Valuefy Solutions interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - 1
Valuefy Solutions
3 rounds | 5 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Journey
In the beginning, I started learning basic concepts such as arrays, strings, stacks, and queues while solving problems on coding platforms. After gaining confidence in these fundamental topics, I moved on to more advanced ones like linked lists, trees, graphs, and dynamic programming. I practiced these topics on various online coding platforms.
Application story
Applied through a referral, and the entire process was conducted online. The first round was an online technical test that contained coding questions. After clearing the online technical round, there was one interview round conducted by SDEs.
Why selected/rejected for the role?
I was selected for the role because I was able to satisfy the interviewer with my answers to all DSA problems as well as competitive mathematical problems.
Preparation
Duration: 3 months
Topics: Data Structures and Algorithms, Operating Systems, DBMS, OOP Concepts, Hashing, and Computer Networks
Tip
Tip 1: You should have excellent problem-solving skills.
Tip 2: Code a lot.
Tip 3: You should be thorough with your concepts of Data Structures and Algorithms.
Tip 4: Know the complexities of the code you’ve written.
Application process
Where: Referral
Eligibility: 7 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1: Mention your important projects in detail.
Tip 2: Try to keep your resume to a single page. Highlight your skills, projects, and work experience more than your CGPA. Ensure proper spacing and a professional font.
Tip 3: Keep it precise and concise.
Tip 4: Mention achievements relevant to the role you are applying for.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Medium
Online Coding Test
Duration50 minutes
Interview date5 Jan 2022
Coding problem2
The test was in the morning from 10:00 to 12:00. It was a two-round test. There was a 45-minute MCQ-based Technical and Cognitive Assessment Round. Only those candidates who cleared this round could sit in the next round, a 45-minute coding test. There was a sectional cutoff that needed to be cleared in order to proceed to the coding round. The CoCubes test platform was fairly easy to understand and user-friendly.
The coding round was fairly simple. It had two very easy array-based questions.
1. All Prime Numbers less than or equal to N
Moderate
10m average time
90% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given a positive integer 'N'. Your task is to return all the prime numbers less than or equal to the 'N'.
Note:
1) A prime number is a number that has only two factors: 1 and the number itself.
2) 1 is not a prime number.
Problem approach
I applied sieve of Eratosthenes to find all prime numbers in that range.
2. Preorder Traversal
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given the root node of a binary tree consisting of ‘N’ nodes. Your task is to return its preorder traversal. The preorder traversal of a binary tree is defined as a process of traversing each node in the following manner-:
1- Visit the root node.
2- Traverse all nodes in the left subtree of the root node.
3- Traverse all the nodes in the right subtree of the root node.
For Example:
For the given tree below,
Preorder traversal for the given tree will be [1, 2, 4, 5, 3]. Hence, the answer is [1, 2, 4, 5, 3].

Example:
Elements are in the level order form. The input consists of values of nodes separated by a single space in a single line. In case a node is null, we take -1 in its place.
