Thought Works interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - 1
Thought Works
3 rounds | 5 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Journey
My seniors advised me to practice DSA from the start of B.Tech, but I did not take that seriously. Honestly speaking, I regretted not taking their advice, and in the third year, I started coding, and I had to increase practice hours because I started late. By the end of the Third year, I was confident in DSA and development, but even then, I kept revising the concepts.
Application story
This company visited my campus for the placement. We just had to upload our resume and fill in all the details in the form. First, they took the online assessment. Later, they called us for the interview rounds.
Why selected/rejected for the role?
The primary reason for my rejection was my knowledge of core DSA fundamentals and my problem-solving ability could improve.
Preparation
Duration: 6 months
Topics: Data Structures, Algorithms, OOPS, Dynamic Programming
Tip
Tip 1: Practice popular questions from Arrays, Binary Trees, and LinkedLists from CodeStudio's Interview Problems
Tip 2: Make sure you are aware of calculating the time and space complexity for every problem you're coding.
Tip 3: Prepare through Mock Interviews to practice explaining your approach while solving in an actual interview.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: Above 7 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Describe best of your projects in minimum words. Don't forget to add buzz words like REST APIs/ DB Indexing/ Benchmarking etc if you worked on backend.
Tip 2 : Don't add school achievements like Olympiads or Class Topper in your resume.
Tip 3 : If you've some work experience, put it in a way ,you're marketing yourself. Add terms like Created/Owned the Project through entire SDLC.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date24 May 2023
Coding problem2
1. K - Sum Path In A Binary Tree
Moderate
35m average time
65% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given a binary tree in which each node contains an integer value and a number ‘K’. Your task is to print every path of the binary tree with the sum of nodes in the path as ‘K’.
Note:
1. The path does not need to start or end at the root or a leaf, but it must go downwards (traveling only from parent nodes to child nodes).
2. Output the paths in the order in which they exist in the tree from left to right. Example: In the below example, path {1,3} is followed by {3,1} and so on.
Example:
For K = 4 and tree given below:
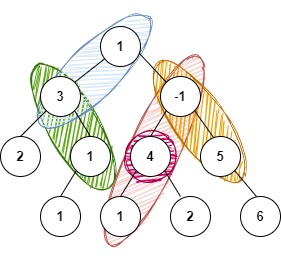
The possible paths are:
1 3
3 1
-1 4 1
4
-1 5
The sum of values of nodes of each of the above-mentioned paths gives a sum of 4.
Problem approach
I was well aware of this problem. Tree Traversal and save paths in a vector with each recursion.
2. Implementation: HashMap
Easy
30m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



Design a data structure that stores a mapping of a key to a given value and supports the following operations in constant time.
1. INSERT(key, value): Inserts an integer value to the data structure against a string type key if not already present. If already present, it updates the value of the key with the new one. This function will not return anything.
2. DELETE(key): Removes the key from the data structure if present. It doesn't return anything.
3. SEARCH(key): It searches for the key in the data structure. In case it is present, return true. Otherwise, return false.
4. GET(key): It returns the integer value stored against the given key. If the key is not present, return -1.
5. GET_SIZE(): It returns an integer value denoting the size of the data structure.
6. IS_EMPTY(): It returns a boolean value, denoting whether the data structure is empty or not.
Note :
1. Key is always a string value.
2. Value can never be -1.
Operations Performed :
First(Denoted by integer value 1): Insertion to the Data Structure. It is done in a pair of (key, value).
Second(Denoted by integer value 2): Deletion of a key from the Data Structure.
Third(Denoted by integer value 3): Search a given key in the Data Structure.
Fourth(Denoted by integer value 4): Retrieve the value for a given key from the Data Structure.
Fifth(Denoted by integer value 5): Retrieve the size of the Data Structure.
Sixth(Denoted by integer value 6): Retrieve whether the Data Structure is empty or not.
02
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date24 May 2023
Coding problem2
1. Ways To Make Coin Change
Moderate
20m average time
80% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given an infinite supply of coins of each of denominations D = {D0, D1, D2, D3, ...... Dn-1}. You need to figure out the total number of ways W, in which you can make a change for value V using coins of denominations from D. Print 0, if a change isn't possible.
2. Non-Decreasing Array
Moderate
35m average time
65% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You have been given an integer array/list 'ARR' of size 'N'. Write a solution to check if it could become non-decreasing by modifying at most 1 element.
We define an array as non-decreasing, if ARR[i] <= ARR[i + 1] holds for every i (0-based) such that (0 <= i <= N - 2).
03
Round
Easy
HR Round
Duration20 minutes
Interview date24 May 2023
Coding problem1
1. Basic HR Questions
Tell me about yourself.
Why should we hire you?
What are your strengths and weaknesses?

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Thought Works
0 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Thought Works
1198 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Thought Works
542 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Thought Works
650 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by BNY Mellon
6315 views
3 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by BNY Mellon
0 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by CIS - Cyber Infrastructure
2179 views
0 comments
0 upvotes




