d if c can be obtained from d by deletion of several elements from the beginning and several elements from the end.
For e.g.- The non-empty subarrays of an array [1,2,3] will be- [1],[2],[3],[1,2],[2,3],[1,2,3].
For Example:
If arr = {-3,4,5}.
All the possible non-empty contiguous subarrays of “arr” are {-3}, {4}, {5}, {-3,4}, {4,5} and {-3,4,5}.
The product of these subarrays are -3, 4, 5, -12, 20 and -60 respectively.
The maximum product is 20. Hence, the answer is 20.
Follow Up:
Can you solve this in linear time and constant space complexity?
Problem approach
Here we use 3 variable called max_so_far, max_ending_here & min_ending_here. For every index the maximum number ending at that index will be the maximum(arr[i], max_ending_here * arr[i], min_ending_here[i]*arr[i]). Similarly the minimum number ending here will be the minimum of these 3
02
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration60 Minutes
Interview date1 Mar 2022
Coding problem2
This round was taken by 2 year experienced engineer. He first asked for my intro and quickly jumped onto coding questions. You should know about space and time complexity of your solution else you are in trouble.
1. Kth Largest Element In A Stream
Moderate
30m average time
65% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You will be given a stream of numbers, and you need to find the 'kth' largest number in the stream at any given time.
As the stream of numbers can not be given during compile time, so you need to design a data structure which can accept infinite numbers and can return the 'kth' largest number at any given time.
The stream of numbers is nothing but a large collection of numbers from which integers are read at runtime, such as the user will never know the upper limit on the number of integers that will be read.
The implemented data structure must support the following operations:
1. add(DATA) :
This function should take one argument of type and store it in its pool and returns the 'kth' largest number from the current pool of integers.
You will be given 'q' queries:
val - For this query, insert the integer into your current pool of integers and return the 'kth' largest integer from the existing pool of integers.
Note
1. The maximum number of integers that will be given will always be under memory limits.
2. You will also be given an initial pool of integers whose size equals k.
3. The maximum number of queries will be less than 10^5.
4. The 'kth' largest element is not the 'kth' distinct element but the 'kth' largest element in the sorted order.
5. There will be at least one query of type 2.
Problem approach
Use custom sorting to sort the array in non-decreasing order.
In the custom sort function there will be two cases :
The size of two passed strings is equal, then swap only when string one is lexicographically smaller than the other.
The size of two passed strings is un-equal, then swap only when the size of one string is smaller than the other.
After sorting print Kth largest integer.
2. Validate BST
Moderate
25m average time
0/80
Asked in companies



You have been given a binary tree of integers with N number of nodes. Your task is to check if that input tree is a BST (Binary Search Tree) or not.
A binary search tree (BST) is a binary tree data structure which has the following properties.
• The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with data less than the node’s data.
• The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with data greater than the node’s data.
• Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
Example :
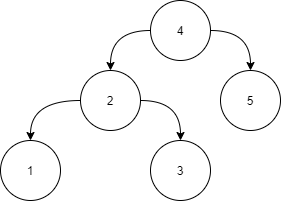
Answer :
Level 1:
All the nodes in the left subtree of 4 (2, 1, 3) are smaller
than 4, all the nodes in the right subtree of the 4 (5) are
larger than 4.
Level 2 :
For node 2:
All the nodes in the left subtree of 2 (1) are smaller than
2, all the nodes in the right subtree of the 2 (3) are larger than 2.
For node 5:
The left and right subtrees for node 5 are empty.
Level 3:
For node 1:
The left and right subtrees for node 1 are empty.
For node 3:
The left and right subtrees for node 3 are empty.
Because all the nodes follow the property of a binary search tree, the above tree is a binary search tree.
Problem approach
check via in-order traversal [we need to check whether that returned elements are in ascending order]
03
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration60 Minutes
Interview date4 Mar 2022
Coding problem2
This round was taken by a lead engineer and was based on system design + coding round.
1. Rotting Oranges
Moderate
30m average time
85% success
0/80
Asked in companies


You are given an integer grid of size ‘N’x’M’, and the cell of the grid contains either of the three values:
Every minute, any fresh orange adjacent(4-directionally) to a rotten orange becomes rotten.
You must return the minimum time after which no fresh oranges are left. Return -1 if it's impossible to rot all the fresh oranges.
Example:
Input: [[2,1,1],[1,1,0],[0,0,0]]
Output: 2
At T=0, only orange at (0,0) is rotten.
At T=1, oranges at (0,0),(0,1) and (1,0) are rotten.
At T=2, oranges at (0,0),(0,1),(1,0),(0,2) and (1,1) are rotten.
No fresh oranges are left after T=2.
Problem approach
Take a queue Data Structure to do BFS traversal and push the starting {row, col} index of all the rotten oranges.
Declare a count variable to calculate the minimum time to get all oranges rotten and declare it with 0.
Run a while loop until queue becomes empty, calculate the initial size of the queue which will tell the number of oranges which get rotten each level.
Do a BFS traversal by running a loop from 0 to size of queue at each level, check if a fresh orange present at all 4 directions which can be rotted from current orange, if yes push this {row, col} index of that fresh orange to queue and mark this cell as rotten also.
After each level check if queue is not empty means it affected any oranges, then increment the count by 1.
After BFS traversal we again check the grid that it contains any fresh oranges or not if (grid[i][j] == 1), if yes, we return -1, else we return the count as our answer.
2. System Design Question
HLD for Whatsapp
Problem approach
Tip 1 : Practice a lot of questions to clear this round in this particular company
Tip 2 : Practice previously asked questions.
Tip 3 : Share your thought process with the interviewer.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by OYO
4782 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
2 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
1011 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Meesho
6543 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 9 problems
Interviewed by Salesforce
3567 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
5 rounds | 12 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
114869 views
24 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
58031 views
5 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
35057 views
7 comments
0 upvotes