For example, the input for the tree depicted in the below image would be :
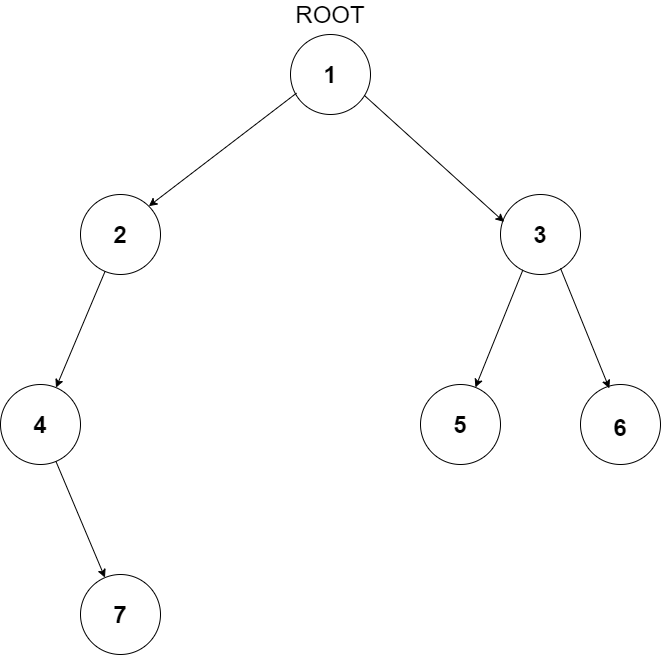
1
2 3
4 -1 5 6
-1 7 -1 -1 -1 -1
-1 -1
Explanation :
Level 1 :
The root node of the tree is 1
Level 2 :
Left child of 1 = 2
Right child of 1 = 3
Level 3 :
Left child of 2 = 4
Right child of 2 = null (-1)
Left child of 3 = 5
Right child of 3 = 6
Level 4 :
Left child of 4 = null (-1)
Right child of 4 = 7
Left child of 5 = null (-1)
Right child of 5 = null (-1)
Left child of 6 = null (-1)
Right child of 6 = null (-1)
Level 5 :
Left child of 7 = null (-1)
Right child of 7 = null (-1)
The first not-null node (of the previous level) is treated as the parent of the first two nodes of the current level.
The second not-null node (of the previous level) is treated as the parent node for the next two nodes of the current level and so on.
The input ends when all nodes at the last level are null (-1).
Note :
The above format was just to provide clarity on how the input is formed for a given tree.
The sequence will be put together in a single line separated by a single space. Hence, for the above-depicted tree, the input will be given as:
1 2 3 4 -1 5 6 -1 7 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1
Problem approach
Recursive approach helps to solve this problem.
02
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration40 minutes
Interview date6 Jan 2022
Coding problem2
1. Cycle Detection in a Singly Linked List
Moderate
15m average time
80% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given a Singly Linked List of integers. Return true if it has a cycle, else return false.
A cycle occurs when a node's next points back to a previous node in the list.
Example:
In the given linked list, there is a cycle, hence we return true.
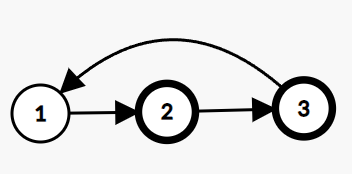
Problem approach
Implemented using the two-pointer concept.
2. Sudoku Solver
Hard
25m average time
75% success
0/120
Asked in companies



You have been given a 9x9 2d integer matrix 'MAT' representing a Sudoku puzzle. The empty cells of the Sudoku are filled with zeros, and the rest of the cells are filled with integers from 1 to 9. Your task is to fill all the empty cells such that the final matrix represents a Sudoku solution.
Note:
A Sudoku solution must satisfy all the following conditions-
1. Each of the digits 1-9 must occur exactly once in each row.
2. Each of the digits 1-9 must occur exactly once in each column.
3. Each of the digits 1-9 must occur exactly once in each of the 9, 3x3 sub-grids of the grid.
You can also assume that there will be only one sudoku solution for the given matrix.
03
Round
Easy
HR Round
Duration30 minutes
Interview date6 Jan 2022
Coding problem1
1. Basic HR Questions
- Introduce yourself.
- What do you do on a stressful day?
- Describe a situation that demonstrates your time management skills.
- What do you know about our company?
- Why did you choose our company?
Problem approach
Tip 1: Be confident when replying.
Tip 2: Put a soft smile on your face.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 8 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
8770 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Analytics Consultant
3 rounds | 10 problems
Interviewed by ZS
937 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
1 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
3406 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 2
4 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by Expedia Group
2660 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by BNY Mellon
6315 views
3 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by BNY Mellon
0 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by CIS - Cyber Infrastructure
2179 views
0 comments
0 upvotes







