VMware Inc interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - 1
VMware Inc
4 rounds | 13 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 6 months
Topics: Data Structures, Algorithms, System Design, Aptitude, OOPS
Tip
Tip 1 : Must do Previously asked Interview as well as Online Test Questions.
Tip 2 : Go through all the previous interview experiences from Codestudio and Leetcode.
Tip 3 : Do at-least 2 good projects and you must know every bit of them.
Application process
Where: Other
Eligibility: Above 7 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Have at-least 2 good projects explained in short with all important points covered.
Tip 2 : Every skill must be mentioned.
Tip 3 : Focus on skills, projects and experiences more.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Medium
Face to Face
Duration60 minutes
Interview date22 May 2015
Coding problem4
Technical Interview round with questions based on DSA.
1. Reverse the String
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given a string 'STR'. The string contains [a-z] [A-Z] [0-9] [special characters]. You have to find the reverse of the string.
For example:
If the given string is: STR = "abcde". You have to print the string "edcba".
follow up:
Try to solve the problem in O(1) space complexity.
Problem approach
This can be done by iterative swapping using two pointers. The first pointer points to the beginning of the string, whereas the second pointer points to the end. Both pointers keep swapping their elements and go towards each other. Essentially, the algorithm simulates the rotation of a string with respect to its midpoint.
Time Complexity : O(n)
2. Flip Bits
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given an array of integers ARR[] of size N consisting of zeros and ones. You have to select a subset and flip bits of that subset. You have to return the count of maximum one’s that you can obtain by flipping chosen sub-array at most once.
A flip operation is one in which you turn 1 into 0 and 0 into 1.
For example:
If you are given an array {1, 1, 0, 0, 1} then you will have to return the count of maximum one’s you can obtain by flipping anyone chosen sub-array at most once, so here you will clearly choose sub-array from the index 2 to 3 and then flip it's bits. So, the final array comes out to be {1, 1, 1, 1, 1} which contains five ones and so you will return 5.
Problem approach
The brute force solution is to consider all subarrays and find a subarray with maximum value of (count of 1s) – (count of 0s). Let this value be max_diff. Finally, return count of zeros in original array plus max_diff.
The problem can also be solved efficiently in O(n) time complexity. This problem can be reduced to largest subarray sum problem. The idea is to consider every 0 as -1 and every 1 as 1, find the sum of largest subarray sum in this modified array. This sum is our required max_diff ( count of 0s – count of 1s in any subarray). Finally we return the max_diff plus count of zeros in original array.
Pseudocode :
findMaxZeroCount(bool array, n)
{
// Initialize count of zeros and maximum difference between count of 1s and 0s in a subarray
orig_zero_count = 0;
// Initiale overall max diff for any subarray
max_diff = 0;
// Initialize current diff
curr_max = 0;
for (int i=0; i {
// Count of zeros in original array
if (arr[i] == 0)
orig_zero_count++;
// Value to be considered for finding maximum sum
val = (arr[i] == 1)? 1 : -1;
// Update current max and max_diff
curr_max = max(val, curr_max + val);
max_diff = max(max_diff, curr_max);
}
max_diff = max(0, max_diff);
return orig_zero_count + max_diff;
}
3. Check If Preorder Traversal Is Valid
Moderate
35m average time
65% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given an array 'ARR' of positive integers. Your task is to check whether the array 'ARR' is a valid Preorder Traversal of a Binary Search Tree.
A binary search tree (BST), also called an ordered or sorted binary tree, is a rooted binary tree whose internal nodes each store a value greater than or equal all the values in the node's left subtree and less than those in its right subtree.
For Example
Consider the array ARR = [ 7, 4, 8 ] having 3 elements.
This array represents the pre-order traversal of the below tree.
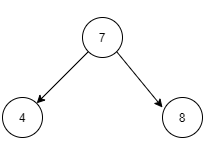
Hence, the above array 'ARR' is a valid Preorder Traversal of a Binary Search Tree.
Problem approach
This problem is similar to Next Greater Element. A stack can be used to find the next greater element and after finding next greater, if we find a smaller element, then return false.
Steps :
1) Create an empty stack.
2) Initialize root as INT_MIN.
3) Do following for every element pre[i]
a) If pre[i] is smaller than current root, return false.
b) Keep removing elements from stack while pre[i] is greater then stack top. Make the last removed item as new root (to be compared next). At this point, pre[i] is greater than the removed root. (That is why if we see a smaller element in step a), we return false)
c) push pre[i] to stack (All elements in stack are in decreasing order)
Time Complexity : O(N)
4. First and Last Position of an Element In Sorted Array
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You have been given a sorted array/list 'arr' consisting of ‘n’ elements. You are also given an integer ‘k’.
