Sprinklr interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - 1
Sprinklr
3 rounds | 14 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Journey
I started my journey by getting admission to NSUT. After exploring different coding languages and taking guidance from seniors, I started coding in C++ as it can help me at a competitive level. After learning this, I started learning full-stack development from Coding Ninjas. I have projects related to full-stack development. After this, in my 3rd year, I made a mini project. During college placements, I got an opportunity to participate in the recruitment process of Sprinklr.
Application story
Sprinklr came to our campus for recruitment. So, I applied on-campus to get recruited. The process was smooth. I had to register on the provided link by Sprinklr. After this, my resume was shortlisted, and I got an online assessment exam link.
Why selected/rejected for the role?
I got rejected in 3rd round i.e. technical round, as I could not give an optimized solution to the DSA problem, they asked me to do.
Preparation
Duration: 3 months
Topics: Data Structures, Pointers, OOPS, System Design, Algorithms, Dynamic Programming, HTML, CSS, NodeJS, react JS.
Tip
Tip 1 : Practice at least 250 coding Questions
Tip 2 : Do at least 2 projects
Tip 3 : Do practice on programming platforms
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: 7.5 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Make your resume short and crisp.
Tip 2 : Do not put false things in your resume
Tip 3 : Don't put irrelevant information in the resume
Interview rounds
01
Round
Medium
Online Coding Test
Duration90 minutes
Interview date13 Jul 2023
Coding problem4
There were 4 coding questions, out of which 2 were of medium difficulty level, and 2 were of Hard level.
1. Maximum Sum Rectangle
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given a matrix ‘ARR’ with ‘N’ rows and ‘M’ columns. Your task is to find the maximum sum rectangle in the matrix.
Maximum sum rectangle is a rectangle with the maximum value for the sum of integers present within its boundary, considering all the rectangles that can be formed from the elements of that matrix.
For Example
Consider following matrix:
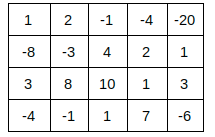
The rectangle (1,1) to (3,3) is the rectangle with the maximum sum, i.e. 29.
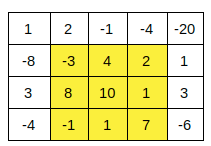
Problem approach
Use the Kadane's algorithm to solve this problem.
- The idea is to fix the left and right columns one by one and find the maximum sum contiguous rows for every left and right column pair.
- I basically find the top and bottom row numbers (which have the maximum sum) for every fixed left and right column pair.
- To find the top and bottom row numbers, calculate the sum of elements in every row from left to right and store these sums in an array, say temp[]. So temp[i] indicates the sum of elements from left to right in row i. If I apply Kadane’s 1D algorithm on temp[] and get the maximum sum subarray of temp[], this maximum sum would be the maximum possible sum with left and right as boundary columns.
- To get the overall maximum sum, we compare this sum with the maximum sum so far.
2. Minimum number of swaps required to sort an array
Easy
10m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You have been given an array 'ARR' of 'N' distinct elements.
Your task is to find the minimum no. of swaps required to sort the array.
For example:
For the given input array [4, 3, 2, 1], the minimum no. of swaps required to sort the array is 2, i.e. swap index 0 with 3 and 1 with 2 to form the sorted array [1, 2, 3, 4].
Problem approach
While iterating over the array, check the current element, and if it is not in the correct place, replace that element with the index of the element that should have come to this place. Greedily doing this will give the optimal answer.
Follow the steps below to solve the problem:
- Create a new array and copy the elements of the input array.
- Sort the new array and declare a variable ans equal to 0.
- Run a for loop to traverse the elements.
- If the current element in the sorted array is not equal to the one in the input array, then increase ans by 1 and swap the current element with the required element at this index.
- Return ans.
3. Maximum meetings
Easy
10m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given the schedule of 'N' meetings with their start time 'Start[i]' and end time 'End[i]'.
You have only 1 meeting room. So, you need to return the maximum number of meetings you can organize.
Note:
The start time of one chosen meeting can’t be equal to the end time of the other chosen meeting.
