Wells Fargo interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
Program Associate
Wells Fargo
3 rounds | 3 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Journey
It was really wonderful session throughout the interview journey and in which I answered properly and hence i got the offer via off campus .It was really very nice session over the interview as well as the test .
Application story
I got this opportunity via off campus and I answered very well in my interview and i was very truthful about my project explaination and don't try to copy paste your project if u haven't done it by your own.
Why selected/rejected for the role?
I got selected for the Program associate role because I gave my answer very well and the interviewer was very satisfied with all of my answers. Also if was not knowing the answer i told directly i don't know .
Preparation
Duration: 6 month
Topics: Data structure and algorithmoperating systemdbmsoopscomputer networkweb developmentSplunk
Tip
Tip 1 : Be very clear with your project explanation.
Tip 2 : Also try to cover all the cs core subjects explanation clearly.
Application process
Where: Naukri
Eligibility: 6.5 cgpa and 65% 12th marks minimun requirement
Resume tip
Tip 1:Make it clean with appropriate kowledge.
Tip 2:Provide true information and avoid telling lie in which You are not sure.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration55minutes
Interview date28 Apr 2022
Coding problem1
It was morning time and from 10:00 am . It happened via the google meet online process and it was very smooth onboarding . Interviewer was very friendly kind of nature .
1. Count Ways To Reach The N-th Stairs
Moderate
30m average time
80% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You have been given a number of stairs. Initially, you are at the 0th stair, and you need to reach the Nth stair.
Each time, you can climb either one step or two steps.
You are supposed to return the number of distinct ways you can climb from the 0th step to the Nth step.
Note:
Note: Since the number of ways can be very large, return the answer modulo 1000000007.
Example :
N=3
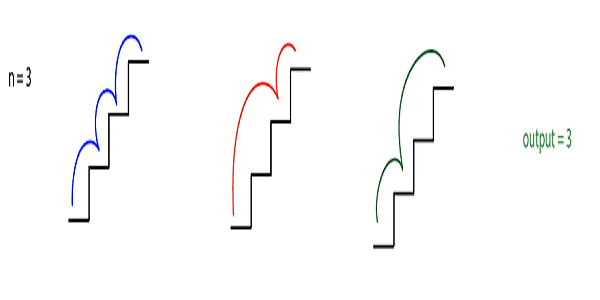
We can climb one step at a time i.e. {(0, 1) ,(1, 2),(2,3)} or we can climb the first two-step and then one step i.e. {(0,2),(1, 3)} or we can climb first one step and then two step i.e. {(0,1), (1,3)}.
Problem approach
int countWays(int n)
{
if(n == 1) return n;
int mod = 1000000000 + 7;
int prev = 2, prev2 = 1, curr = 0;
for(int i = 2 ; i < n ; i++){
curr = (prev + prev2) % mod;
prev2 = prev;
prev = curr;
}
return prev ;
}
02
Round
Hard
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date28 Apr 2022
Coding problem1
It was again the morning session and the interviewer was very supportive in nature and gave me the hint too to think the approach and finally i came up the solution which he was expecting.
1. Kth Largest Element in BST
Moderate
0/80
Asked in companies



Given the root node of a Binary Search Tree (BST), you have to return the Kth largest element in the BST.
For Example:
If K is 4 and the tree is depicted by the following image then,
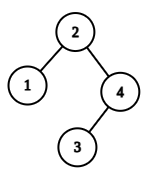
The 4th largest element in the given BST is 1. So the output will be 1.
Follow-up :
Try to do it in O(1) space without using recursion.
Problem approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Tree Node
struct Node {
int data;
Node *left;
Node *right;
Node(int val) {
data = val;
left = right = NULL;
}
};
// Function to Build Tree
Node* buildTree(string str)
{
// Corner Case
if(str.length() == 0 || str[0] == 'N')
return NULL;
// Creating vector of strings from input
// string after spliting by space
vector ip;
istringstream iss(str);
for(string str; iss >> str; )
ip.push_back(str);
// Create the root of the tree
Node* root = new Node(stoi(ip[0]));
// Push the root to the queue
queue queue;
queue.push(root);
// Starting from the second element
int i = 1;
while(!queue.empty() && i < ip.size()) {
// Get and remove the front of the queue
Node* currNode = queue.front();
queue.pop();
// Get the current node's value from the string
string currVal = ip[i];
// If the left child is not null
if(currVal != "N") {
// Create the left child for the current node
currNode->left = new Node(stoi(currVal));
// Push it to the queue
queue.push(currNode->left);
}
// For the right child
i++;
if(i >= ip.size())
break;
currVal = ip[i];
// If the right child is not null
if(currVal != "N") {
// Create the right child for the current node
currNode->right = new Node(stoi(currVal));
// Push it to the queue
queue.push(currNode->right);
}
i++;
}
return root;
}
// } Driver Code Ends
/*The Node structure is defined as
struct Node {
int data;
Node *left;
Node *right;
Node(int val) {
data = val;
left = right = NULL;
}
};
*/
// return the Kth largest element in the given BST rooted at 'root'
class Solution
{public:
void solve(Node*root,int k,int&c,int &ans){
if(root==NULL||c>=k){
return ;
}
solve(root->right,k,c,ans);
c++;
if(c==k){
ans=root->data;
return;
}
solve(root->left,k,c,ans);
}
public:
int kthLargest(Node *root, int k)
{
int c=0;int ans;
solve(root,k,c,ans);
return ans;
}
};
// { Driver Code Starts.
int main()
{
int t;
cin>>t;
getchar();
while(t--)
{
string s;
getline(cin,s);
Node* head = buildTree(s);
int k;
cin>>k;
getchar();
Solution ob;
cout << ob.kthLargest( head, k ) << endl;
}
return 1;
} }
03
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration30 minute
Interview date11 May 2022
Coding problem1
It was late evening and happened in a very smooth way.
1. OS Questions
Ques: What is thread in OS?
Problem approach
Ans: Thread is a path of execution that is composed of a program counter, thread id, stack, and set of registers within the process. It is a basic unit of CPU utilization that makes communication more effective and efficient, enables utilization of multiprocessor architectures to a greater scale and greater efficiency, and reduces the time required in context switching. It simply provides a way to improve and increase the performance of applications through parallelism. Threads are sometimes called lightweight processes because they have their own stack but can access shared data.
Multiple threads running in a process share: Address space, Heap, Static data, Code segments, File descriptors, Global variables, Child processes, Pending alarms, Signals, and signal handlers.
Each thread has its own: Program counter, Registers, Stack, and State.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
Program Associate
3 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Wells Fargo
1788 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Program Associate
4 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Wells Fargo
0 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Program Associate
3 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Wells Fargo
802 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Program Associate
3 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Wells Fargo
915 views
0 comments
0 upvotes



