Synopsys interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - 1
Synopsys
3 rounds | 7 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Journey
There are two halves to my journey. Phase I: On CodingNinjas, we started with some simple DSA coding questions. Averaging 8 coding problems per day, I solved up to 250–300 questions that covered all the DSA principles, including dynamic programming, linked lists, arrays, trees, and graphs. Operating systems, computer networks, algorithms, databases, COA, and aptitude were all covered in Phase II.
Application story
I applied for this position on campus. It starts with an online placement test as the first elimination round. After that, I completed three interviews: two technical interviews and one HR interview. After these interviews, all the candidates selected on the same day were announced.
Why selected/rejected for the role?
I was not selected for this role due to a lack of interaction with the interviewer, as he couldn't understand my approach during the interview for a recursion-based problem. The lack of communication between our thoughts led to my rejection in the second round of interviews. However, I had prepared all the essential topics covering algorithms and data structures well.
Preparation
Duration: 2 months
Topics: Algorithms, Java, Operating Systems, Database Management Systems, Dynamic Programming, Computer Networks, and Data Structures
Tip
Tip 1: Always strive to offer the best answers to any coding challenges presented during interviews.
Tip 2: Work on your soft skills.
Tip 3: Good projects should be mentioned on your resume, and you should have questions well-prepared for them.
Tip 4: Practice at least 250–300 DSA coding questions, including dynamic programming and all other data structures.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: 6.5 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1: Mention good projects with in-depth knowledge on your resume.
Tip 2: Do not include false information on your resume.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Hard
Online Coding Interview
Duration120 minutes
Interview date16 Apr 2023
Coding problem2
This round was held in the evening, with approximately 100 candidates attending it. Audio and webcam were enabled. All the core CS subjects-related MCQs were asked, covering DSA, operating systems, databases, computer networks, and aptitude. There were a total of 4 sections with sectional cutoffs and time limits. The sections were Aptitude, CS subjects, Programming-based questions, and Digital Logic-based questions.
1. Next Greater Element
Easy
10m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given an array 'a' of size 'n'.
Print the Next Greater Element(NGE) for every element.
The Next Greater Element for an element 'x' is the first element on the right side of 'x' in the array, which is greater than 'x'.
If no greater elements exist to the right of 'x', consider the next greater element as -1.
For example:
Input: 'a' = [7, 12, 1, 20]
Output: NGE = [12, 20, 20, -1]
Explanation: For the given array,
- The next greater element for 7 is 12.
- The next greater element for 12 is 20.
- The next greater element for 1 is 20.
- There is no greater element for 20 on the right side. So we consider NGE as -1.
Problem approach
This problem can be solved easily and efficiently by using the stack data structure, as it is based on the Last In First Out (LIFO) principle.
Steps Followed:
- To find the next greater element, we start traversing the given array from the right.
- For the rightmost element, there is no other element to its right.
- Hence, we assign -1 at its index in the resultant array.
- Since this element could be the next greater element (NGE) for some other element, we push it onto the stack S.
- We continue checking for other elements.
2. Left View Of a Binary Tree
Easy
10m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You have been given a binary tree of integers. You are supposed to find the left view of the binary tree. The left view of a binary tree is the set of all nodes that are visible when the binary tree is viewed from the left side.