For example:
'N' = 3, Start = [1, 3, 6], End = [4, 8, 7].
You can organize a maximum of 2 meetings. Meeting number 1 from 1 to 4, Meeting number 3 from 6 to 7.
Problem approach
Assuming that time T starts at 0, the task is to find the maximum number of lectures that are ongoing at a particular instance of time. This will give the minimum number of halls required to schedule all the lectures.
To find the number of lectures ongoing at any instance of time, maintain a prefix_sum[] which will store the number of lectures ongoing at any instance of time t. For any lecture with timings between [s, t], do prefix_sum[s]++ and prefix_sum[t + 1]–.
Afterward, the cumulative sum of this prefix array will give the count of lectures going on at any instance of time. The maximum value for any time instant t in the array is the minimum number of halls required.
4. Find Duplicates In Array
Easy
15m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given an array/list 'ARR' consisting of N integers, which contains elements only in the range 0 to N - 1. Some of the elements may be repeated in 'ARR'. Your task is to find all such duplicate elements.
Note:
1. All the elements are in the range 0 to N - 1.
2. The elements may not be in sorted order.
3. You can return the duplicate elements in any order.
4. If there are no duplicates present then return an empty array.
Problem approach
Follow the steps to implement the approach:
Iterate Through the Array
Calculate an index based on the absolute value of each element.
If the index is equal to ‘n,‘ count it as the largest element.
If the element at the calculated index is negative, add (index – 1) to the result vector and modify the element at that index.
If there are more than one largest elements, add ‘n – 1’ to the result vector.
If the result vector is empty, add ‘-1‘ to it.
Otherwise, sort the result vector.
Return the Result Vector
02
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration90 minutes
Interview date17 Jul 2023
Coding problem4
The interviewer was calm and composed. He first made me comfortable by asking my introduction, then he started asking questions from my resume and gave 2 coding questions to solve.
1. Balanced parentheses
Moderate
10m average time
90% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Given an integer ‘N’ representing the number of pairs of parentheses, Find all the possible combinations of balanced parentheses with the given number of pairs of parentheses.
Note :
Conditions for valid parentheses:
1. All open brackets must be closed by the closing brackets.
2. Open brackets must be closed in the correct order.
For Example :
()()()() is a valid parentheses.
)()()( is not a valid parentheses.
Problem approach
The idea is to put all the opening brackets in the stack. Whenever you hit a closing bracket, search if the top of the stack is the opening bracket of the same nature. If this holds then pop the stack and continue the iteration. In the end if the stack is empty, it means all brackets are balanced or well-formed. Otherwise, they are not balanced.
2. Convert binary tree to mirror tree
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



Given a binary tree, convert this binary tree into its mirror tree.
A binary tree is a tree in which each parent node has at most two children.
Mirror of a Tree: Mirror of a Binary Tree T is another Binary Tree M(T) with left and right children of all non-leaf nodes interchanged.
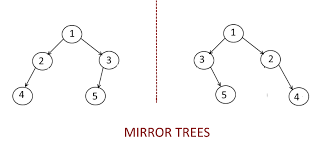
Note:
1. Make in-place changes, that is, modify the nodes given a binary tree to get the required mirror tree.
Problem approach
The idea is to traverse recursively and swap the right and left subtrees after traversing the subtrees.
Follow the steps below to solve the problem:
Call Mirror for left-subtree i.e., Mirror(left-subtree)
Call Mirror for right-subtree i.e., Mirror(right-subtree)
Swap left and right subtrees.
temp = left-subtree
left-subtree = right-subtree
right-subtree = temp
4. Project Based Question
Explain any one of your project? Why you have use react Js in this project.
03
Round
Hard
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date19 Jul 2023
Coding problem6
I was given DSA coding problems to solve. Interviewer asked me questions related to DBMS and some questions related to full stack development
1. Palindrome Partitioning
Moderate
25m average time
75% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given a string 'S'. Your task is to partition 'S' such that every substring of the partition is a palindrome. You need to return all possible palindrome partitioning of 'S'.