Now, your task is to find the first and last occurrence of ‘k’ in 'arr'.
Note :
1. If ‘k’ is not present in the array, then the first and the last occurrence will be -1.
2. 'arr' may contain duplicate elements.
Example:
Input: 'arr' = [0,1,1,5] , 'k' = 1
Output: 1 2
Explanation:
If 'arr' = [0, 1, 1, 5] and 'k' = 1, then the first and last occurrence of 1 will be 1(0 - indexed) and 2.
Problem approach
The Naive approach is to remove every second element from the array until the size of the array becomes equals to ‘1’.
The time complexity of this approach is O(n2).
The Efficient approach is to use recursion. Let’s consider n to be even. In one traversal, numbers 2, 4, 6 … N will be removed and we start again from 1. Thus, exactly n/2 numbers are removed, and we start as if from 1 in an array of N/2 containing only odd digits 1, 3, 5, … n/2.
Thus the recursive formula can be written as :
If n is even:
solve(n) = 2 * solve(n/2) - 1
else
solve(n) = 2 * solve((n-1) / 2) + 1
Base condition would occur when n = 1, then answer would be 1.
02
Round
Medium
Face to Face
Duration60 minutes
Interview date22 May 2015
Coding problem4
Technical round with questions based on DSA, OS, OOPS etc.
1. Intersection Of Two Arrays
Easy
10m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given two arrays 'A' and 'B' of size 'N' and 'M' respectively. Both these arrays are sorted in non-decreasing order. You have to find the intersection of these two arrays.
Intersection of two arrays is an array that consists of all the common elements occurring in both arrays.
Note :
1. The length of each array is greater than zero.
2. Both the arrays are sorted in non-decreasing order.
3. The output should be in the order of elements that occur in the original arrays.
4. If there is no intersection present then return an empty array.
Problem approach
Union :
1) Initialize an empty hash set or hash map mp;
2) Iterate through the first array and put every element of the first array in the set mp.
3) Repeat the process for the second array.
4) Print the set mp.
Time complexity : O(m+n) under the assumption that hash table search and insert operations take O(1) time.
Space complexity : O(m+n) in case of Union and O(min(m,n)) in case of Intersection
2. Remove Duplicates From Unsorted Linked List
Moderate
15m average time
85% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given a linked list of N nodes. Your task is to remove the duplicate nodes from the linked list such that every element in the linked list occurs only once i.e. in case an element occurs more than once, only keep its first occurrence in the list.
For example :
Assuming the linked list is 3 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 2 -> 3 -> NULL.
Number ‘2’ and ‘3’ occurs more than once. Hence we remove the duplicates and keep only their first occurrence. So, our list becomes : 3 -> 2 -> 4 -> NULL.
Problem approach
The brute force approach is to use nested loops. Outer loop is used to pick the elements one by one and the inner loop compares the picked element with the rest of the elements.
An efficient approach would be to use hashing. Traverse the link list from head to end. For every newly encountered element, check whether it is in the hash table: if yes, we remove it; otherwise put it in the hash table.
Time Complexity : O(N)
3. OS Question
Difference between Paging and Swapping
Problem approach
1. Swapping is procedure of copying out the entire process.Paging is a technique of memory allocation.
2. Swapping occurs when whole process is transferred to disk. Paging occurs when some part of process is transfers to disk.
3. In swapping, process is swapped temporarily from main memory to secondary memory. In paging, the contiguous block of memory is made non-contiguous but of fixed size called frame or pages.
4. Swapping can be performed without any memory management. There is Non-contiguous Memory Management in paging.
5. Swapping is done by inactive processes. Only active process can perform paging.
4. OS Question
Example of deadlock
Problem approach
A real-world example would be traffic, which is going only in one direction.
Here, a bridge is considered a resource. So, when Deadlock happens, it can be easily resolved if one car backs up (Preempt resources and rollback). Several cars may have to be backed up if a deadlock situation occurs.
So starvation is possible.
03
Round
Medium
Face to Face
Duration60 minutes
Interview date22 May 2015
Coding problem4
Technical Interview round with questions on DSA, OOPS and Puzzles.
1. Segregate Odd-Even
Moderate
25m average time
75% success
0/80
Asked in companies



There is a wedding ceremony at NinjaLand. The bride and groom want everybody to play a game and thus, they have blindfolded the attendees. The people from the bride’s side are holding odd numbers and people from the groom’s side are holding the even numbers. For the game to start quickly, all the bride’s side people should come first, followed by the groom’s side people in the same order.