Example:
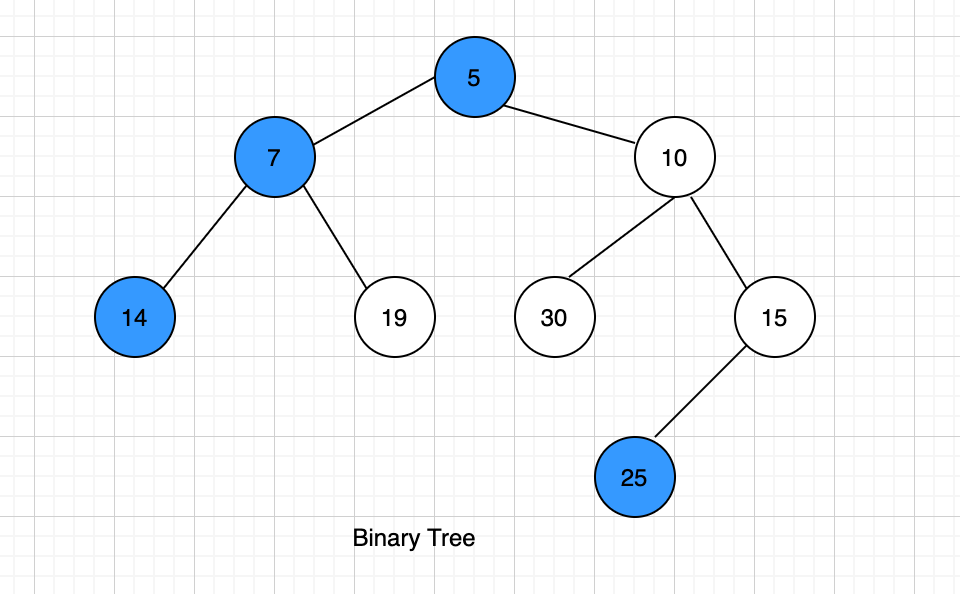
The left view of the above binary tree is {5, 7, 14, 25}.
Problem approach
Steps Followed:
- Create a vector data structure inside both the left and right side view functions.
- Call the recursive _left and _right functions respectively with the parameters (root, level, vector). The level will initially be passed as 0.
- Return the vector.
- Now, in the recursive_left function:
- If the vector size is equal to the level, push back the node value into the vector data structure.
- Otherwise, call recursive_left for (node->left, level + 1, vector).
- Call recursive_left for (node->right, level + 1, vector).
- Now, in the recursive_right function:
- If the vector size is equal to the level, push back the node value into the vector data structure.
- Otherwise, call recursive_right for (node->right, level + 1, vector).
- Call recursive_right for (node->left, level + 1, vector).
02
Round
Medium
Online Coding Test
Duration45 minutes
Interview date20 May 2023
Coding problem3
This round lasted about 45 minutes in the morning. They wanted me to share my screen and open any coding platform to solve my coding questions. They also asked me to elaborate on my project, after which they asked about my previous experiences. Following that, they asked questions specifically about linked lists and trees.
1. Delete Kth Node From End
Moderate
15m average time
95% success
0/80
Asked in companies



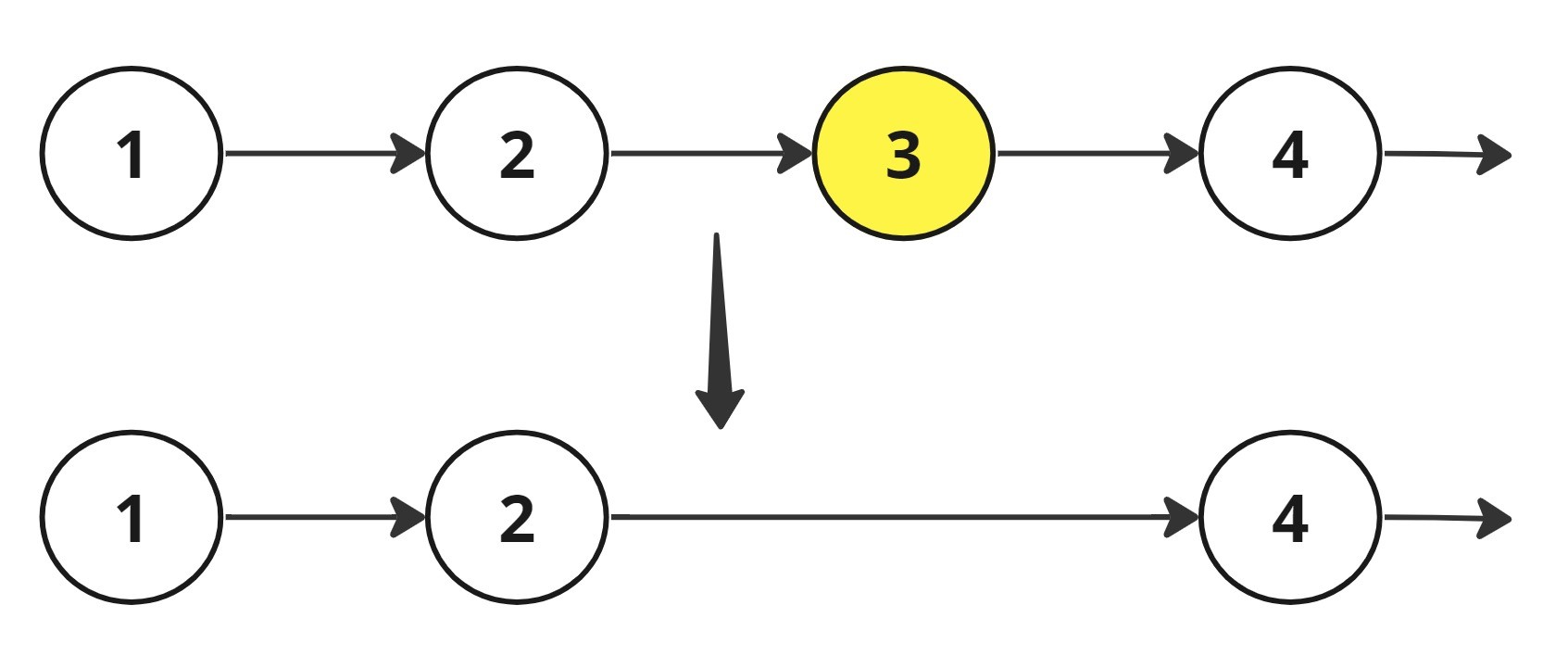
You have been given a singly Linked List of 'N' nodes with integer data and an integer 'K'.
Your task is to remove the 'K'th node from the end of the given Linked List and return the head of the modified linked list.
Example:
Input : 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 'NULL' and 'K' = 2
Output: 1 -> 2 -> 4 -> 'NULL'
Explanation:
After removing the second node from the end, the linked list become 1 -> 2 -> 4 -> 'NULL'.
Problem approach
- Take two dummy nodes, whose next will be pointing to the head.
