Twilio interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE
Twilio
3 rounds | 6 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Journey
I started doing coding in Java by taking course from coding ninjas in 2nd year. Before this I was exploring different programming like python, c++ , java. So I choose java. After completing the course i started practicing on geeksforgeeks and leetcode. After this in 3rd year I have made mini project. I have also taken inhouse training on ML.
Application story
Company organize a nation wide test for the selection i have applied on the company website for the same
Why selected/rejected for the role?
I was rejected because i was not able to provide them the solution and explanation they want me to give to them.
Preparation
Duration: 4 months
Topics: Data Structures, Pointers, OOPS, System Design, Algorithms, Dynamic Programming
Tip
Tip 1 : Must do Previously asked Interview as well as Online Test Questions.
Tip 2 : Go through all the previous interview experiences from Codestudio and Leetcode.
Tip 3 : Do at-least 2 good projects and you must know every bit of them.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: Above 7 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Have some projects on resume.
Tip 2 : Do not put false things on resume.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date10 Feb 2023
Coding problem2
1. Spiral Order Traversal of a Binary Tree
Easy
20m average time
75% success
0/40
Asked in companies


You have been given a binary tree of 'N' nodes. Print the Spiral Order traversal of this binary tree.
For example
For the given binary tree [1, 2, 3, -1, -1, 4, 5, -1, -1, -1, -1]
1
/ \
2 3
/ \
4 5
Output: 1 3 2 4 5
Problem approach
Approach 1 (Using Level Order Traversal) :
Steps :
1) Initialize an array ‘spiral’ to store the result.
2) Initialize a variable ‘direction’ to keep track of traversing direction with 1(denoting left to right)
3) Find the height of the given tree and store it in a variable ‘height’.
4) Run a loop - level : 1 to height, to traverse through every level.
4.1) Find level order traversal in the current direction.and store in ‘spiral’
4.2) Toggle the direction.
5) Return ‘spiral’
TC : O(N^2), where ‘N’ is the number of nodes in the binary tree.
SC : O(h), where 'h' is the height of the binary tree.
Approach 2 (Using Stack) :
Steps :
1) We will maintain two stacks, one for each direction i.e. leftToRight and rightToleft.
2) We will do a level order traversal of the given binary tree and push nodes of each level onto one of the
stack according to the current direction of traversal.
3) After we’ve pushed all nodes of a level onto one stack, we’ll start popping those nodes.
4) While popping the nodes we will push their children (if any) onto our other direction stack, so that the
next level be traversed in reverse order.
TC : O(N), where ‘N’ is the number of nodes in the binary tree.
SC : O(N)
2. Conceptual Question
Difference between structure and union and what are the pros and cons of both?
Problem approach
Answer :
Structure : Structure is a user-defined data type in C programming language that combines logically related data items of different data types together.
All the structure elements are stored at contiguous memory locations. Structure type variable can store more than one data item of varying data types under one name.
Union : Union is a user-defined data type, just like a structure. Union combines objects of different types and sizes together. The union variable allocates the memory space equal to the space to hold the largest variable of union. It allows varying types of objects to share the same location.
Key differences b/w Structure and Union :
1) Every member within structure is assigned a unique memory location while in union a memory location is shared by all the data members.
2) Changing the value of one data member will not affect other data members in structure whereas changing the value of one data member will change the value of other data members in union.
3) Structure is mainly used for storing various data types while union is mainly used for storing one of the many data types.
4) In structure, you can retrieve any member at a time on the other hand in union, you can access one member at a time.
5) Structure supports flexible array while union does not support a flexible array.
Advantages and Disadvantages of using Structure :
Advantages :
1) Structures gather more than one piece of data about the same subject together in the same place.
2) It is helpful when you want to gather the data of similar data types and parameters like first name, last
name, etc.
3) It is very easy to maintain as we can represent the whole record by using a single name.
Disadvantages :
1 )If the complexity of IT project goes beyond the limit, it becomes hard to manage.
2) Change of one data structure in a code necessitates changes at many other places. Therefore, the
changes become hard to track.
3) Structure is slower because it requires storage space for all the data.
02
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date10 Feb 2023
Coding problem2
1. Diameter Of Binary Tree
Easy
10m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given a Binary Tree.
Return the length of the diameter of the tree.
Note :
The diameter of a binary tree is the length of the longest path between any two end nodes in a tree.
The number of edges between two nodes represents the length of the path between them.
Example :
Input: Consider the given binary tree:
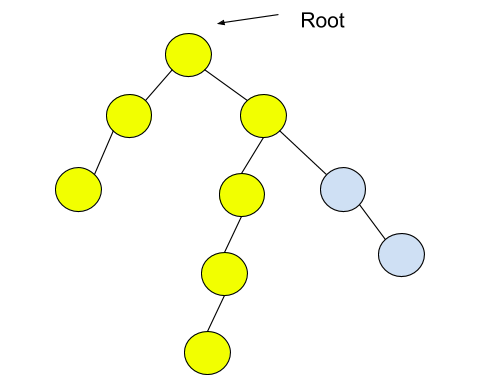
Output: 6
Explanation:
Nodes in the diameter are highlighted. The length of the diameter, i.e., the path length, is 6.
Problem approach
You are given a Binary Tree. You are supposed to return the length of the diameter of the tree.
2. Shortest Path in a Binary Matrix
Moderate
37m average time
65% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You have been given a binary matrix of size 'N' * 'M' where each element is either 0 or 1. You are also given a source and a destination cell, both of them lie within the matrix.
Your task is to find the length of the shortest path from the source cell to the destination cell only consisting of 1s. If there is no path from source to destination cell, return -1.
Note:
1. Coordinates of the cells are given in 0-based indexing.
2. You can move in 4 directions (Up, Down, Left, Right) from a cell.
3. The length of the path is the number of 1s lying in the path.
4. The source cell is always filled with 1.
For example -
1 0 1
1 1 1
1 1 1
For the given binary matrix and source cell(0,0) and destination cell(0,2). Few valid paths consisting of only 1s are
X 0 X X 0 X
X X X X 1 X
1 1 1 X X X
The length of the shortest path is 5.
Problem approach
Approach : I solved this problem using BFS.
Breadth-First-Search considers all the paths starting from the source and moves ahead one unit in all those paths at the same time. This makes sure that the first time when the destination is visited, it is the path with the shortest length.
Steps :
1) Create an empty queue and enqueue source cell and mark it as visited
2) Declare a ‘STEPS’ variable, to keep track of the length of the path so far
3) Loop in level order till the queue is not empty
3.1) Fetch the front cell from the queue
3.2) If the fetched cell is the destination cell, return ‘STEPS’
3.3) Else for each of the 4 adjacent cells of the current cell, we enqueue each valid cell into the queue
and mark them visited.
3.4) Increment ‘STEPS’ by 1 when all the cells in the current level are processed.
4) If all nodes in the queue are processed and the destination cell is not reached, we return -1.
TC : O(N*M), where ‘N’ and ‘M’ are the number of rows and columns in the Binary Matrix respectively.
SC : O(N*M)
03
Round
Easy
HR Round
Duration20 minutes
Interview date10 Feb 2023
Coding problem2
1. Basic HR Questions
How do you feel about working nights and weekends?
Can you work under pressure?
2. Basic HR Questions
Are you willing to relocate or travel?
What are your goals?
What motivates you to do good job?

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Twilio
806 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Twilio
821 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Twilio
655 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by Twilio
494 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE
3 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by PhonePe
0 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE
5 rounds | 8 problems
Interviewed by Mathworks
1214 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE
4 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by PhonePe
0 views
0 comments
0 upvotes






