UST Global interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
Software Engineer
UST Global
3 rounds | 11 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 4 months
Topics: Data Structures, Algorithms, Aptitude, DBMS, OOPS
Tip
Tip 1 : Must do Previously asked Interview as well as Online Test Questions.
Tip 2 : Go through all the previous interview experiences from Codestudio and Leetcode.
Tip 3 : Do at-least 2 good projects and you must know every bit of them.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: Above 7 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Have at-least 2 good projects explained in short with all important points covered.
Tip 2 : Every skill must be mentioned.
Tip 3 : Focus on skills, projects and experiences more.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Medium
Online Coding Interview
Duration150 minutes
Interview date29 Nov 2021
Coding problem3
It was an Aptitude test and Technical objective test of 60 minutes followed by a Coding test of 90 minutes.There was a 1 hour gap b/w the two tests.
1. Compress the String
Moderate
32m average time
60% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Write a program to do basic string compression. For a character which is consecutively repeated more than once, replace consecutive duplicate occurrences with the count of repetitions.
Example:
If a string has 'x' repeated 5 times, replace this "xxxxx" with "x5".
The string is compressed only when the repeated character count is more than 1.
Note:
Consecutive count of every character in the input string is less than or equal to 9. You are not required to print anything. It has already been taken care of. Just implement the given function and return the compressed string.
Problem approach
This was nothing but the Run Length Encoding Algorithm which I was familiar with. So I coded it preety fast.
Algorithm :
1) Pick the first character from the source string.
2) Append the picked character to the destination string.
3) Count the number of subsequent occurrences of the picked character and append the count to the destination string.
4) Pick the next character and repeat steps (2),(3) and (4) if the end of the string is NOT reached.
TC : O(N), where N=length of the string
SC : O(1)
2. Count all k-sum paths in a Binary Tree
Moderate
35m average time
65% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given a binary tree in which each node contains an integer value and a number ‘K’. Your task is to print every path of the binary tree with the sum of nodes in the path as ‘K’.
Note:
1. The path does not need to start or end at the root or a leaf, but it must go downwards (traveling only from parent nodes to child nodes).
2. Output the paths in the order in which they exist in the tree from left to right. Example: In the below example, path {1,3} is followed by {3,1} and so on.
Example:
For K = 4 and tree given below:
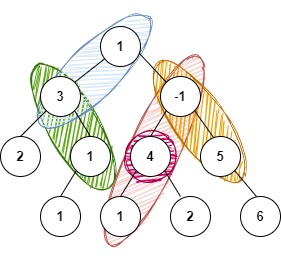
The possible paths are:
1 3
3 1
-1 4 1
4
-1 5
The sum of values of nodes of each of the above-mentioned paths gives a sum of 4.
Problem approach
The idea is simple: along the path, record all prefix sums in a hash table. For current prefix sum x, check if (x - target) appears in the hash table.
Steps :
1) We will be using a unordered map which will be filled with various path sum.
2) For every node we will check if current sum and root’s value equal to k or not. If the sum equals to k then increment the required answer by one.
3) Then we will add all those path sum in map which differs from current sum+root->data value by a constant integer k.
4) Then we will be inserting the current sum + root->data value in the map.
5) We will recursively check for left and right subtrees of current root
6) After the right subtree is also traversed we will remove the current sum + root->data value from the map so that it is not taken into consideration in further traversals of other nodes other than the current root’s.
TC : O(N) , where N is the total number of nodes in the tree
SC : O(N)
3. Longest Increasing Subsequence
Moderate
30m average time
65% success
0/80
Asked in companies



For a given array with N elements, you need to find the length of the longest subsequence from the array such that all the elements of the subsequence are sorted in strictly increasing order.
Strictly Increasing Sequence is when each term in the sequence is larger than the preceding term.
For example:
[1, 2, 3, 4] is a strictly increasing array, while [2, 1, 4, 3] is not.
Problem approach
Approach (Using DP) :
1) dp[i] stores the max length of the LIS ending at position ‘i’.
2) In order to find out dp[i + 1], we need to try to append the current element in every possible increasing subsequence up to the i’th index, such that the new sequence formed by adding the current element is also an increasing subsequence.
3) Thus, we can easily determine dp[i] using :
dp[i + 1] = max(dp[j]) + 1, ∀ 0 ≤ j <= i and arr[i + 1] > arr[j]
4) In the end, the maximum out of all the dp[i]'s to determine the final result.
TC : O(N^2), where N=size of the array
SC : O(N)
02
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration50 minutes
Interview date29 Nov 2021
Coding problem3
This was also a Data Structures and Algorithms round where I was asked to solve 2 coding problems explaining my approach with proper Complexity Analysis . After the coding questions were over there was some time left so the interviewer asked me some concepts related to DBMS.