Note: A substring is a contiguous segment of a string.
For Example:
For a given string “BaaB”
3 possible palindrome partitioning of the given string are:
{“B”, “a”, “a”, “B”}
{“B”, “aa”, “B”}
{“BaaB”}
Every substring of all the above partitions of “BaaB” is a palindrome.
Problem approach
The problem can be solved by
1) finding the suffix starting from j and ending at index i, (1 <= j <= i <= n – 1), which are palindromes.
2) we can make a cut here that requires 1 + min cut from rest substring [0, j – 1].
3) For all such palindromic suffixes starting at j and ending at i, keep minimising in minCutDp[i].
4) Similarly, we need to compute results for all such i. (1 <= i <= n – 1) and
5) finally, minCutDp[n – 1] will be the minimum number of cuts needed for palindrome partitioning of the given string.
2. Bottom View Of Binary Tree
Moderate
10m average time
90% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given a 'Binary Tree'.
Return the bottom view of the binary tree.
Note :
1. A node will be in the bottom-view if it is the bottom-most node at its horizontal distance from the root.
2. The horizontal distance of the root from itself is 0. The horizontal distance of the right child of the root node is 1 and the horizontal distance of the left child of the root node is -1.
3. The horizontal distance of node 'n' from root = horizontal distance of its parent from root + 1, if node 'n' is the right child of its parent.
4. The horizontal distance of node 'n' from root = horizontal distance of its parent from the root - 1, if node 'n' is the left child of its parent.
5. If more than one node is at the same horizontal distance and is the bottom-most node for that horizontal distance, including the one which is more towards the right.
Example:
Input: Consider the given Binary Tree:
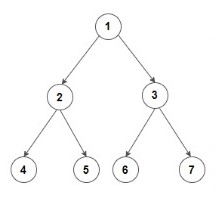
Output: 4 2 6 3 7
Explanation:
Below is the bottom view of the binary tree.
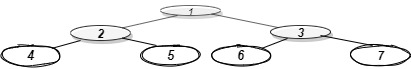
1 is the root node, so its horizontal distance = 0.
Since 2 lies to the left of 0, its horizontal distance = 0-1= -1
3 lies to the right of 0, its horizontal distance = 0+1 = 1
Similarly, horizontal distance of 4 = Horizontal distance of 2 - 1= -1-1=-2
Horizontal distance of 5 = Horizontal distance of 2 + 1= -1+1 = 0
Horizontal distance of 6 = 1-1 =0
Horizontal distance of 7 = 1+1 = 2
The bottom-most node at a horizontal distance of -2 is 4.
The bottom-most node at a horizontal distance of -1 is 2.
The bottom-most node at a horizontal distance of 0 is 5 and 6. However, 6 is more towards the right, so 6 is included.
The bottom-most node at a horizontal distance of 1 is 3.
The bottom-most node at a horizontal distance of 2 is 7.
Hence, the bottom view would be 4 2 6 3 7
Problem approach
Store tree nodes in a queue for the level order traversal. Start with the horizontal distance (hd) as 0 for the root node. Using a map that stores key-value pairs sorted by key, keep adding the left child to the queue along with the horizontal distance as hd-1 and the right child as hd+1.
Every time a new horizontal distance or an existing horizontal distance is encountered, put the node data for the horizontal distance as the key. For the first time, it will add it to the map; the next time, it will replace the value. This will ensure that the bottom-most element for that horizontal distance is present in the map, and if you see the tree from beneath, you will see that element. At last, traverse the keys of the map and print their respective values.
3. Theory Questions
Explain Insertion sort, merge sort, and heap sort. Discuss algorithmic space complexity and auxiliary space complexity. (Learn)
5. DBMS
What are joins? (Learn)
6. Theory Questions
What is the difference between HTML and React event handling?
Differentiate between process.nextTick() and setImmediate()?

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Sprinklr
1295 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Sprinklr
822 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Sprinklr
981 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Sprinklr
839 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
5 rounds | 12 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
114869 views
24 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
58030 views
5 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
35057 views
7 comments
0 upvotes