The attendees of the wedding with their numbers are given in the form of a Singly Linked List, arranged randomly.
A singly linked list is a type of linked list that is unidirectional; that is, it can be traversed in only one direction from head to the last node (tail).
Example:
The attendees holding numbers from 1, 4, 3 are shown:
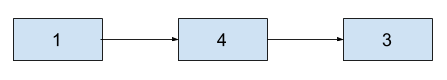
As the organizers are busy, you have to arrange all the people by arranging the bride’s side people first followed by the groom’s side people sequentially.
Note:
For the above example 1 -> 4 -> 3, 1 -> 3 -> 4 is the only correct answer, i.e nodes should be grouped sequentially. Hence, 3 -> 1 -> 4 is the wrong answer as we have to preserve the same order.
Problem approach
Algorithm :
1) Initialize two index variables left and right:
left = 0, right = size -1
2) Keep incrementing left index until we see an even number.
3) Keep decrementing right index until we see an odd number.
4) If left < right then swap arr[left] and arr[right]
2. Convert Sorted Array to BST
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies


You have been given a sorted array of length ‘N’. You need to construct a balanced binary search tree from the array. If there can be more than one possible tree, then you can return any.
Note:
1. A balanced binary tree is a binary tree structure in which the left and right subtrees of every node differ in height by no more than 1.
2. A binary search tree is a binary tree data structure, with the following properties
a. The left subtree of any node contains nodes with value less than the node’s value.
b. The right subtree of any node contains nodes with values equal to or greater than the node’s value.
c. Right, and left subtrees are also binary search trees.
Example:
Below tree, is a balanced binary search tree
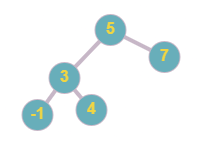
Below tree is not a balanced tree as the height of the left subtree and right subtree of node ‘5’ differs by more than 1. Moreover, the tree is also not a BST as node ‘2’ is less than node ‘3’ but ‘2’ is the right child of ‘3’.
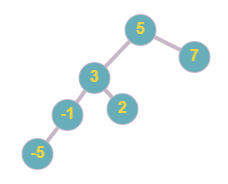
Problem approach
Recursion can be applied here.
Steps:
• Get the middle of the array and make it as root.
• Take the left half of the array, call recursively and add it to root.left.
• Take the right half of the array, call recursively and add it to root.right.
• Return root.
3. Puzzle
There are eight identical-looking coins; one of these coins is counterfeit and is known to be lighter than the genuine coins. What is the minimum number of weighings needed to identify the fake coin with a two-pan balance scale without weights?
Problem approach
Select from the given coins two groups of three coins each and put them on the opposite cups of the scale. If they weigh the same, the fake is among the remaining two coins, and weighing these two coins will identify the lighter fake. If the first weighing does not yield a balance, the lighter fake is among the three lighter coins. Take any two of them and put them on the opposite cups of the scale. If they weigh the same, it is the third coin in the lighter group that is fake; if they do not weigh the same, the lighter one is the fake.
4. Technical Question
Difference between MVC and MVT Design Pattern
Problem approach
1. MVC has controller that drives both Model and View. MVT has Views for receiving HTTP request and returning HTTP response.
2. View tells how the user data will be presented in MVC. Templates are used in MVT for that purpose.
3. In MVC, we have to write all the control specific code. Controller part is managed by the framework itself in MVT.
4. MVC is Highly coupled. MVT is Loosely coupled.
5. Modifications are difficult in MVC. Modifications are easy in MVT.
6. MVC is suitable for development of large applications but not for small applications. MVT is suitable for both small and large applications.
04
Round
Easy
HR Round
Duration30 minutes
Interview date22 May 2015
Coding problem1
HR round with typical behavioral problems.
1. Basic HR Questions
Q1. Why VMware ?
Q2. What are your goals and ambitions?
Problem approach
Tip 1 : The cross questioning can go intense some time, think before you speak.
Tip 2 : Be open minded and answer whatever you are thinking, in these rounds I feel it is important to have opinion.
Tip 3 : Context of questions can be switched, pay attention to the details. It is okay to ask questions in these round, like what are the projects currently the company is investing, which team you are mentoring. How all is the work environment etc.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by VMware Inc
825 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by VMware Inc
1124 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by VMware Inc
333 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by VMware Inc
343 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
5 rounds | 12 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
114869 views
24 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
58031 views
5 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
35057 views
7 comments
0 upvotes