1. Trapping Rainwater Problem
Moderate
15m average time
80% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You have been given a long type array/list 'arr’ of size 'n’.
It represents an elevation map wherein 'arr[i]’ denotes the elevation of the 'ith' bar.
Print the total amount of rainwater that can be trapped in these elevations.
Note :
The width of each bar is the same and is equal to 1.
Example:
Input: ‘n’ = 6, ‘arr’ = [3, 0, 0, 2, 0, 4].
Output: 10
Explanation: Refer to the image for better comprehension:

Note :
You don't need to print anything. It has already been taken care of. Just implement the given function.
Problem approach
Approach :
1) Get the ‘PEAK’ value.
2) Move from left to right in the elevation map towards the ‘PEAK’. Maintain three variables :
2.1) ‘maxSoFar’ is the maximum elevation that has been encountered on the way towards ‘PEAK’.
2.2) ‘countSubmerged’ which are the elevations that are smaller than the ‘maxSoFar’.
2.3) ‘submergedArea’ which is ‘ARR[i]' * 1.
3) Now, every time a new ‘maxSoFar’ is reached, add ('maxSoFar' * ‘countSubmerged’ - ‘submergedArea’) to a running sum.
4) Repeat the same from right to left.
TC : O(N), where N=total number of elevations in the map.
SC : O(1)
2. Implement next_permutation function.
Moderate
15m average time
85% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You have been given a permutation of ‘N’ integers. A sequence of ‘N’ integers is called a permutation if it contains all integers from 1 to ‘N’ exactly once. Your task is to rearrange the numbers and generate the lexicographically next greater permutation.
To determine which of the two permutations is lexicographically smaller, we compare their first elements of both permutations. If they are equal — compare the second, and so on. If we have two permutations X and Y, then X is lexicographically smaller if X[i] < Y[i], where ‘i’ is the first index in which the permutations X and Y differ.
For example, [2, 1, 3, 4] is lexicographically smaller than [2, 1, 4, 3].
Problem approach
Approach :
1) Find the first pair of two successive numbers a[i] and a[i-1] , from the right, which satisfy a[i] > a[i−1].
2) Rearrange the numbers to the right of a[i-1] including itself.
3) Replace the number a[i-1] with the number which is just larger than itself among the numbers lying to its right section, say a[j].
4) Swap the numbers a[i-1] and a[j] .
5) Reverse the numbers following a[i-1] to get the next smallest lexicographic permutation.
TC : O(N)
SC : O(1)
3. DBMS Question
Explain Indexing in Databases.
Problem approach
Answer :
Indexing : Indexing is a way to optimize the performance of a database by minimizing the number of disk accesses required when a query is processed. It is a data structure technique which is used to quickly locate and access the data in a database.
Index Structure : Indexes can be created using some database columns.
1) The first column of the database is the search key that contains a copy of the primary key or candidate key of the table. The values of the primary key are stored in sorted order so that the corresponding data can be accessed easily.
2) The second column of the database is the data reference. It contains a set of pointers holding the address of the disk block where the value of the particular key can be found.
Indexing Methods :
There are primarily three methods of indexing :
1) Clustered Indexing
2) Non-Clustered or Secondary Indexing
3) Multilevel Indexing
1) Clustered Indexing :
When more than two records are stored in the same file these types of storing known as cluster indexing. By using the cluster indexing we can reduce the cost of searching reason being multiple records related to the same thing are stored at one place and it also gives the frequent joining of more than two tables (records).
1.1) Primary Indexing : This is a type of Clustered Indexing wherein the data is sorted according to the search key and the primary key of the database table is used to create the index. It is a default format of
indexing where it induces sequential file organization.
2) Non-clustered or Secondary Indexing :
A non clustered index just tells us where the data lies, i.e. it gives us a list of virtual pointers or references to the location where the data is actually stored. Data is not physically stored in the order of the index. Instead, data is present in leaf nodes.
3) Multilevel Indexing :
With the growth of the size of the database, indices also grow. As the index is stored in the main memory, a single-level index might become too large a size to store with multiple disk accesses. The multilevel indexing segregates the main block into various smaller blocks so that the same can stored in a single block.
03
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date29 Nov 2021
Coding problem5
This round was also held on Google Meet where I was supposed to code 2 problems in a Google Doc. After the coding questions , I was asked some core concepts related to OS.
1. Two Sum Problem
Easy
10m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given an array of integers 'ARR' of length 'N' and an integer Target. Your task is to return all pairs of elements such that they add up to Target.
Note:
We cannot use the element at a given index twice.
Follow Up:
Try to do this problem in O(N) time complexity.
