Titan interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - 1
Titan
3 rounds | 7 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Journey
When I joined college, I was unaware of this Data Structure and Algorithm, which made my journey to getting an internship way more complicated. From that point, I started doing questions on leetcode and code studio.
Application story
This company visited to my campus for the placement where I applied for it .
Why selected/rejected for the role?
I was rejected because I was not able to provide a good approach to the DSA question which are being asked
Preparation
Duration: 4 months
Topics: Data Structures, Pointers, OOPS, System Design, Algorithms, Dynamic Programming
Tip
Tip 1 : Practice from Leetcode, solve Leetcode medium level problems.
Tip 2 : Brush up computer fundamentals from subjects like OS, DBMS and CN.
Tip 3 : Have a good project or good internship experience and have in-depth knowledge regarding what you have done.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: Above 7 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Have some projects on resume.
Tip 2 : Do not put false things on resume.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Hard
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date17 Jan 2022
Coding problem2
1. Preorder traversal of a BST
Moderate
15m average time
85% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You have been given an array/list 'PREORDER' representing the preorder traversal of a BST with 'N' nodes. All the elements in the given array have distinct values.
Your task is to construct a binary search tree that matches the given preorder traversal.
A binary search tree (BST) is a binary tree data structure that has the following properties:
• The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with data less than the node’s data.
• The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with data greater than the node’s data.
• Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
Note:
It is guaranteed that a BST can be always constructed from the given preorder traversal. Hence, the answer will always exist.
Example:
From PREORDER = [20, 10, 5, 15, 13, 35, 30, 42] , the following BST can be constructed:
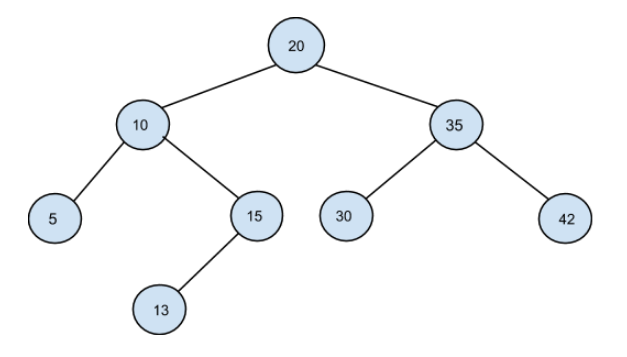
Problem approach
You have been given an array/list 'PREORDER' representing the preorder traversal of a BST with 'N' nodes. All the elements in the given array have distinct values.
Your task is to construct a binary search tree that matches the given preorder traversal.
2. Check if number is Binary
Easy
10m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



Given a string of integers ‘bin’. Return 'true' if the string represents a valid binary number, else return 'false'. A binary number is a number that has only 0 or 1 in it.
Problem approach
Given a string of integers ‘bin’. Return 'true' if the string represents a valid binary number, else return 'false'. A binary number is a number that has only 0 or 1 in it.
02
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date17 Jan 2022
Coding problem3
1. Rearrange The Array
Easy
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given an array/list NUM of integers. You are supposed to rearrange the elements of NUM such that no two adjacent elements will be the same or find out if it not possible.
For example:
Input: arr[] = {1,1,1,2,2,2}
Output: {1,2,1,2,1,2}
Note: {2,1,2,1,2,1} is also valid because there are no two adjacent elements which are the same.
Problem approach
You are given an array/list 'NUM' of integers. You are supposed to rearrange the elements of the given 'NUM' so that after rearranging the given array/list there are no two adjacent elements present in the rearranged 'NUM' which will be the same.
2. Theoretical Questions
How to find the pre order traversal of a tree?
State complexity of merge sort
Questions based on radix sort
Problem approach
Tip 1 : Practice preorder, postorder and inorder traversal questions of a tree
Tip 2 : Understand merge sort
Tip 3 : Have complete understanding of Radix sort
3. Partition to k equal sum subsets
Moderate
40m average time
70% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given an array of 'N' integers, and a positive integer 'K'. You need to determine if it is possible to divide the array into 'K' non-empty subsets such that the sum of elements of each subset is equal.
Note:
1. The array can have duplicate elements.
2. Each of the array elements must belong to exactly one of the 'K' subsets.
3. The elements chosen for a subset may not be contiguous in the array.
Problem approach
You are given an array of 'N' integers, and a positive integer 'K'. You need to determine if it is possible to divide the array into 'K' non-empty subsets such that the sum of elements of each subset is equal.
03
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date17 Jan 2022
Coding problem2
1. Partition a set into two subsets such that the difference of subset sums is minimum
Hard
10m average time
85% success
0/120
Asked in companies



You are given an array 'arr' containing 'n' non-negative integers.
Your task is to partition this array into two subsets such that the absolute difference between subset sums is minimum.
You just need to find the minimum absolute difference considering any valid division of the array elements.
Note:
1. Each array element should belong to exactly one of the subsets.
2. Subsets need not always be contiguous.
For example, for the array : [1, 2, 3], some of the possible divisions are
a) {1,2} and {3}
b) {1,3} and {2}.
3. Subset-sum is the sum of all the elements in that subset.
Example:
Input: 'n' = 5, 'arr' = [3, 1, 5, 2, 8].
Ouput: 1
Explanation: We can partition the given array into {3, 1, 5} and {2, 8}.
This will give us the minimum possible absolute difference i.e. (10 - 9 = 1).
Problem approach
You are given an array containing N non-negative integers. Your task is to partition this array into two subsets such that the absolute difference between subset sums is minimum.
You just need to find the minimum absolute difference considering any valid division of the array elements.
2. Find prime numbers
Easy
15m average time
80% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given a positive integer ‘N’. Your task is to print all prime numbers less than or equal to N.
Note: A prime number is a natural number that is divisible only by 1 and itself. Example - 2, 3, 17, etc.
You can assume that the value of N will always be greater than 1. So, the answer will always exist.
Problem approach
You are given a positive integer ‘N’. Your task is to print all prime numbers less than or equal to N.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Titan
1008 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 8 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
8770 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
1 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
3407 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 2
4 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by Expedia Group
2661 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
5 rounds | 12 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
114869 views
24 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
58031 views
5 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
35057 views
7 comments
0 upvotes