- Take another node to store the head, initially, a dummy node (start), and the next node will be pointing to the head. The reason we use this extra dummy node is that there is an edge case. If the node is equal to the length of the linked list, then this slow will point to slow’s next → next. And we can say our dummy start node will be broken and will be connected to slow's next → next.
- Start traversing until the fast pointer reaches the nth node.
- Now start traversing one step at a time for both pointers until the fast pointer reaches the end.
- When the traversal is done, just do the deleting part. Make the slow pointer's next point to the next of the slow pointer to ignore/disconnect the given node.
- Finally, return to the next start.
2. Cycle Detection in a Singly Linked List
Moderate
15m average time
80% success
0/80
Asked in companies



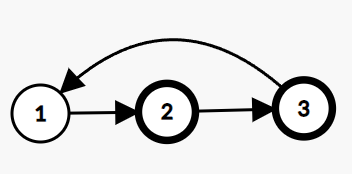
You are given a Singly Linked List of integers. Return true if it has a cycle, else return false.
A cycle occurs when a node's next points back to a previous node in the list.
Example:
In the given linked list, there is a cycle, hence we return true.
Problem approach
- Take two pointers, namely fast and slow. The fast pointer takes 2 steps ahead and the slow pointer takes 1 step ahead.
- Iterate through the list until the fast pointer is equal to NULL. This is because NULL indicates that there is no cycle present in the given list.
- A cycle can be detected when the fast and slow pointers collide.
3. Binary Tree To BST
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You have been given a binary tree consisting of ‘N’ nodes where nodes have distinct integer values. Your task is to convert the given Binary Tree to a Binary Search Tree(BST).
Note: The conversion must be done in such a way that keeps the original structure of the Binary Tree.
A binary search tree (BST) is a binary tree data structure which has the following properties.
• The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with data less than the node’s data.
• The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with data greater than the node’s data.
• Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
For Example:
For the given binary tree :
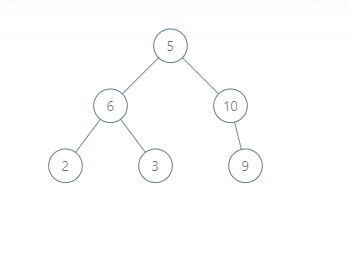
The BST will be:
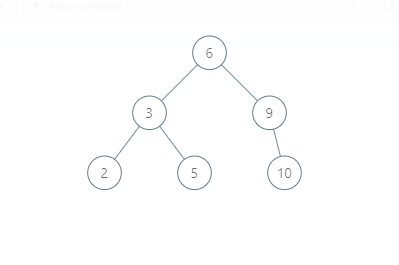
Note: Each node is associated with a unique integer value.
Problem approach
- If the current node is null, then return true.
- If the value of the left child of the node is greater than or equal to the current node, then return false.
- If the value of the right child of the node is less than or equal to the current node, then return false.
- If the left subtree or the right subtree is not a BST, then return false.
- Else, return true.
03
Round
Hard
Face to Face
Duration60 minutes
Interview date20 Jul 2023
Coding problem2
This round was a bit more difficult than the previous one because here the interviewer focuses on DSA concepts in depth, with some topics like recursion and binary trees as well. They try to gather all your knowledge of how you approach a problem.
1. Tower of Hanoi
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



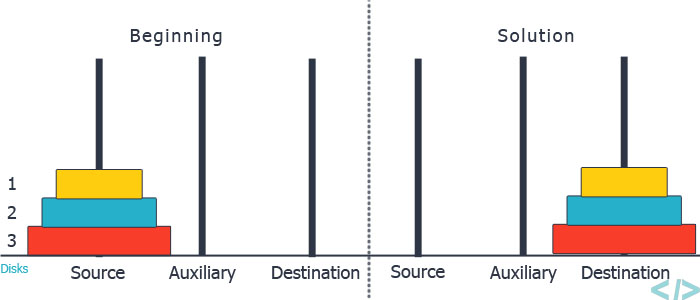
You are given three rods (numbered 1 to 3), and ‘N’ disks initially placed on the first rod, one on top of each other in increasing order of size ( the largest disk is at the bottom). You are supposed to move the ‘N’ disks to another rod(either rod 2 or rod 3) using the following rules and in less than 2 ^ (N) moves.
1. You can only move one disk in one move.
2. You can not place a larger disk on top of a smaller disk.
3. You can only move the disk at the top of any rod.
Note :
You may assume that initially, the size of the ‘i’th disk from the top of the stack is equal to ‘i’, i.e. the disk at the bottom has size ‘N’, the disk above that has size ‘N - 1’, and so on. The disk at the top has size 1.
Example :
Problem approach
Steps to be followed:
- Create a function towerOfHanoi where you pass N (the current number of disks), from_rod, to_rod, and aux_rod.
- Make a function call for the N – 1th disk.
- Then, print the current disk along with from_rod and to_rod.
- Again, make a function call for the N – 1th disk.
2. Construct BST from Level Order
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You have been given an array ‘levelOrder’ consisting of ‘N’ elements. The array represents the level order traversal of a Binary Search Tree(BST). You need to construct the BST from this level order traversal.
A Binary Search Tree (BST) is a binary tree data structure that has the following properties -
• The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with data less than the node’s data.
• The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with data greater than the node’s data.
• Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
For Example:
For the given level order traversal: 5 3 6 2 4 7
The BST will be:
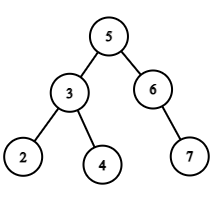
The Inorder Traversal of this BST is 2 3 4 5 6 7.
Problem approach
The idea was to keep track of the number of child nodes in the left and right subtrees, and then make the decision based on these counts.
Approach:
- When the count of child nodes in the left and right subtrees is equal, the node must be inserted into the left subtree by creating a new level in the binary tree.
- When the count of child nodes in the left subtree is greater than in the right subtree, there are two cases:
a. If the left subtree is a perfect binary tree, the node must be inserted into the right subtree.
b. If the left subtree is not a perfect binary tree, the node must be inserted into the left subtree.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Synopsys
3101 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Synopsys
1790 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Synopsys
1745 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 9 problems
Interviewed by Synopsys
1700 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by BNY Mellon
6316 views
3 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by BNY Mellon
0 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by CIS - Cyber Infrastructure
2180 views
0 comments
0 upvotes