Problem approach
Approach :
1) We can store the frequency of every element in the array in a hashmap.
2) We will loop over every index i, and check the frequency of (Target - ARR[i]) is the hashmap :
2.1) If (Target - ARR[i]) is equal to ARR[i], we will check if frequency of ARR[i] . If it is greater than 1 then we will decrease the frequency of ARR[i] by 2 and add a pair (ARR[i] , ARR[i]) to our answer.
2.2) Else, if the frequency of ARR[i] and Target - ARR[i] is greater than equal to 1 then we add pair (ARR[i], Target - ARR[i]) to our answer and decrease the frequency of both by 1.
3) If no valid pairs exist, we will return [[-1,-1]].
TC : O(N), where N=size of the array
SC : O(N)
2. Convert Sentence
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given a sentence in the form of a string ‘S’. You have to convert ‘S’ into its equivalent mobile numeric keypad sequence, i.e. print the sequence in such a way that if it is typed on the given keypad, the output should be the string ‘S’. A keypad for the reference is shown below.

Note:
1. There will be only lower case letters.
2. There will not be any special characters or capital letters in the input string.
3. There will be no spaces in the string.
Problem approach
Approach :
1) For each character, we can store what should be typed on the keypad. We can store this information in a string array named ‘freq’.
2) The size of freq[] will be 26 and index 0 will store the pattern for ‘a’, index 1 will store the pattern for ‘b’ and so on..Index 25 will store the pattern for ‘z’.
3) The pattern for ‘a’ is 2, for ‘z’ is 9999, for ‘n’ is 66 and so on.
4) After storing the pattern in the array, we will take an output string and while traversing the string and we will get the pattern corresponding to the current character from the freq array and add it to our output string.
TC : O(N), where N=size of the string
SC : O(26)
3. Operating System Question
What do you mean by FCFS?
Problem approach
1) FCFS (First Come First Serve) is a type of OS scheduling algorithm that executes processes in the same order in which processes arrive.
2) In simple words, the process that arrives first will be executed first. It is non-preemptive in nature.
3) FCFS scheduling may cause the problem of starvation if the burst time of the first process is the longest among all the jobs.
4) Burst time here means the time that is required in milliseconds by the process for its execution.
5) It is also considered the easiest and simplest OS scheduling algorithm as compared to others.
6) Implementation of FCFS is generally managed with help of the FIFO (First In First Out) queue.
4. Operating System Question
Print 1 to 100 using more than two threads(optimized approach).
Problem approach
Prerequisite to solve this problem : Multithreading
The idea is to create two threads and print even numbers with one thread and odd numbers with another thread.
Below are the steps :
1) Create two threads T1 and T2 , where T1 and T2 are used to print odd and even numbers respectively.
2) Maintain a global counter variable and start both threads.
3) If the counter is even in the Thread T1, then wait for the thread T2 to print that even number. Otherwise, print that odd number, increment the counter and notify to the Thread T2 .
4)If the counter is odd in the Thread T2, then wait for the thread T1 to print that even number. Otherwise, print that even number, increment the counter and notify the Thread T1.
5. Operating System Question
Difference between Process and Thread
Problem approach
Process : A process is the execution of a program that allows us to perform the appropriate actions specified in a program. It can be defined as an execution unit where a program runs. The OS helps us to create, schedule, and terminates the processes which is used by CPU. The other processes created by the main process are called child process.
Thread : Thread is an execution unit that is part of a process. A process can have multiple threads, all executing at the same time. It is a unit of execution in concurrent programming. A thread is lightweight and can be managed independently by a scheduler. It helps us to improve the application performance using parallelism.
Major Differences b/w Process and Thread :
1) Process means a program is in execution, whereas thread means a segment of a process.
2) A Process is not Lightweight, whereas Threads are Lightweight.
3) A Process takes more time to terminate, and the thread takes less time to terminate.
4) Process takes more time for creation, whereas Thread takes less time for creation.
5) Process likely takes more time for context switching whereas as Threads takes less time for context switching.
6) A Process is mostly isolated, whereas Threads share memory.
7) Process does not share data, and Threads share data with each other.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
Software Analyst
3 rounds | 17 problems
Interviewed by UST Global
2154 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Trainee Engineer
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by UST Global
3228 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by UST Global
1270 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 9 problems
Interviewed by Salesforce
3567 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
Software Engineer
4 rounds | 1 problems
Interviewed by Newgen Software
3238 views
2 comments
0 upvotes
Software Engineer
3 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by HashedIn
2621 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Software Engineer
2 rounds | 2 problems
Interviewed by Ernst & Young (EY)
0 views
0 comments
0 upvotes








